Abstract
The study of the vulnerability of historical masonry structures during earthquakes is gaining much attention in the recent decades due to the increasing awareness in the conservation of the built ancient heritage so that life and property must be preserved. Historical masonry structures were designed for gravity loads, there were no earthquake resistant provision in those times, and they are vulnerable hence required to be safeguard against seismic forces. Various failures of such structures were reported in literature due to earthquakes. Masonry structures are usually associated to a high seismic vulnerability mainly due to the property of materials (high specific mass, low tensile strength, moderate shear strength and the low ductility). In addition to the influence of the material properties, the seismic behavior of masonry buildings depends on factors such as geometry of the structure, weak connections between floors and load bearing walls, high mass of masonry wall, stiffness of the floors and the behavior of the non-structural elements. For these reasons, the seismic performance of old masonry buildings has received much attention in the last decades. Masonry arches, vaults & domes have demonstrated to be one of the critical elements in the seismic vulnerability of historic constructions. The seismic capacity of masonry arches and vaults has been assessed through pushover analysis. Damage and collapses caused by earthquakes shows that masonry arches and vaults are one of the most vulnerable elements in historic constructions. In the present study, the structure is modeled using finite element software assuming a homogeneous and non-linear behavior of the material. The results thus obtained will be useful for detecting the weak failure zone of the structure under future earthquake forces. Seismic vulnerability of historical masonry is very tricky as in most cases direct retrofitting applications are not allowed as it may spoil the aesthetic architectural point of view hence some proper strengthening techniques have to be adopted in order to safeguard the structures during future earthquakes.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
1 Introduction
Most of the ancient constructions are made up of masonry that is one of the earliest building material. Several historical and ancient masonry buildings are characterized by the presence of arches and vaults. In the nutshell, we can say that the arches are a fundamental constructive element which is having both load bearing as well as ornamental function. Found in the Alpine-Himalayan earthquake belt, Iran has a history of terrible earthquakes. The Tabas earthquake of 1978, Manjil earthquake in 1990, Bam earthquake of 2003 and Dahoeieh Zarand earthquake in 2005 are only the more recent examples of the many earthquakes that have occurred in the region in the past few hundred years. Being one of the oldest civilizations, the Iranian plateau comprises some of the oldest buildings and most attractive historical places in the world. The typology of these heritage buildings are usually capable of resisting the vertical loads safely but they are weak in resisting the seismic forces.
Even though several studies, have been undertaken in the past, both experimentally and numerically for predicting the lateral strength, mechanical behavior of the units and prism and seismic response of historical masonry buildings that have been made of adobe pier and brick vault using clay or gypsum-clay mortars. For example, Maheri et al. performed standard tests on brick units, gypsum-clay mortar, and brickwork. These studies focused on the design of jack arch masonry slabs that were made of lightweight perforated brick and gypsum-clay mortar. Ghannad et al. and Kuwata et al. studied mechanical properties of local adobes. Recently, Mahini et al. determined the mechanical properties of the units, mortars and adobe piers and roof vault of the Ighbal heritage complex located in Yazd city, Iran. In their studies, standard testing machines and the four point bending test were employed to evaluate the tensile and compressive strengths and also the modulus of elasticity of the brick vault, adobe piers, the units and the mortars. D’Ayala had performed the research for analytical estimation of thrust which is responsible for collapse mechanism of arches and vaults. The research work which he has done gives the crack pattern, field of stress, & horizontal thrust which is based on fixed boundary condition at the supports.
Usually, the approach towards numerical representation of masonry structures is the micro-modelling of the individual components, namely unit (brick, adobe, etc.) and mortar, or the macro-modelling of masonry as a composite. Units, mortar and unit-mortar interface are smeared out in the continuum. Macro modelling is more concerned with due to the lesser time and memory necessities as well as user friendly mesh generation. This type of modelling is most valuable when a compromise between accuracy and efficiency is needed. Considering these advantages, macro-modelling of masonry has been implemented in this paper in order to predict the behavior of masonry.
Using non-linear finite element modelling, the present paper focuses on the evaluation of the lateral resistance, collapse mechanisms and to analyze the cracking pattern of the case study vault subjected to lateral loads. The vault is part of Ighbal historical complex already mentioned. The material properties of the continuum masonry obtained experimentally by Mahini et al. have been used in this paper.
