Abstract
Background
Ultrasonography (US) is an essential tool for the diagnosis of acute gynecological conditions. General practice (GP) residents are involved in the first-line management of gynecologic emergencies. They are not familiar with US equipment. Initial training on simulators was conducted.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of simulation-based training on the quality of the sonographic images achieved by GP residents 2 months after the simulation training versus clinical training alone.
Methods
Young GP residents assigned to emergency gynecology departments were invited to a one-day simulation-based US training session. A prospective controlled trial aiming to assess the impact of such training on TVS (transvaginal ultrasound scan) image quality was conducted. The first group included GP residents who attended the simulation training course. The second group included GP residents who did not attend the course. Written consent to participate was obtained from all participants. Images achieved 2 months after the training were scored using standardized quality criteria and compared in both groups. The stress generated by this examination was also assessed with a simple numeric scale.
Results
A total of 137 residents attended the simulation training, 26 consented to participate in the controlled trial. Sonographic image quality was significantly better in the simulation group for the sagittal view of the uterus (3.6 vs 2.7, p = 0.01), for the longitudinal view of the right ovary (2.8 vs 1.4, p = 0.027), and for the Morrison space (1.7 vs 0.4, p = 0.034), but the difference was not significant for the left ovary (2.9 vs 1.7, p = 0.189). The stress generated by TVS after 2 months was not different between the groups (6.0 vs 4.8, p = 0.4).
Conclusion
Simulation-based training improved the quality of pelvic US images in GP residents assessed after 2 months of experience in gynecology compared to clinical training alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Ultrasound has become an indispensable tool for the identification of most gynecologic emergencies [1]. However, it is highly operator-dependent. A novice operator can easily miss a diagnosis. In France, during their residency, more than 50% of general practice (GP) residents are assigned to gynecology units for 6 months. They are involved in the first-line management of gynecologic emergencies and have to recognize them [2,3,4]. Their training field in gynecology lasts one semester, and GP residents have to acquire ultrasound skills rather quickly, especially for a transvaginal ultrasound scan (TVS).
Traditionally, GP residents practice TVS by a combination of observing senior gynecologists and practicing themselves under the supervision of seniors [5]. However, because it is invasive, TVS may create patient discomfort, especially if performed by a novice or, even more, by several operators.
As a response to this problem, new learning methods were developed in the last decade using simulation. These methods represent a solution for teaching TVS without involving any patients, according to the ethical recommendation “never the first time on a patient” [6]. In the context of emergencies, TVS aims to identify the main diagnosis using standardized planes [7]. However, for beginners, the 3D representation, the systematization of US examinations, and image optimization may represent difficulties that could be solved by simulation training [8].
TVS simulators are now available with endovaginal probes. These simulators allow to train to obtain the right planes, know how to zoom, and to optimize the image (gain, depth, and focus) [9].
However, only a few studies have assessed skill transfer from the simulator to real practice [10,11,12]. To justify the cost of these simulators, it is important to know whether the training has an impact on the management of patients and whether it lasts over time [9]. Tolsgaard et al. did demonstrate a sustained effect 2 months after simulation training on performance of OB/GYN residents, in terms of image optimization, equipment knowledge, systematization of the examination, and image interpretation [13]. TVS images produced by residents are a key element in patient medical files. It is important to assess the impact of simulation on the quality of images produced by GP residents.
The objective of this study was therefore to evaluate the quality of ultrasound images produced by GP residents 2 months after simulation training compared to clinical training alone.
Methods
This prospective controlled trial study included GP residents in Ile De France who began their semester in the gynecology department in November 2015 or in May 2016. All of the residents were invited to a theoretical lecture on gynecologic ultrasound followed by simulation training at the beginning of their semester in gynecology. Residents who consented to participate in the study were included in the simulation group. Residents who did not show up to this course because of timing conflicts but who volunteered to participate in the study were considered as the control group.
The theoretical part of the course recalled the physical basis of ultrasound, first-trimester obstetrical pathology, and ultrasound findings in first-trimester pathologies. In the second part, residents trained on pelvic simulators, the Blue Phantom® models (CAE HealthCare, USA, Fig. 1). Real echographs (Voluson E8, General Electric, USA) were used to perform the ultrasound scan on models. Residents were individually trained on the simulator. Instructors who were senior gynecologists taught the residents how to obtain the correct standardized planes in gynecology: the sagittal view of the uterus, right ovary, and left ovary. The Morrison space, or hepatorenal recess defined by the space that separates the liver from the right kidney, was not practiced on models. Different situations were found on the models: ectopic pregnancy, intrauterine pregnancy, and myoma.
In both groups, GP residents practiced TVS in gynecology units in hospitals of Ile De France. The course was conducted 20 days after their starting in the gynecology department. The protocol for all of them was to request help in the case of difficulty in performing the examination or suspicion of pathology.
