Abstract
The solar quiet (Sq) source morphology changes on a daily basis and becomes disturbed during periods of increased magnetic activity. Therefore, it may be preferable to use single-day magnetic field recordings for the analysis of Sq variations. However, in short recordings, Sq and ocean tidal magnetic signals are often indistinguishable because of the close periods. As a result, the tidal magnetic signals can be erroneously attributed to signals of Sq origin, which can potentially lead to wrong interpretations, especially when small signals, such as those induced by the 3-D heterogeneities in the mantle, are sought. In this work, we quantitatively estimate the effect of ocean tidal signals in daily variations by performing rigorous 3-D modeling and comparing the results with real measurements from ground and sea floor observatories. We found that the vertical magnetic field component, Z, is affected the most such that at some locations the tidal signals explain the majority of the observed daily variation. Further, horizontal tidal magnetic fields at the sea floor are larger in amplitude and exhibit different spatial structures compared to signals estimated at the sea level. We propose a scheme aimed at correcting data for the ocean tidal signals and show that such correction suppresses the tidal signals in the observed field variations.

Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Electromagnetic (EM) induction sounding with natural sources contributes to our knowledge of the composition, temperature, and presence of fluids in the Earth’s interior. Among other methods, daily ionospheric solar quiet (Sq) variations can be used to probe the electrical conductivity of the upper mantle (e.g., Schmucker 1999b; Olsen 1998; Koch and Kuvshinov 2013, 2015). Sq variations originate from an Sq electric current system flowing in a thin ionospheric E-layer. This current system is driven by atmospheric tides of predominantly thermal origins in the ambient magnetic field of the Earth and is active on the sunlit side at midlatitudes (Campbell 1989; Yamazaki and Maute 2017).
The Sq source morphology varies daily, seasonally, and yearly depending on short- and long-term solar magnetic activity and the Earth’s orbital position. Therefore, in order to mitigate these various effects, it is reasonable to work with single-day magnetic recordings when analyzing Sq variations. In addition, bearing in mind the complex geometry of the Sq source, one should preferably choose geomagnetically quiet days during or close to the time around equinoxes (March–April, September–October) so that the source will have a relatively simple, symmetric double vortex structure. Moreover, by choosing equinoctial months, we can further avoid possible magnetic field daily variations caused by the magneto-tail current during solstice months (Lühr et al. 2017).
Assuming that Sq variations are periodic, one can represent them via a sum of time harmonics with periods of 24, 12, 8, 6, etc., h (Matsushita and Maeda 1965). At the same time, diurnal and semidiurnal lunar and solar oceanic tides induce magnetic signals with periods close or equal to 12 and 24 h (Egbert and Erofeeva 2002). In short time series, e.g., in single-day data, signals with close periods become inseparable (see “Appendix” for more details). Consequently, ocean tidal signals inevitably affect Sq variations at periods of 12 and 24 h if the length of the time series is as short as one day. If not accounted for, the effect of ocean tidal signals in Sq variations can be mistakenly attributed to being part of the Sq signals, for instance, those induced by the mantle conductivity anomalies. This prompted us to assess the effect of the ocean tidal signals in daily variations and implement a correction scheme for them.
Governing equations
For this study, the problem is governed by Maxwell’s equations, which are presented here in the frequency domain
where \({\mathbf {j}}^{\text {ext}}\) is the extraneous electric current, \({\mathbf {B}}\) and \({\mathbf {E}}\) are the magnetic and electric fields, respectively, \(\mu _0\) is the magnetic permeability of free space, \(\sigma \) is the electrical conductivity, and \(\omega \) is the angular frequency. The expressions for the Sq and ocean tidal extraneous currents will be given in sections “Modeling of Sq magnetic signals” and “Modeling of tidal magnetic signals”, respectively. We neglect displacement currents in the considered period range and adopt the Fourier transform convention \(\text {exp}(\text {i}\omega t)\).