2 Research Significance
The main aim of the present paper is to study the behavior of arches and vaults with respect to cracking, identification of weak zones and damage with increasing intensity under lateral loads. The paper deals with the pushover analysis of the arches, vaults and analyzing the nonlinear behavior of the structure under increasing lateral load simulating the earthquake load and to monitor the pattern of damage and cracking of analytical model.
3 Geometry and Mechanical Properties of the Vault
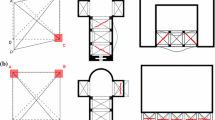
Yazd is an ancient city with hundreds of historical buildings built of adobe with clay mortar and/or brick with gypsum-clay mortar. In this study, the lateral resistance and performance of a vault belonging to the Ighbal historical complex is analyzed. The overall view of this monument and the external view of the vault are shown in Figs. 1 and 2, respectively. The geometry as well as non-structural components of the vault are shown in Fig. 3. The structural system of the roof has been covered by brick masonry units, while the side piers have been made with adobe masonry units (Table 1).
3.1 Brick Vault Prism
Brick and gypsum-clay prisms were built from the original units as a part of brick vaults in order to measure the compressive strength of the vault prism. The arrangement of bricks and the direction of loading were similar to the vaults of the case study building as used by Maheri et al. The stress-strain diagrams for specimen and the equivalent multi-linear diagram are illustrated in Fig. 4. The modulus of elasticity of specimen was obtained based on the initial stiffness obtained from the stress-strain relations. The first point of the equivalent multi-linear diagram was calculated from the average elastic compressive stresses of specimens and the average modulus of elasticity of 4.65 MPa and 1660 MPa, respectively. The average compressive strength of the brickwork is about 8.72 MPa. The tensile strength for the brick specimen were obtained by four point bending test and is found to be 0.084 MPa. Based on the experimental testing done by Maheri et al. the mechanical properties of the test results and compressive stress-strain curve for brick prism were plotted as shown in Table 2 and Fig. 4, respectively.
3.2 Adobe Pier Prism
The piers of the vault had been built with adobe and clay mortar. Compressive strengths of the adobe prism were measured by the standard compression machine. The stress-strain relations of all specimen and the equivalent multi-linear diagram have been shown in Fig. 5. Based on the curve, the initial modulus of elasticity of each adobe prism has been calculated. The average modulus of elasticity and compressive strength of the adobe prism were calculated to be 214 MPa and 1.12 MPa, respectively. The tensile strength of adobe piers was measured using a similar testing set-up for brick prism. This shows very low tensile strength of adobe prism which is roughly 0.015 MPa. The mechanical properties of specimen and also the average values are tabulated in Table 3.
4 Finite Element Analysis and Verification
To analyze the nonlinear performance of the vault, three dimensional linear and nonlinear analyses were performed using ANSYS. The concept of homogenized material and smeared cracking law was used. This technique has been utilized and found to be a simple and accurate model to predict the performance of buildings. In order to properly know the nonlinear behavior, a three-dimensional solid element, solid 65, has been used as applied in this study. This element has property to model concrete, but also has the capability of modeling cracking and crushing.
The fragile behavior of masonry has been modeled through a suitable failure criterion, defined by two parameters ft (uniaxial tensile strength) and fc (uniaxial compressive strength). A shear transfer coefficient β has been introduced (which depends on crack status: open; βt or re closed; βc), represents a shear strength reduction factor. The failure surface assumed is the Willam and Warnke surface. Masonry compressive strength of fc = 7.5 MPa and masonry tensile strength of ft = 0.3 MPa have been taken from the related studies performed by Vermeltfoort and Milani et al. which were similar to the current study. In order to find the shear transfer parameters, βt and βc, a number of analyses were performed until eventually the amounts of 0.25 and 0.99 were considered for βt and βc, respectively as shown in Table 4.
5 Finite Element Analysis and Case Study of Vault
Analysis of historical buildings is relatively a tough task. It is because of numerical modeling of the nonlinear behavior of masonry material in which there is nearly no tensile strength, and secondly due to the inadequate experimental mechanical properties of the masonry structural elements and the complication of the typological pattern. Possessing no tensile strength, arch and vault structures must be secured from horizontal movements resulting due to horizontal component of earthquake; else they may damage. Taking in account the support provided by end-to-end structures, for middle vaults and arches there is no need to be worried about these forces, it should be needed to use reinforcement to resist these horizontal forces. Linear and non-linear analyses were executed under gravity loads. In order to decrease the analysis period, only 1 m width of the vault was considered for the numerical analysis (Tables 5 and 6).