It was recommended that the residents participating in the study provide one standardized image performed from one patient consulting to the gynecology department for pelvic pain or vaginal bleeding (sagittal view of the uterus, longitudinal view of both ovaries, and Morrison space) within 2 months after the training. The patients were selected by the resident. Their oral and written consent for sharing of images was collected, and images were systematically anonymized.
Images performed in the early pregnancy department were sent after they were anonymized by electronic mail. A visit to their hospital allowed the images of non-respondent residents to be obtained between the second and the third month after the course. The same images were asked to the control group during the same period.
Images gathered after the training were blindly scored by a senior obstetrician according to quality criteria validated by Salomon et al. [7]. These criteria are presented in Table 1. The quality criteria produced by the training group were compared to those of the control group.
The main outcome was the score obtained on four images performed on real patients 2 months after the simulation training. Eligible patients were women who presented with gynecology emergencies requiring TVS (bleeding or pain in the first trimester of pregnancy).
An auto-evaluation of the residents’ stress generated by TVS was measured using a simple numeric scale from 1 to 10, as a secondary outcome.
Data were stored in an Excel 2013 table and were analyzed with a Mann-Whitney test for quantitative variables with a non-normal distribution and a chi-squared test for qualitative variables using BiostatTGV®.
Results
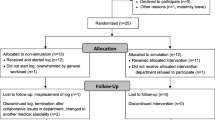
A total of 137 GP residents participated in the training. Among them, 36 GP residents provided consent to participate in the controlled trial, 26 in the simulation group and 10 in the control group (Fig. 2). Student characteristics were similar in both groups (Table 2).
The quality of images provided 2 months after the simulation training was significantly better in the simulation group for the sagittal view of the uterus (3.6 vs 2.7, p = 0.01), for the longitudinal view of the right ovary (2.8 vs 1.4, p = 0.027), and for the Morrison space (1.7 vs 0.4, p = 0.034). The difference was not significant for the left ovary (2.9 vs 1.7, p = 0.189) (Table 3).
In the simulation group, the global score obtained was satisfactory (quality score > 10) for 70% of the residents versus 20% in the control group (p = 0.027) (Table 4). The strict sagittal plane of the uterus was more accessible in both groups, but it was also the plane on which the training had the greatest impact. Ovary examination was problematic for residents who did not attend the training. The percentage of non-satisfactory images (score < 2/4) was 22.5% in the simulation group versus 70% in the control group (p = 0.0004). The examination was complete (the presence of four views) for 65% of the trained residents versus 30% of the control group (p = 0.15).
The stress experienced by GP residents about performing TVS was not different between the groups at the beginning of the semester (4.8 vs 5.7, p = 0.46) versus after 2 months (2.3 vs 3.3, p = 0,42) (Table 5).
Discussion
In this study, we found that initial simulation training for TVS permitted to improve the quality of images produced by GP residents in gynecology units after 2 months compared to clinical training alone.
Simulation is one of the options offered by the university for invasive procedures training [14]. The main goal of simulation in obstetrics and gynecology is to train students to procedures involving the genital sphere without mobilizing volunteers [15]. Most women consider TVS to be at least uncomfortable [16]. Task trainers for teaching vaginal digital examinations already exist. TVS simulators recently appeared and represent a revolution for the residency curriculum [17].
A metanalysis by Cook et al. compared the effectiveness of technology-enhanced simulation versus traditional training. Simulation training was effective for student satisfaction, knowledge, and skills [18]. Skill improvement on simulators was therefore expected. However, transfer of skills to clinical practice and patient effects after simulation training are not well known [19]. The Kirkpatrick pyramid can be used to rank medical education studies depending on the main outcome in four levels: 1—student satisfaction; 2—progress in theoretical and practical knowledge outside the clinic; 3—impact on clinical skills; and 4—impact or benefit for the patient [20]. As our primary outcome is image quality when performed on real patients, our study can be ranked as level 3.
To justify the costs that are invested in this type of training [9, 18, 21], it is necessary to know whether simulation training has a sustained impact on trainees’ skills [22]. Although an immediate effect of simulation is well known, only a few studies have assessed the long-term retention of the skills [23]. In a randomized prospective study, Tolsgaard et al. assessed the sustained effect of TVS simulation training using the Objective Structured Assessment of Ultrasound Skills (OSAUS). Ultrasound competence can be assessed using this valid score. The pass/fail scores may be used to help determine whether trainees are qualified for independent practice [24]. In this study, Tolsgaard et al. Demonstrated that simulation allowed significantly better image optimization, better approach systematization, better image interpretation, and a better decision-taking process with a sustained effect at 2 months. Participants reached the expert level on the simulator in a mean time of 3 h 16 min [13].