Modeling of Sq magnetic signals
Frequency domain modeling
We represent the extraneous current responsible for Sq variations on the ground in the following form (e.g., Schmucker 1984)
where the current sheet density, \({\mathbf {J}}_{\text {H}}\), reads
Equations (2)–(3) indicate that \({\mathbf {j}}^{\text {ext}}\) flows in a thin spherical shell just above the Earth’s surface, \(a^+\). Here, \({\mathbf {e}}_r\) is an outward unit vector, r is the distance from the Earth’s center, \(a = 6371.2\) km for Earth’s mean radius, and \(\nabla _H \mathrm {\Psi }\) is the tangential gradient of the stream function
where terms \(\epsilon _n^m\) correspond to coefficients describing the external part of the magnetic potential (Olsen et al. 2010), \(\vartheta \) denotes the colatitude, and \(\varphi \) denotes the longitude; n and m are, respectively, the degree and order of the spherical harmonic (SH) \(Y_{n}^{m} = P_n^{\left| m\right| } (\cos \vartheta ) e^{\text {i}m\varphi }\) with \(P_n^{\left| m\right| }\) given by the Schmidt quasi-normalized associated Legendre polynomials. Note that the stream function, \(\mathrm {\Psi }\), enables a condensed representation of the Sq current system (Sq source); for example, the contours and sign of the stream function specify the direction of \({\mathbf {J}}_{\text {H}}\).
The Sq source is determined by a set of \(\epsilon _n^m\) coefficients. The n, m combinations describing the Sq source are adopted from Schmucker’s paper (Schmucker 1999a). Following his method (see Appendix B in Schmucker 1999a), the double sum in Eq. (4) is given by
with \(p = 1, 2, \ldots , 6\), where p are time harmonics with characteristic Sq variation periods \(T = \frac{24}{p}\). The amplitudes of Sq variations subside toward higher p values, and the time harmonics \(p>6\) corresponding to variations with periods shorter than 4 h no longer contribute to the total signal. By setting \(K = 4\) and \(L=1\), which control the number of, respectively, local-time terms (\(m = p\)) and general terms (\(m \ne p\)) per time harmonic (Schmucker 1999a), we obtain 12 SH combinations for each p, except the \(p=1, n=0, m=0\) combination, which is forbidden since \(\nabla \cdot {\mathbf {B}} = 0\) should be satisfied everywhere (Sabaka et al. 2010). Hence, Eq. (5) gives a total of 71 SH functions (11 for \(p=1\) and \(5\times 12\) for \(p = 2,\ldots ,6\)) which are listed in Table 1.
To estimate the source coefficients \(\epsilon _n^m\), we used the S3D method presented in Koch and Kuvshinov (2013). It computes source coefficients while taking into account the 3-D ocean effect commonly observed at coastal and oceanic observatories (Kuvshinov and Olsen 2005). The extraneous current from Eqs. (2)–(3) can be expressed as a sum of “unit currents” scaled by the source coefficients (cf. Eq. 4)
with
where \(\nabla _\perp = r \nabla _H\). Within the S3D method, we numerically solve the system of Eq. (1) for each \({\mathbf {j}}_n^{m,\text {unit}}\) (Koch and Kuvshinov 2013)
by using a volume integral equation solver given by Kuvshinov (2008), hereinafter called X3DG. This solver computes an EM field induced by (arbitrary) sources for a specified 3-D conductivity model of the Earth. Our 3-D model consists of a 1-D mantle model complemented by a thin layer of laterally varying 2-D conductance (see Fig. 1). This layer captures the non-uniform distribution of the continents and oceans. The system (8) is solved for a total of 71 unit magnetic fields \({\mathbf {B}}^{m,\text {unit}}_n\) (11 for \(p=1\) and 5 × 12 for other p). The unit magnetic fields are calculated on a regular, global grid at an observation level r, which can be at the ground, \(r = a\), at the sea floor, \(r < a\), or above the ground, \(r > a\), e.g., at a satellite altitude.