-
(i)
Modal Analysis
Modal analysis is performed to find the Eigen values and the corresponding mode shapes of the arch for 1 m of width. For reducing the computational time only six mode shapes are extracted.
-
(ii)
Non-linear Static Pushover Analysis
Non-linear analysis is performed for a force of 35 kN. The behaviour of the structure is analysed for the total amount of loading that is applied to the vault. A three-dimensional model of the vault has been generated using the ANSYS software. For the convenience and to decrease the computational time, one meter width of the vault was used for analysis.
The lateral loading is applied on the mid nodes up to the top of piers. The base of the structure is properly constrained, the effect of gravity considering the self-weight of the vault is also considered in the analysis. The loading condition is as shown in the Fig. 6. A uniform lateral loading of increasing intensity in applied up to the top of both the piers. The loading has been done using a number of small sub steps with the use of Newton Raphson’s approach. A pushover analysis is performed based on the vertical load, derived from gravity loads and lateral load of increasing strength that are constantly dispersed along the height of the vault simulating seismic loads. The mechanical properties of masonry have been taken according to the experimental study conducted by Eslami et al. (2009).
5.1 Results of the Pushover Analysis, Deformed Shapes, Stress Pattern and Cracking
The deformed shape of the arch portion due to last sub step of loading has been shown in the Figs. 7 and 8. The top circular portion of the vault deviates in the direction of applied lateral load. Since the masonry structures have the property that they are capable of bearing the compressive forces more easily but the behaviour of masonry becomes weak when tensile force is developed in structure. When the lateral load is applied on both of the adobe pier up to the top of the pier the top circular portion of an arch i.e. the extrados portion comes under compression whereas the inner portion i.e. the intrados develops tension. Figures 9 and 10 shows the pattern of cracking in the top circular portion of an arch at the springing. The cracking occurs when the forces acting on the structure reaches the tensile capacity of the material. From the behaviour of cracks the tension zones which may fail due to cracking due to an earthquake.
For obtaining the non-linear static pushover curve the loading is applied in small increment of loading. The Newton- Raphson’s iteration method is used for obtaining the load versus displacement curve. This method is used, so that the tangent stiffness matrix is generated at each sub step of loading to obtain the correct solution. The whole process continues until the problem converges. After the convergence, has been achieved the deformed shape of the original structure at the last step of loading is demonstrated in Fig. 11.
The pushover curve shows the maximum horizontal displacement at the last sub step occurred on a small area on the right-hand side. Figure 11 shows, the displacement diagram at the node in which the maximum displacement has occurred, vs. the total lateral load is depicted. With respect to finite element results, the total lateral load carrying capacity of the unreinforced vault was around 35 kN while the obtained maximum lateral displacement, was 10.658 mm.
5.2 Cracking and Crushing Pattern
In order to find the cracking and crushing pattern for the crown portion of an arch a uniform loading of 1 kN is applied at the crown of the arch portion the deformed shape as well as cracking pattern shown in Figs. 12 and 13 respectively.
5.3 Lateral Load Analysis and Performance Analysis of Domed Vault
Many of the masonry domes, which are found in historical structures throughout the world, are in as state of structurally vulnerable which appears in the form of cracking. There are several examples regarding the damage occurred to the dome structures like the dome of Florence with equally dispersed cracks of different width. The width of these cracks grows due to natural causes like aging, and material deterioration.
Masonry domed structures under the excessive loads as well as support movement develops parallel and meridional cracks, which is the main cause for the decrease in the rigidity of the structure. On account of this reduction in stiffness can be can be measured using natural frequencies of the dome.
Besides from reduction in stiffness, the development of meridional cracks and parallel cracks also reduces the strength of domes. That is why the drop-in strength results in decrease in load carrying capacity. Moreover, the dome has the symmetric boundary conditions whereas the bottom edge of the dome is kept restrained in all directions. In order to analyse the behaviour of the dome that how the pattern of stress and weaker zones which are susceptible to different force leading to the cracks, pendentive dome geometry is taken for the analysis.
