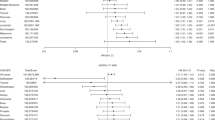
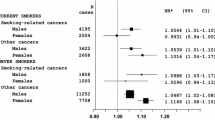
Abstract
Recent analyses of large cohort studies indicate that adult height is associated with cancer at specific sites. In this overview, we review (1) the epidemiology of the association of height with specific cancer sites/types, focusing on the consistency and magnitude of the association and the possibility of confounding; (2) genome-wide association studies (GWASs) of variants associated with height; (3) studies using Mendelian randomization to investigate the association with several types of cancer; (4) studies of dietary and hormonal exposures associated with linear growth, particularly milk intake and circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), that might mediate an association of height with cancer; and (5) the possibility that greater organ size associated with greater height may explain part of the association. We conclude that epidemiologic studies strongly suggest that height is associated with certain cancer sites/types and not with others, and propose a number of avenues for beginning to elucidate the pathways underlying this association.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Valaoras V, MacMahon B, Trichopoulos D, Polychronopoulou A. Lactation and reproductive histories of breast cancer patients in greater Athens, 1965-67. Int J Cancer. 1969;4:350–63.
De Waard F. Breast cancer incidence and nutritional status with particular reference to body weight and height. Cancer Res. 1975;35:3351–6.
Albanes D, Jones DY, Schatzkin A, Micozzi MS, Taylor PR. Adult stature and risk of cancer. Cancer Res. 1988;48:1658–62.
Swanson CA, Jones DY, Schatzkin A, Brinton LA, Ziegler RG. Breast cancer assessed by anthropometry in the NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study. Cancer Res. 1988;48:5363–7.
Albanes D, Taylor PR. International differences in body height and weight and their relationship to cancer incidence. Nutr Cancer. 1990;14:69–77.
Leon DA, Davey Smith G, Shipley M, Strachan D. Adult height and mortality in London: early life, socioeconomic confounding, or shrinkage? J Epidemiol Community Health. 1995;45(49):5–9.
Hebert PR, Ajani U, Cook NR, Lee I-M, Chan KS, Hennekens CH. Adult height and incidence of cancer in male physicians. Cancer Causes Control. 1997;8:591–7.
Tulinius H, Sifusson N, Sigvaldason H, Bjarnadottir K, Tryggvadottir L. Risk factors for malignant diseases: a cohort study on a population of 22,946 Icelanders. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1997;6:863–73.
Smith GD, Shipley M, Leon DA. Height and mortality from cancer among men: prospective observational study. BMJ 1998; 317-1351-1352.
Okasha M, McCarron P, McEwen J, Davey SG. Height and cancer mortality: results from the Glasgow university student cohort. Publ Health. 2000;114:451–5.
Jousilahti P, Tuomilehto J, Vartiainen E, Eriksson J, Puska P. Relation of adult height to cause-specific and total mortality: a prospective follow-up study of 31,199 middle aged men and women in Finland. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151:1112–20.
Giovannucci E, Rimm EB, Liu Y, Willett WC. Height, predictors of C-peptide and cancer risk. Int J Epidemiol. 2004;33:217–25.
Batty GD, Shipley MJ, Langenberg C, Marmot MG, Davey SG. Adult height in relation to mortality from 14 cancer sites in men in London (UK): evidence from the original Whitehall study. Ann Oncol. 2006;17:157–66.
Sung J, Song Y-M, Lawlor DA, Davey Smith G, Ebrahim S. Height and site-specific cancer risk: a cohort study of a Korean adult population. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170:53–64.
Batty GD, Barzi F, Woodward M, Jamrozik K, Woo J, Kim HC, et al. Adult height and cancer mortality in Asia: the Asia pacific cohort studies collaboration. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:646–54.
Green J, Cairns BJ, Casabonne D, Wright FL, Reeves G, Beral V. Height and cancer incidence in the million women study: prospective cohort, and meta-analysis of prospective studies of height and total cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:785–94.
Kabat GC, Heo M, Kamensky V, Miller AB, Rohan TE. Adult height in relation to risk of cancer in a cohort of Canadian women. Int J Cancer. 2012;132:1125–32.
The Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Adult height and the risk of cause-specific death and vascular morbidity in 1 million people: individual participant meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol. 2012;41:1419–33.