Other researchers have reported positive impacts of ultrasound simulation in residency curricula in other areas [25]. In traumatology, for instance, the ultrasound skills of GP residents trained by simulation were similar to those who trained on real patients [26].
In our study, we focused on GP residents. Their training field in gynecology is short, but the flow of patients is huge. They have to become autonomous very quickly. They are not familiar with TVS. The number of US scans necessary to acquire competency in first-line TVS is not known [11, 27]. It is definitely not necessary to teach GP residents expert TVS. However, some diagnosis in gynecology (pregnancy localization, hemoperitoneum) are easily identifiable thanks to a few standardized planes [3]. The four planes that are required are the sagittal view of the uterus, longitudinal views of both ovaries, and the Morrison space [28].
Another advantage of simulation training is that students face many conditions in a very short time. The models showed various situations: intrauterine pregnancy with the possibility of determining gestational age, myoma, ectopic pregnancy, and hemoperitoneum.
Our study had methodological weaknesses, mostly because the number of participants was small. There was no sample size calculation. Another bias was the absence of randomization of the groups. Residents who volunteered for the study were recruited after they did or did not show up to the courses. Our selection was therefore prone to bias. Plus, selection of patients to collect images from for assessment was not standardized. Despite those bias, it was noteworthy that the residents in the simulation group had a significantly better systematic approach and more respect for the standardized quality criteria.
Patient benefits of ultrasound simulation in the area of gynecology, in terms of morbidity or mortality, have not yet been demonstrated. Further research in this area is needed. However, one can assume that better systematization of TVS may avoid misdiagnosis (cysts complications, ectopic pregnancies).
Other benefits for patients were demonstrated in a previous study by Tolsgaard et al. During TVS, patients felt less discomfort and more confidence during TVS when the operator was trained by simulation [29].
Finally, in the area of education, Chalouhi et al. suggested that the use of ultrasound simulators was possible for the National Examination. Indeed, images obtained by residents on simulators were correlated to those obtained on real patients [30]. This implies that volunteers for National examination are no longer necessary.
Simulation has its place in the initial training of GP residents in gynecology. Studies have shown benefits in gynecology and in obstetrics for fetal defect screening. The benefits in terms of public health and impact on the detection of pathologies are, however, difficult to evaluate.
Conclusion
Simulation-based training improved the quality of pelvic US images in GP residents assessed after 2 months of experience in gynecology compared to clinical training alone
References
Moore CL, Copel JA. Point-of-care ultrasonography. N Engl J Med 24 févr 2011;364(8):749–757.
Popowski T, Huchon C, Fathallah K, Falissard B, Dumont A, Fauconnier A. Impact of accreditation training for residents on sonographic quality in gynecologic emergencies. J Ultrasound Med mai 2015;34(5):829–835.
Popowski T, Huchon C, Toret-Labeeuw F, Chantry AA, Aegerter P, Fauconnier A. Hemoperitoneum assessment in ectopic pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet févr 2012;116(2):97–100.
Toret-Labeeuw F, Huchon C, Popowski T, Chantry AA, Dumont A, Fauconnier A. Routine ultrasound examination by OB/GYN residents increase the accuracy of diagnosis for emergency surgery in gynecology. World J Emerg Surg. 2013;8(1):16.
Nitsche JF, Brost BC. Obstetric ultrasound simulation. Semin Perinatol juin 2013;37(3):199–204.
Simulation en santé - Rapport [Internet]. [cité 10 févr 2016]. Disponible sur: http://www.has-sante.fr/portail/plugins/ModuleXitiKLEE/types/FileDocument/doXiti.jsp?id=c_1173128
Salomon LJ, Nassar M, Bernard JP, Ville Y, Fauconnier A, Société Française pour l’Amélioration des Pratiques Echographiques (SFAPE). A score-based method to improve the quality of emergency gynaecological ultrasound examination. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol avr 2009;143(2):116–120.
Reliable and valid assessment of ultrasound operator competence in obstetrics and gynecology. - PubMed [Internet]. [cité 18 févr 2016]. Disponible sur: about:reader?url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov%2Fpubmed%2F23996613.
Zendejas B, Wang AT, Brydges R, Hamstra SJ, Cook DA. Cost: the missing outcome in simulation-based medical education research: a systematic review. Surgery févr 2013;153(2):160–176.
Cook DA, Hatala R, Brydges R, Zendejas B, Szostek JH, Wang AT, et al. Technology-enhanced simulation for health professions education: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 7 sept 2011;306(9):978–988.
Madsen ME, Konge L, Nørgaard LN, Tabor A, Ringsted C, Klemmensen AK, et al. Assessment of performance measures and learning curves for use of a virtual-reality ultrasound simulator in transvaginal ultrasound examination. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol déc 2014;44(6):693–699.
Blum T, Rieger A, Navab N, Friess H, Martignoni M. A review of computer-based simulators for ultrasound training. Simul Healthc avr 2013;8(2):98–108.