The geometry of the pendentive is taken from the FRI (Forest Research Institute) building, Dehradun, Uttarakhand India as in Fig. 14. From the survey, it has been laid in a lime and sand mortar construction. The building was constructed during the period of (1923–1929) A.D. by using brick as units of ashlar masonry in lime mortar.
The radius of the pendentive dome is found to be 1.48 m. The domes are made up of brick tiles which are having the thickness 110 mm. The modelling of the dome is done by using the SHELL181 element. Shell 181 is appropriate for analysing thin moderately thick shell structures. It is a four-node element with six degree of freedom at each node: translation in the nodal x, y, and z direction, and rotation about the x, y, and z-axes. If the membrane option is used, the element has translation degree of freedom only.
5.4 Material Properties and Description of Dome
The material properties of the vaulted dome geometry have been taken from the past literature. The modulus of elasticity and the Poisson’s ratio has been taken from the experimental work Tomar (2015). “The modulus of elasticity of brick masonry prism has been evaluated using stress-strain curve obtained for evaluating compressive strength of masonry prism. From the guidelines of FEMA-274, the secant modulus of elasticity E m, has been used to represent the modulus of elasticity of brick masonry prism where secant modulus of elasticity is the slope of stress-strain curve in the range \( 0.05f_{m}^{{}} - 0.33f_{m} \).
-
(i)
Boundary Conditions
In order to simulate the boundary conditions for the vaulted pendentive dome the base of the dome has been restrained in all the direction. The radial circular opening of the domes is restrained in the x and z direction respectively, as shown in Fig. 16.
-
(ii)
Loading Condition and Results
To analyse the behaviour and performance of the dome for the case of earthquake loading, a pressure force of 20 kN is applied on the top surface of the dome. This amount of loading is calculated based on the material that are placed over the actual structure, in the form of dead load.
Also, a horizontal line pressure force of magnitude 30 kN is applied on the radial circular portion of pendentive in the negative z direction. After the application of loads the non-linear analysis has been performed. The non-linearity of the material is taken from the compressive stress-stain curve as shown in previous Fig. 15.
The deformed shape of the dome along with the nodal displacements and the various stress patterns of the pendentive dome have been shown here. The motive behind this study is to analyse the behaviour of the dome during the incremental lateral loading. One can conclude from the above analysis that the chances of cracks in the dome portion are mostly found out to be above the pendentive portion of the dome. This is because when an earthquake occurs the forces shall act in all the directions, hence, the pendentive portions of the dome must be sufficiently stiffer so that they can withstand the seismic forces (Figs. 17, 18, 19 and 20).
6 Conclusions
In this paper, lateral resistance of the masonry arch of the Ighbal heritage complex was investigated using a homogenization method. The mechanical properties of the adobe piers and brick vault determined by experimental tests done by Mahini et al. on brick vault and adobe pier prisms and the results have been utilized for numerical analysis of the model. A well-known FE program (ANSYS) was employed to carry out nonlinear analysis of the case study building. The outcomes of the pushover FE analysis confirms the efficiency of improving the load carrying capacity of the historical masonry building considered in this research. Non-linear static pushover analysis has shown that the concentration of stress at arch and vaults springing were the main reasons for the development of damages in arches and vaults. Higher stress at vaults intrados and extrados are also observed which explains the damage at the vault springing. The stress pattern from the deformed shapes of the vault shows that the concentrations of stress are higher at the cracked regions, which signifies that the vaults are vulnerable to the seismic forces. If it is necessary, the tension capacities of the masonry members can be enhanced using the appropriate strengthening techniques.
After that the behavior of the vaulted dome taken from the FRI (Forest research Institute) Building situated at Dehradun Uttarakhand, India is taken for the analysis purpose. The results of the analysis show the concentration of stresses at the pendentive portion of the domed vault. Also, the pendentive portion is very susceptible to cracking leading to the collapse of the domes. Generally, tension rings or buttresses should be provided in large span masonry domes, specifically to hemispherical domes.