Kabat GC, Anderson ML, Heo M, Hosgood III HD, Kamensky V, Bea JW, et al. Adult stature and risk of cancer at different anatomic sites in a cohort of postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2013;22:1353–63.
Wiren S, Häggström C, Ulmer H, Manjer J, Bjørge T, Nagel G, et al. Pooled cohort study on height and risk of cancer and cancer death. Cancer Causes Control. 2014;25:151–9.
Walter RB, Brasky TM, Buckley SA, Potter JD, White E. Height as an explanatory factor for sex differences in human cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:860–8.
Kabat GC, Kim MY, Hollenbeck AR, Rohan TE. Attained height, sex, and risk of cancer at different anatomic sites in the NIH-AARP diet and health study. Cancer Causes Control. 2014;25:1697–706.
Park PH, Hoffmann K, Allen N, van Gils CH, Khaw K-T, Tehard B, et al. Body size and breast cancer risk: findings from the european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC). Int J Cancer. 2004;111:762–71.
Lahmann PH, Hoffman K, Allen N, van Gils CH, Khaw KT, Tehard B, et al. Body size and breast cancer risk: findings from the european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC). Int J Cancer. 2004;111:762–71.
White KK, Park SY, Kolonel LN, Henderson BE, Wilkens LR. Body size and breast cancer risk: the multiethnic cohort. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:E705–16.
Fagherazzi G, Vilier A, Boutron-Ruault MC, Clavel-Chapelon R, Mesrine S. Height, sitting height, and leg length in relation to breast cancer risk in the E3N cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2012;21:1171–5.
Pischon T, Lahmann PH, Boeing H, Friedenreich C, Norat T, Tjonneland A, et al. Body size and risk of colon and rectal cancer in the european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC). J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:920–31.
Park JY, Mitrou PN, Keogh RH, Luben RN, Wareham NJ, Khaw K-T. Self-reported and measured anthropometric data and risk of colorectal cancer in the EPIC-Norfolk study. Int J Obes. 2012;36:107–18.
Kitahara CM, Gamborg M, Berrington de Gonzalez A, Sorensen TI, Baker JL. Childhood height and body mass index were associated with risk of adult thyroid cancer in a large cohort study. Cancer Res. 2014;74:235–42.
Farfel A, Kark JD, Derazne E, Tzur D, Barchana M, Lazar L, et al. Predictors of thyroid carcinoma in Israel: a national cohort of 1,624,310 adolescents followed for up to 40 years. Thyroid. 2014;24:987–93.
Kvaskoff M, Bijon A, Mesrine S, Vilier A, Clavel-Chapelon F, Boutron-Ruault MC. Anthropometric features and cutaneous melanoma risk: a prospective cohort study in french women. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014;38:357–63.
Bjørge T, Engeland A, Tretli S, Weiderpass E. Body size in relation to cancer of the uterine corpus in 1 million Norwegian women. Int J Cancer. 2007;120:378–83.
Cook MB, Gamborg M, Aarestrup J, Sorensen TI, Baker JL. Childhood height and birth weight in relation to future prostate cancer risk: a cohort study on the Copenhagen school health records register. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2013;22:2232–40.
Aarestrup A, Gamborg M, Cook MB, Baker JL. Childhood height increases the risk of prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2015;51:1340–5.
Patel AV, Diver WR, Teras LR, Birmann BM, Gapstur SM. Body mass index, height and risk of lymphoid neoplasms in a large United States cohort. Leuk Lymphoma. 2013;54:1221–7.
Roswell N, Freisling H, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Ros M, Christensen J, Overvad K, et al. Anthropometric measures and bladder cancer risk: a prospective cohort study in the EPIC cohort. Int J Cancer. 2014;135:2918–29.
Lahmann PH, Cust AE, Friedenreich CM, Schultz M, Lukanova A, Kaaks R, et al. Anthropometric measures and epithelial ovarian cancer risk in the european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:2404–15.
Pischon T, Lahmann PH, Boeing H, Tjønneland A, Halkjaer J, Overad K, et al. Body size and risk of renal cell carcinoma in the european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC). Int J Cancer. 2006;118:728–38.
Kitahara CM, Gamborg M, Rajaraman P, Sorensen TI, Baker JL. A prospective study of height and body mass index in childhood, birth weight, and risk of adult glioma over 40 years of follow-up. Am J Epidemiol. 2014;180:821–9.