Conductivity model used for modeling Sq and tidal EM fields. Left: 1-D conductivity model obtained from inversion of satellite and observatory data (Püthe et al. 2015). Right: 2-D conductance map (first 10 km). Sediment conductance values were taken from (Alekseev et al. 2015), and seawater conductivity came from (Grayver et al. 2016)
Four snapshots of the Sq current system (in a form of stream function; in kA) estimated for a quasi-equinoctial day (March 16, 2011). Currents of the northern vortex move counterclockwise, and those of the southern vortex move clockwise. Dashed black lines show geomagnetic latitude ranges (between \(\pm\, 6^{\circ }\) and \(\pm\, 60^{\circ }\)). All observatories used for Sq source estimation lie within these boundaries
By virtue of linearity of Maxwell’s equations with respect to the source, magnetic fields at any location \(\mathbf{r}_j =(r_j,\vartheta _j,\varphi _j)\) can be expressed by a sum of the unit magnetic fields scaled by the unknown source coefficients (Koch and Kuvshinov 2013)
where \(\omega _p = \frac{2\pi }{24}p\). We estimate \(\epsilon _n^m\) by using a robust least-squares fitting of the observed magnetic fields (corrected for core and crustal contributions with the CHAOS-6 model Finlay et al. 2016) from a number of globally distributed magnetic observatories. Note that S3D allows us to estimate \(\epsilon _n^m\) from any combination of magnetic field components. In particular, since horizontal components are less influenced by the 3-D induction, we exclude the vertical component while estimating the external source coefficients. As an example, Fig. 2 depicts the Sq source field determined with the S3D method for a geomagnetically quiet, almost equinoctial day of March 16, 2011.
Time domain modeling
Given \(\epsilon _n^m\), we can calculate the synthetic Sq variations in the frequency domain by multiplying the source coefficients with the unit fields
where \(\mathbf{r} =(r,\vartheta ,\varphi )\). We then transform the synthetic fields into the time domain by using a Fourier series
The work-flow chart shown in Fig. 3 summarizes the steps described in this section.
Modeling of tidal magnetic signals
Frequency domain modeling
An ocean tidal constituent is a periodic movement of ocean water caused by the gravitational forces between the Earth, Sun, and Moon (NOAA 2016). Among the large number of tidal constituents, several solar and lunar diurnal and semidiurnal constituents dominate. Table 2 lists the constituents with the largest global amplitudes that were considered in this work.
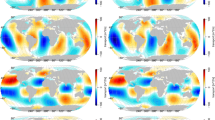
Modeled X component at a period of 12 h at the surface level. Top and bottom are the Sq and tidal field, respectively. Left and right are the real and imaginary parts, respectively. Green circles denote, from left to right, CZT (Crozet Archipelago), T12-2 (Philippine Sea), SHU (Alaska), VAL (Ireland), and TDC (Tristan da Cunha). Note the different scales for top and bottom plots
Same as Fig. 6, but at the sea floor
The extraneous current due to the ocean tidal flows is given by (e.g., Maus and Kuvshinov 2004)
where \({\mathbf {J}}_{\text {H}}\) reads
with \(\mathbf{r}_a = (a, \vartheta , \varphi )\), k represents the kth tidal constituent, \(\omega _k\) is the corresponding angular frequency, \(\sigma _s\) is the depth-averaged seawater conductivity, \({\mathbf {u}}\) are the depth-integrated seawater transport, and \({\mathbf {B}}^{\text {main}}\) is Earth’s main magnetic field. Note that, in contrast to the Sq extraneous current that flows above the Earth’s surface, the tidal extraneous current is confined to the oceans. We used the TPXO8-atlas global ocean tide model (Egbert and Erofeeva 2002) for the seawater transport \({\mathbf {u}}\), the IGRF-12 model (Thébault et al. 2015) for \({\mathbf {B}}^{\text {main}}\), and a climatological-derived model for \(\sigma _s\) (Grayver et al. 2016). We calculate the magnetic fields \({\mathbf {B}}^{\text {Tides}}\) due to \({\mathbf {j}}^{\text {ext}}\) by solving the system of Eq. (1).
Time domain modeling
In order to transform the tidal magnetic fields from the frequency to time domain, the conventional Fourier transform is complemented with amplitude and phase correction factors resulting in
Here, \(V_{0,k}\) is an astronomical argument, \(t_0\) represents the time on January 1, 1992, at 00:00:00, and \(u_k\) and \(f_k\) are, respectively, the phase and amplitude modulating factors that incorporate the 18.6-y variation in tide-producing forces caused by the lunar regression cycle (Parker 2007). \(f_k\) and \(u_k\) are taken as constant values over a year, and we retrieved them from Oregon State University Tidal Prediction Software (OTPS2) (Egbert and Erofeeva 2002). As an example, Table 3 lists \(f_k\) and \(u_k\) values for the year 2011. Equation (14) is adapted from Lord Kelvin’s tide prediction equation originally designed for the calculation of tidal heights (NOAA 2016). Note that OTPS2 uses this equation for prediction of both tidal elevations and tidal transports. A summary of the modeling steps described in this section is shown in Fig. 4.