References
ANSYS v.14.5. ANSYS Manual Set, ANSYS, Inc. is certified to ISO 9001 (2011)
Chiorino, M.A., Spadafora, A., Calderini, C., Lagomarsino, S.: Modelling strategies for world’s largest elliptical dome at vicoforte. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2(3), 274–303 (2008)
Chopra, A.K., Goel, R.K.: A modal pushover analysis procedure to estimate seismic demands for unsymmetrical-plan buildings. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 33, 903–927 (2004)
Croci, G.: Seismic behavior of masonry domes and vaults of Hagia Sophia in Istanbul and St. Francis in Assisi. In: First European Conference on Earthquake Engineering, 3–8 September 2006
D’Ayala, D., Dan, M.B., Akut, A.: Vulnerable dwelling typologies in European Countries affected by recent earthquakes. In: 13th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, no. 832 (2004)
Eslami, A., Mahini, S.S., Morshed, R.: An experimental investigation into the mechanical properties of brick vaults and adobe piers- a historical case study. In: Proceeding of 8th International Congress on Civil Engineering, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran (2009)
Ghannad, M.A., Bakhshi, A., Mousavi Eshkiki, S.E., Khosravifar, A., Bozorgnia, Y., Taheri Behbahani, A.A.: A study on seismic vulnerability of rural houses in Iran. In: Proceedings of first European Conference on Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, paper no. 680, Geneva, Switzerland (2006)
Giordano, A., Mele, E., De Luca, A.: Assessment of the seismic capacity of triumphal arches. In: Lourenço, P.B., Roca, P. (eds.) Proceeding of Historical Constructions, Guimarães, Portugal (2001)
Kuwata, Y., Takada, S., Bastami, M.: Building damage and human casualties during the Bam-Iran earthquake. Asian J. Civ. Eng. (Buil. Hous.) 6(1–2), 1–19 (2005)
Mahdi, T.: Performance of traditional arches, vaults and domes in the 2003 Bam Earthquake. Asian J. Civ. Eng. (Build. Hous.) 5(3–4), 209–221 (2004)
Mahini, S.S., Eslami, A.: Mechanical properties of brick vault and adobe piers – a heritage case study. In: Proceeding of 3rd International Workshop on Conservation of Heritage Structures using FRM and SHM (CSHM-3), Ottawa- Gatineau, Canada, pp. 147–160, 11–13 August 2010
Mahini, S.S., Ronagh, H.R., Eslami, A.: Lateral performance and load carrying capacity of an unreinforced, CFPR-retrofitted historical masonry vault-a case study. Constr. Build. Mater. 28, 146–156 (2012)
Mahini, S.S., Ronagh, H.R., Eslami, A.: Seismic rehabilitation of historical masonry vaults using FRPs – a case study. In: Proceeding of Asia-Pacific Conference on FRP in Structures (APFIS 2007), Hong Kong, China, vol. 1 (2007)
Vermeltfoort, A.T.: Analysis and experiments of masonry arches. In: Lourenço, P.B., Roca, P. (eds.) Proceeding of Historical Constructions, Guimarães, Portugal (2001)
Willam, K.J., Warnke, E.P.: Constitutive model for the triaxial behaviour of concrete. In: Proceedings of the IASBE Seminar on Concrete Structures Subjected to Triaxial Stresses, Bergamo, Italy, 17–19 May 1974, vol. 19, pp. 1–30. International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering, Zurich (1974)
Acknowledgements
This research paper is made possible through the help and support from everyone, including: parents, teachers, family, friends and in essence, all sentient beings. Especially, please allow me to dedicate my acknowledgement of gratitude towards the following significant advisors and contributors:
First and foremost, I would like to thank GOD for his unconditional guidance and wisdom as I make my research.
Secondly, I would like to thank my guide my mentor Dr. D. K. Paul for his support and encouragement for giving me this research. This gives me the experience on how to cooperate and encourage ourselves in a serious project.
Finally, I sincerely thank to my parents, my family members Dr. Nida Fatima, Saima Khan Afridi, Dr. Farheen Khan, and especially my senior fellow Dr. Anshu Tomar for his advice and support. The product of this research paper would not be possible without all of them.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Khan, M.A., Paul, D.K. (2018). Seismic Performance of Masonry Arches and Vaults. In: Rodrigues, H., Elnashai, A., Calvi, G. (eds) Facing the Challenges in Structural Engineering. GeoMEast 2017. Sustainable Civil Infrastructures. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61914-9_3
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61914-9_3
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-61913-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-61914-9
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)