Etemadi A, O’Doherty MG, Freedman ND, Hollenbeck AR, Dawsey SM, Abnet CC. A prospective cohort study of body size and risk of head and neck cancers in the NIH-AARP diet and health study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23:2422–9.
Camargo MC, Freedman ND, Hollenbeck AR, Abnet CC, Rabkin CS. Height, weight, and body mass index associations with gastric cancer subsites. Gastric Cancer. 2014;17:463–8.
Olsen CM, Green AC, Zens MS, Stukel TA, Bataille V, Berwick M, et al. Anthropometric factors and risk of melanoma in women: a pooled analysis. Int J Cancer. 2008;122:1100–8.
Aune D, Navarro Rosenblatt DA, Chan DSM, Vingeliene S, Abar L, Vieira AR, et al. Anthropometric factors and endometrial cancer risk; a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Ann Oncol. 2015. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdv142.
Zuccolo L, Harris R, Gunnell D, Oliver S, Lane JA, Davis M, et al. Height and prostate cancer risk: a large nested case-control study (ProtecT) and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:2325–36.
Shouten LJ, Rivera C, Hunter DJ, Spiegelman D, Adami HO, Arslan A, et al. Height, body mass, and ovarian cancer: a pooled analysis of 12 cohort studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:902–12.
Aune D, Navarro-Rosenblatt DA, Chan DSM, Abar L, Vingeliene S, Vieira AR, et al. Anthropometric factors and ovarian cancer risk: a systematic review and nonlinear dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:1888–98.
Liang S, LV G, Chen W, Jiang J, Wang J. Height and kidney cancer risk: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015;141:1799–807. doi:10.1007/s00432-014-1870-5.
Aune D, Vieira AR, Chan DSM, Navarro-Rosenblatt DA, Vieira R, Greenwood DC, et al. Height and pancreatic cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Cancer Causes Control. 2012;23:1213–22.
Genkinger JM, Spiegelman D, Anderson KE, Bernstein L, van den Brandt PA, Calle EE, et al. A pooled analysis of 14 cohort studies of anthropometric factors and pancreatic cancer risk. Int J Cancer. 2011;129:1708–17.
Leoncini E, Ricciardi W, Cadoni G, Arzani D, Petrelli L, Paludetti G, et al. Adult height and head and neck cancer: a pooled analysis within the INHANCE consortium. Eur J Epidemiol. 2014;29:35–48.
Gunnell D, Okasha M, Smith GD, Oliver SE, Sandhu J, Holly JM. Height, leg length, and cancer risk a systematic review. Epidemiol Rev. 2001;23:313–42.
Batty GD, Shipley MJ, Gunnell D, Huxley R, Kivimaki M, Woodward M, et al. Height, wealth, and health: an overview with new data from three longitudinal studies. Econ Hum Biol. 2009;7:137–52.
Lettre G. Recent progress in the study of the genetics of height. Hum Genet. 2011;129:465–72.
McEvoy BP, Visscher PM. Genetics of human height. Encon Human Biol. 2009;7:294–306.
Wood AR, Esko T, Yang J, Vedantam S, Pers TH, Gustafsson S, et al. Defining the role of common variation in the genomic and biological architecture of adult human height. Nat Genet. 2014;46(11):1173–86. This analysis of genetic variation and height using GWAS data from over a quarter of a million subjects estimates the heritability of adult height captured by common variants.
Beauchamp JP, Cesarini D, Johnanesson M, Lindqvist E, Apicella C. On the sources of the height-intelligence correlation: new insights from a bivariate ACE model with assortative mating. Behav Genet. 2011;41:242–52.
Renehan AG. Height and cancer: consistent links, but mechanisms unclear. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12:716–7. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70193-0.
Gelfand LA, Baraldi AN. Height as a sex-cancer mediator? interpret with caution. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:843–4. doi:10.1093/jnci/djt131.
Hirschhorn JN, Lettre G. Progress in genome-wide association studies of human height. Horm Res. 2009;71 Suppl 2:5–13.
Lango Allen H, Estrada K, Lettre G, Berndt SI, Weedon MN, Rivadeneira F, et al. Hundreds of variants clustered in genomic loci and biological pathways affect human height. Nature. 2010;467(7317):832–8.
N’Diaye A, Chen GK, Palmer CD, Ge B, Tayo B, Mathias RA, et al. Identification, replication, and fine-mapping of loci associated with adult height in individuals of african ancestry. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(10), e1002298.