Same as Fig. 8, but at the sea floor
Modeled Z component at a period of 12 h at the surface level. Top and bottom are the Sq and tidal fields, respectively. Left and right are the real and imaginary parts, respectively. Note the different scales for top and bottom plots, as well as with respect to the X, Y component plots. Because of the continuity of the Z component across the ocean column, Z at the sea floor is not shown
Modeled X component at a period of 24 h at the sea level. Top and bottom are the Sq and tidal field, respectively. Left and right are the real and imaginary parts, respectively. Green circles denote from left to right CZT (Crozet Archipelago), T12-2 (Philippine Sea), SHU (Alaska), VAL (Ireland), and TDC (Tristan da Cunha). Note the different scales for top and bottom plots
Results
In what follows, all results are presented by using \({\mathrm {X}} = -{\mathrm {B}}_{\vartheta }\), \({\mathrm {Y}} = {\mathrm {B}}_{\varphi }\), and \({\mathrm {Z}} = -{\mathrm {B}}_r\) conventions.
Comparison of tidal and Sq magnetic fields
By using the methodology described in sections “Modeling of Sq magnetic signals” and “Modeling of tidal magnetic signals”, we modeled Sq and tidal magnetic fields in the time domain on the geomagnetically quiet, almost equinoctial day of March 16, 2011. Following ISGI (2016), a day is considered quiet if \(\text {mean}(aa)<13\) nT and \(\sum \text {p} <6\) were fulfilled over a 48-h interval (CC48 day). In this manner, we can ensure that the chosen day has no significant disturbances 12 h before and after the day of interest. Here, \(\text {p}\) should not be mistaken with the time harmonic p, and it denotes a weight assigned to an individual aa value according to ISGI (2016). For the chosen day, \(\text {mean}(aa) = 3\) nT and \(\sum \text {p} = 0\). Further, to minimize the influence from auroral and equatorial electrojets, only data from 73 midlatitude observatories between \(\pm\, 6^{\circ }\) and \(\pm\, 60^{\circ }\) geomagnetic latitudes were used.
We start by comparing observed and synthesized vertical magnetic fields at two coastal and two island observatories on this day. Figure 5 depicts solely the Sq signal (\({\mathbf {b}}^{\text {Sq}}\)) in blue and a sum of the Sq and tidal fields, denoted as “Sq+Tides” (\({\mathbf {b}}^{\text {Sq}}\) + \({\mathbf {b}}^{\text {Tides}}\)), in dashed red. For all four observatories, the “Sq+Tides” signals matched the observations better than the Sq signals alone.
Same as Fig. 11, but at the sea floor
Same as Fig. 13, but at the sea floor
Next, we show the effect of tidal magnetic signals in daily variations at periods of 12 and 24 h at one surface and one sea floor location. We chose CZT (Crozet Archipelago) as the surface observatory and T12-2 (Philippine Sea; deployed in the framework of the Stagnant Slab Project Baba et al. 2010) as the sea floor site. Tables 4 and 5 present absolute values of \({\mathbf {B}}^{\text {Sq}}\) and \(\widetilde{{\mathbf {B}}}^{\text {Tides}}\) at these periods, where \({\mathbf {B}}^{\text {Sq}}\) comes from Eq. (10) and \(\widetilde{{\mathbf {B}}}^{\text {Tides}}\) denotes the discrete Fourier transform of \({\mathbf {b}}^{\text {Tides}}\) from Eq. (14). At the surface observatory, the tidal fields at the period of 12 h are up to 4 times stronger than those at the period of 24 h. In comparison, at the sea floor site this factor does not exceed 2.5. For the horizontal components, the Sq signal is stronger than the tidal signal. The situation is different for the Z component at the surface. For instance, the Z component of the tidal signals at CZT at a period of 12 h is more than 2 times larger than the Sq signal. In fact, the tidal field at CZT on this day accounts for 70% of the sum (Sq+Tides). This indicates that the tidal magnetic signals at some locations significantly contribute to the observed daily variations.