Tolsgaard MG, Ringsted C, Dreisler E, Nørgaard LN, Petersen JH, Madsen ME, et al. Sustained effect of simulation-based ultrasound training on clinical performance: a randomized trial. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol sept 2015;46(3):312–318.
Nitsche J, Morris D, Shumard K, Akoma U. Vaginal delivery simulation in the obstetrics and gynaecology clerkship. Clin Teach 20 oct 2015;13(5):343–347.
Arias T, Tran A, Breaud J, Fournier JP, Bongain A, Delotte J. A prospective study into the benefits of simulation training in teaching obstetric vaginal examination. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 23 févr 2016;133(3):380–384.
Tutschek B, Tercanli S, Chantraine F. Teaching and learning normal gynecological ultrasonography using simple virtual reality objects: a proposal for a standardized approach. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol mai 2012;39(5):595–596.
Tolsgaard MG, Jepsen RMHG, Rasmussen MB, Kayser L, Fors U, Laursen LC, et al. The effect of constructing versus solving virtual patient cases on transfer of learning: a randomized trial. Perspect Med Educ févr 2016;5(1):33–38.
Cook DA, Brydges R, Hamstra SJ, Zendejas B, Szostek JH, Wang AT, et al. Comparative effectiveness of technology-enhanced simulation versus other instructional methods: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Simul Healthc oct 2012;7(5):308–320.
Mema B, Harris I. The barriers and facilitators to transfer of ultrasound-guided central venous line skills from simulation to practice: exploring perceptions of learners and supervisors. Teach Learn Med juin 2016;28(2):115–124.
Mosley C, Dewhurst C, Molloy S, Shaw BN. What is the impact of structured resuscitation training on healthcare practitioners, their clients and the wider service? A BEME systematic review: BEME guide no. 20. Med Teach. 2012;34(6):e349–85.
Tolsgaard MG, Tabor A, Madsen ME, Wulff CB, Dyre L, Ringsted C, et al. Linking quality of care and training costs: cost-effectiveness in health professions education. Med Educ déc 2015;49(12):1263–1271.
Sheakley ML, Gilbert GE, Leighton K, Hall M, Callender D, Pederson D. A brief simulation intervention increasing basic science and clinical knowledge. Med Educ Online. 2016;21:30744.
Tolsgaard MG, Madsen ME, Ringsted C, Oxlund BS, Oldenburg A, Sorensen JL, et al. The effect of dyad versus individual simulation-based ultrasound training on skills transfer. Med Educ mars 2015;49(3):286–95.
Tolsgaard MG, Ringsted C, Dreisler E, Klemmensen A, Loft A, Sorensen JL, et al. Reliable and valid assessment of ultrasound operator competence in obstetrics and gynecology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol avr 2014;43(4):437–443.
Burden C, Preshaw J, White P, Draycott TJ, Grant S, Fox R. Usability of virtual-reality simulation training in obstetric ultrasonography: a prospective cohort study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol août 2013;42(2):213–217.
Bentley S, Mudan G, Strother C, Wong N. Are live ultrasound models replaceable? Traditional versus simulated education module for FAST exam. West J Emerg Med nov 2015;16(6):818–822.
Green J, Kahan M, Wong S. Obstetric and gynecologic resident ultrasound education project: is the current level of gynecologic ultrasound training in Canada meeting the needs of residents and faculty? J Ultrasound Med sept 2015;34(9):1583–1589.
Popowski T, Huchon C, Fathallah K, Bouhanna P, Bernard J-P, Fauconnier A. [Standardization of the gynecological emergency ultrasound examination]. Gynecol Obstet Fertil mars 2012;40(3):182–188.
Tolsgaard MG, Ringsted C, Rosthøj S, Nørgaard L, Møller L, Freiesleben NLC, et al. The effects of simulation-based transvaginal ultrasound training on quality and efficiency of care: a multicenter single-blind randomized trial. Ann Surg 25 janv. 2016;265(3):630–37.
Chalouhi GE, Bernardi V, Gueneuc A, Houssin I, Stirnemann JJ, Ville Y. Evaluation of trainees’ ability to perform obstetrical ultrasound using simulation: challenges and opportunities. Am J Obstet Gynecol avr 2016;214(4):525.e1–525.e8.
Acknowledgments
We thank the students who participated in this study.
Funding
None
Availability of data and materials
The authors attest the availability of data and material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors met the criteria for authorship and have read and approved the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All students gave their consent to participate.
Consent for publication
All participants gave their consent for publication.
Competing interests
The models were loaned by General Electric.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Le Lous, M., De Chanaud, N., Bourret, A. et al. Improving the quality of transvaginal ultrasound scan by simulation training for general practice residents. Adv Simul 2, 24 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41077-017-0056-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41077-017-0056-z