Carty CL, Johnson NA, Hutter CM, Reiner AP, Peters U, Tang H, et al. Genome-wide association study of body height in African Americans: the Women’s health initiative SNP health association resource (SHARe). Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21(3):711–20.
He M, Xu M, Zhang B, Liang J, Chen P, Lee JY, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of adult height in East Asians identifies 17 novel loci. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(6):1791–800.
Zhang G, Karns R, Sun G, Indugula SR, Cheng H, Havas-Augustin D, et al. Finding missing heritability in less significant Loci and allelic heterogeneity: genetic variation in human height. PLoS One. 2012;7(12), e51211.
Paternoster L, Howe LD, Tilling K, Weedon MN, Freathy RM, Frayling TM, et al. Adult height variants affect birth length and growth rate in children. Hum Mol Genet. 2011;20(20):4069–75.
van der Valk RJ, Kreiner-Moller E, Kooijman MN, Guxens M, Stergiakouli E, Saaf A, et al. A novel common variant in DCST2 is associated with length in early life and height in adulthood. Hum Mol Genet. 2015;24(4):1155–68.
Law MH, Bishop DT, Lee JE, Brossard M, Martin NG, Moses EK, et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies five new susceptibility loci for cutaneous malignant melanoma. Nat Genet. 2015;47:987–95. doi:10.1038/ng.3373.
Iles, M. M., Law, M. H., Stacey, S. N., Han, J., Fang, S., Pfeiffer, R., et al. A variant in FTO shows association with melanoma risk not due to BMI. Nat Genet 45, 428-432, 432e421, 10.1038/ng.2571 2013.
Michailidou K, Beesley J, Lindstrom S, Canisius S, Dennis J, Lush M, et al. Genome-wide association analysis of more than 120,000 individuals identifies 15 new susceptibility loci for breast cancer. Nat Genet. 2015;47:373–80. doi:10.1038/ng.3242.
Siddiq A, Couch FJ, Chen GK, Lindstrom S, Eccles D, Millikan RC, et al. M. A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of breast cancer identifies two novel susceptibility loci at 6q14 and 20q11. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:5373–84. doi:10.1093/hmg/dds381.
Peters U, Jiao S, Schumacher FR, Hutter CM, Aragaki AK, Baron JA, et al. Identification of genetic susceptibility loci for colorectal tumors in a genome-wide meta-analysis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144:799–807 e724. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.12.020.
Schumacher FR, Schmit SL, Jiao S, Edlund CK, Wang H, Zhang B, et al. Genome-wide association study of colorectal cancer identifies six new susceptibility loci. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7138. doi:10.1038/ncomms8138.
Wu X, Scelo G, Purdue MP, Rothman N, Johansson M, Ye Y, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies a novel susceptibility locus for renal cell carcinoma on 12p11.23. Hum Mol Genet. 2012;21:456–62.
Gudmundsson J, Sulem P, Gudbjartsson DF, Masson G, Petursdottir V, Hardarson S, et al. A common variant at 8q24.21 is associated with renal cell cancer. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2776. doi:10.1038/ncomms3776.
Thrift AP, Gong J, Peters U, Chang-Claude J, Rudolph A, Slattery ML, et al. Mendelian randomization study of height and risk of colorectal cancer. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44:662–72. doi:10.1093/ije/dyv082.
Zhang B, Shu XO, Delahanty RJ, Zeng C, Michailidou K, Bolla MK, et al. Height and breast cancer risk: evidence from prospective studies and Mendelian randomization. J Natl Cancer Inst 2015;107. doi:10.1093/jnci/djv219. This Mendelian randomization study provides strong evidence that adult height is a risk factor for breast cancer in women and that certain genetic factors and biological pathways affecting adult height may play an important role in the etiology of breast cancer.
Thrift AP, Risch HA, Onstad L, Shaheen NJ, Casson AG, Bernstein L, et al. Risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma decreases with height, based on consortium analysis and confirmed by Mendelian randomization. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;12:1667–76.
Barker DJ. A new model for the origins of chronic disease. Med Health Care Philos. 2001;4:31–5.
Power C, Kuh D, Morton S. From developmental origins of adult disease to life course research on adult disease and aging: insights from birth cohort studies. Annu Rev Public Health. 2013;34:7–28.
Okasha M, Gunnell D, Holly J, Davey SG. Childhood growth and adult cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;16:225–41.