In addition to looking at specific locations, we show global maps (with resolutions of \(1^{\circ } \times 1^{\circ }\)) of \({\mathbf {B}}^{\text {Sq}}\) and \(\widetilde{{\mathbf {B}}}^{\text {Tides}}\). Figures 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 show \({\mathbf {B}}^{\text {Sq}}\) (top) and \(\widetilde{{\mathbf {B}}}^{\text {Tides}}\) (bottom) at a period of 12 h, while Figs. 11, 12, 13, 14 and 15 depict the results at the 24-h period. Since Sq and tidal vertical components of the magnetic field are continuous across the air–ocean interface, only fields at the sea level are shown. In contrast, horizontal magnetic fields are shown at the sea level and the sea floor because they experience a jump across the ocean (e.g., see Appendix G in Kuvshinov and Semenov 2012)
Here, superscripts “+” and “−” stand for the sea surface and sea floor, respectively, \(S=\sigma d\) is the conductance, d is the depth of the ocean, and \(\mathbf{E}_H\) is the horizontal electric field. The latter equation tells us that—along with the vertical magnetic field—Sq and tidal horizontal electric fields are continuous across the air–sea interface. Note that Eq. (15) is valid at periods longer than several hours.
Modeled Z component at a period of 24 h at the sea level. Top and bottom are the Sq and tidal field, respectively. Left and right are the real and imaginary parts, respectively. Note the different scales for top and bottom plots, as well as with respect to the X, Y component plots. Because of the continuity of the Z component across the ocean column, Z at the sea floor is not shown
Synthesized Z from a sum of eight tidal constituents (cf. Table 2) at VAL (upper panel) and T12-2 (lower panel) for the year 2011
Since the tidal magnetic signals at the period of 12 h are dominated by the semidiurnal M2 tide, which is known to generate the largest magnetic fields among all tidal constituents (Kuvshinov 2008), it is no surprise that the tidal signals at a period of 12 h, both at the sea level and sea floor (cf. bottom plots of Figs. 6, 7, 8, 9, 10), have larger amplitudes than those at the period of 24 h (cf. bottom plots of Figs. 11, 12, 13, 14, 15). Further, the Sq signals at the 24-h period have larger amplitudes than those at the 12-h period.
Figures 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 14 also show that sea floor horizontal tidal magnetic fields exhibit a considerably different spatial pattern than those at the sea level. Overall, tidal signals at the sea floor are 2–3 times stronger than those at the sea level. The situation is opposite with the Sq signals; specifically, they are 2–3 times weaker at the sea floor due to the 3-D nature of the problem, namely the heterogeneous conductance of the continents and oceans. Maximum amplitudes of Sq signals are a few times larger than those of tidal signals both at the surface and sea floor. However, due to different global patterns of Sq and tidal signals, tidal signals may become comparable in amplitude and even exceed Sq signals at specific locations. This effect is more pronounced at the period of 12 h than that at 24 h for all three components, with the Z component affected most (cf. Figs. 10, 15).
The results presented in Figs. 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 refer to a specific day—March 16, 2011. However, the results of our modeling show that tidal signals vary substantially over the year since individual constituents modulate total signals depending on the phase (cf. Eq. 14). This behavior is shown in Fig. 16 for the geomagnetic observatory VAL (Ireland) and the sea floor site T12-2. Clearly, the peak amplitudes reach up to 5 nT and go as low as 1 nT.
The correction scheme and its validation
The main findings of the previous subsection are that tidal signals can significantly contribute to daily variations and become commensurate with the internal induced signals. Further, this contribution varies over the year. Based on these findings, we propose to correct data for the effect of tidal magnetic signals in addition to core and crustal corrections as follows
To validate the correction scheme, we performed an experiment using 1 y of data at a ground observatory and sea floor site. The yearly time series are sufficiently long to enable the separation of the effects from Sq and tides in the spectral domain. This can be observed in the power spectral density (PSD) plots of yearly magnetic fields at VAL (Fig. 17, left) and T12-2 (Fig. 17, right). Peaks at precisely 12 and 24 h correspond to the dominant periods of Sq variations, whereas most prominent 12- and 24-h side peaks are induced by, respectively, the M2 and O1 tidal constituents. One can observe that the 24-h side peak is better seen in the sea floor results.
Figure 17 shows data before and after correction for the tidal magnetic signals. At the ground-based site, the 12-h side peak due to the M2 tide is significantly reduced in its amplitude for Y and Z. The remaining, unaccounted semidiurnal variations in X and diurnal variations are probably attributed to atmospheric lunar tidal variations with the same periods or imprecisions in the source definition and conductivity model. At the sea floor site, the tidal signals (both M2 and O1) are well suppressed in all components. Moreover, the corrected signal is reduced at a period of 12 h in the Y and Z components, which is most likely associated with the correction for the S2 tide. For all three components, small reductions in amplitude are also evident at the periods corresponding to the N2 and Q1 tides.
Conclusions
In this paper, we assessed the effect of tidal and Sq magnetic signals in daily variations at the surface and sea floor. As expected, sea floor horizontal tidal magnetic fields differ substantially from those at the surface both in amplitude and in spatial structure. In comparison with the surface modeling results, sea floor tidal signals are 2–3 times stronger, while sea floor Sq signals are 2–3 times weaker. Even though Sq signals are a few times larger than the tidal signals for most regions, owing to their substantially different global patterns, tidal signals may exceed Sq signals at many locations. This, in particular, is plausible for the vertical magnetic field component Z of the daily variations.
We compared observed and modeled daily variations at several coastal and island observatories and concluded that at some locations the tidal signals could in fact explain the majority of the observed daily variations. We showed that the effect of tidal magnetic signals at numerous locations might be sufficiently strong relative to Sq variations, and neglecting tidal signals might lead to a misinterpretation of data when analyzing daily variations and assuming that these variations are of purely Sq origin. Furthermore, in the context of internal studies, where smaller internally induced Sq signals are to be delineated, the contribution of tidal magnetic signals becomes a significant deteriorating factor.
We proposed a numerical scheme to correct for the effect of tidal magnetic signals. Specifically, we proposed the subtraction of the modeled tidal magnetic fields from observations. Modeling was performed by using realistic tidal transports and conductivity models of the Earth. We validated the correction scheme by using 1-y long time series of magnetic fields at one ground-based and one sea floor site where the tidal signals appear to be substantial. We showed that such correction enables efficient suppression of the tidal signals in the observations.
Abbreviations
- Sq:
-
solar quiet
- EM:
-
electromagnetic
- SH:
-
spherical harmonics
- 3-D:
-
three-dimensional
- S3D:
-
a scheme for a source determination incorporating the 3-D ocean effect
- X3DG:
-
a code to compute the EM field in a spherical model of the Earth with a 3-D conductivity distribution
- TPXO8-atlas:
-
global model of ocean tides
References
Alekseev D, Kuvshinov A, Palshin N (2015) Compilation of 3D global conductivity model of the Earth for space weather applications. Earth Planets Space 67(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0272-5
Baba K, Utada H, Goto T-N, Kasaya T, Shimizu H, Tada N (2010) Electrical conductivity imaging of the Philippine Sea upper mantle using seafloor magnetotelluric data. Phys Earth Planet Inter 183(1):44–62
Campbell WH (1989) An introduction to quiet daily geomagnetic fields. Pure Appl Geophys 131(3):315–331
Egbert GD, Erofeeva SY (2002) Efficient inverse modeling of barotropic ocean tides. J Atmos Ocean Technol 19(2):183–204
Finlay CC, Olsen N, Kotsiaros S, Gillet N, Tøffner-Clausen L (2016) Recent geomagnetic secular variation from Swarm. **Earth Planets Space 68(1):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-016-0486-1
Grayver AV, Schnepf NR, Kuvshinov AV, Sabaka TJ, Manoj C, Olsen N (2016) Satellite tidal magnetic signals constrain oceanic lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary. Sci Adv 2(9):1600798
ISGI. http://isgi.unistra.fr/indices_aa.php. Accessed 8 Dec 2016