Baik I, Devito WJ, Ballen K, Becker PS, Okulicz W, Liu Q, et al. Association of fetal hormone levels with stem cell potential: evidence for early life roots of human cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:358–263.
Martin RM, Holly JM, Gunnell D (2011) Milk and linear growth: programming of the IGF-I axis and implication for health in adulthood. In: Clemens RA, Hernell O, Michaelsen KF (eds.), Milk and milk products in human nutrition. Nestle Nutrition Institute Workship Series: Pediatric Program. Vol. 67. Nestec Ltd., Vevey/S. Karger AG, Basel, Switzerland; 2011, p. 79-97
Rogers I, Emmett P, Gunnell D, Dunger D, Holly J, The ALSPAC Study Team. Milk as a food for growth? The IGF link. Publ Health Nutr 20069:359-368.
Rogers I, Metcalfe C, Gunnell D, Emmett P, Dunger D, Holly J, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 and growth in height, leg length, and trunk length between ages 5 and 10 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:2514–9.
Berkey CS, Colditz GA, Rockett RH, Frazier AL, Willett WC. Dairy consumption and female height growth: prospective cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:1881–7.
Hoppe C, Mølgaard C, Michaelsen KF. Cow’s milk and linear growth in industrialized and developing countries. Annu Rev Nutr. 2006;26:131–73.
Ben Slomo Y, Holly J, McCarthy A, Savage P, Davies D, Gunnell D, et al. An investigation of fetal, postnatal and childhood growth with insulin-like growth factor 1 and binding protein 3 in adulthood. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2003;59:366–73.
Ben-Slomo Y, Holly J, McCarthy A, Savage P, Davies D, Davey SG. Pre- and post-natal milk supplementation and adult insulin-like growth factor-1: Long-term follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14:1336–9.
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O’Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet. 2004;363:1346–53.
Clayton PE, Bannerjee I, Murray PG, Renehan AG. Growth hormone, the insulin-like growth factor axis, insulin and cancer risk. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2011;7:11–24.
Ish-Shalom D, Christoffersen CT, Vorwerk P, Sacerdoti-Sierra N, Naor D, De Meyts P. Mitogenic properties of insulin and insulin analogues mediated by the insulin receptor. Diabetologia. 1997;40 Suppl 2:S25–31.
Milazzo G, Giorgino F, Damante F, Sung C, Stampfer MR, Vigneri R, et al. Insulin receptor expression and function in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1992;52:3924–30.
Berkey CS, Frazier AL, Gardner JD, Colditz GA. Adolescence and breast carcinoma risk. Cancer. 1999;85:2400–9.
Lagiou P, Hsieh CC, Lipworth L, Samoli E, Okulicz W, Troisi R, et al. Insulin-like growth factor levels in cord blood, birth weight and breast cancer risk. Br J Cancer. 2009;2:1794–8.
Lawlor DA, Okasha M, Gunnell D, Smith GD, Ebrahim S. Associations of adult measures of childhood growth with breast cancer: findings from the British Women’s heart and health study. Br J Cancer. 2003;89:81–7.
Ahlgren M, Melbye M, Wohlfahrt J, Sorensen TIA. Growth patterns and the risk of breast cancer. New Engl J Med. 2004;351:1619–26.
Forman MR, Cantwell MM, Ronckers C, Zhang Y. Through the looking glass at early-life exposures and breast cancer risk. Cancer Investig. 2005;23:609–24.
Mellemkjaer L, Christensen J, Frederiksen BJL, Olsen A, Sorensen TL, et al. Leg length, sitting height and postmenopausal breast cancer risk. Br J Cancer. 2012;107:165–8.
Hung RJ, Ulrich CM, Goode EL, Brhane Y, Muir K, Chan AT, et al. Cross cancer genomic investigation of inflammation pathway for five common cancers: lung, ovary, prostate, breast, and colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 107. doi:10.1093/jnci/djv246 2015.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Robert E. Tarone for valuable comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Geoffrey C. Kabat, H. Dean Hosgood III, and Thomas E. Rohan declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
As a review article, this article does not present primary data obtained from human or animal subjects.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Cancer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabat, G.C., Hosgood, H.D. & Rohan, T.E. Adult Height in Relation to the Incidence of Cancer at Different Anatomic Sites: the Epidemiology of a Challenging Association. Curr Nutr Rep 5, 18–28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-016-0152-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-016-0152-z