Koch S, Kuvshinov A (2013) Global 3-D EM inversion of Sq variations based on simultaneous source and conductivity determination: concept validation and resolution studies. Geophys J Int 195(1):98–116
Koch S, Kuvshinov A (2015) 3-D EM inversion of ground based geomagnetic Sq data. Results from the analysis of Australian array (AWAGS) data. Geophys J Int 200(3):1284–1296
Kuvshinov AV (2008) 3-D global induction in the oceans and solid Earth: recent progress in modeling magnetic and electric fields from sources of magnetospheric, ionospheric and oceanic origin. Surv Geophys 29(2):139–186
Kuvshinov A, Semenov A (2012) Global 3-D imaging of mantle electrical conductivity based on inversion of observatory C-responses—I. An approach and its verification. Geophys J Int 189(3):1335–1352
Kuvshinov A, Olsen N (2005) Modelling the ocean effect of geomagnetic storms at ground and satellite altitude. In: Earth observation with CHAMP. Springer, Berlin, pp 353–358
Lühr H, Xiong C, Olsen N, Le G (2017) Near-earth magnetic field effects of large-scale magnetospheric currents. Space Sci Rev 206:521–545
Matsushita S, Maeda H (1965) On the geomagnetic solar quiet daily variation field during the IGY. J Geophys Res 70(11):2535–2558
Maus S, Kuvshinov A (2004) Ocean tidal signals in observatory and satellite magnetic measurements. Geophys Res Lett 31(15):15313
NOAA. https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/. Accessed 26 Oct 2016
Olsen N (1998) The electrical conductivity of the mantle beneath Europe derived from C-responses from 3 to 720 hr. Geophys J Int 133(2):298–308
Olsen N, Glassmeier K-H, Jia X (2010) Separation of the magnetic field into external and internal parts. Space Sci Rev 152(1–4):135–157
Parker BB (2007) Tidal analysis and prediction. NOAA Special Publication NOS CO-OPS 3
Püthe C, Kuvshinov A, Khan A, Olsen N (2015) A new model of Earth’s radial conductivity structure derived from over 10 yr of satellite and observatory magnetic data. Geophys J Int 203(3):1864–1872
Sabaka TJ, Hulot G, Olsen N (2010) Mathematical properties relevant to geomagnetic field modeling. In: Freeden W, Nashed MZ, Sonar T (eds) Handbook of geomathematics. Springer, Berlin, pp 503–538
Schmucker U (1984) Sources of the geomagnetic field. In: Landolt-Börnstein. Numerical data and functional relationships in science and technology. New Series. Group V: Geophysics and space research, vol 2: geophysics of the solid earth, the moon and the planets. Subvolume b. Springer, Berlin, pp 31–99
Schmucker U (1999a) A spherical harmonic analysis of solar daily variations in the years 1964–1965: response estimates and source fields for global induction—I. Methods. Geophys J Int 136(2):439–454
Schmucker U (1999b) A spherical harmonic analysis of solar daily variations in the years 1964–1965: response estimates and source fields for global induction—II. Results. Geophys J Int 136(2):455–476
Thébault E, Finlay CC, Beggan CD, Alken P, Aubert J, Barrois O, Bertrand F, Bondar T, Boness A, Brocco L et al (2015) International geomagnetic reference field: the 12th generation. Earth Planets Space 67(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-015-0228-9
Yamazaki Y, Maute A (2017) Sq and EEJ—a review on the daily variation of the geomagnetic field caused by ionospheric dynamo currents. Space Sci Rev 206:299–405
Authors’ contributions
MG estimated the Sq source and analyzed the data. MG and AG performed the modeling of the tidal magnetic signals. AK provided the three-dimensional modeling code X3DG. AG and AK created the concept of the study. MG drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the British Geological Survey for collecting and distributing high-quality data for INTERMAGNET stations and the staff at the Pacific21 data center for making the data from the Stagnant Slab Project open. We further thank Takao Koyama and two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments. This study was supported by the ETH Grant No. ETH-3215-2.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Separation of signals in the frequency domain
Appendix: Separation of signals in the frequency domain
The minimal length of the time series needed for a successful separation of two signals can be expressed by the following equation
where \(f_s\) is the sampling frequency, \(f_1=1/T_1\) and \(f_2=1/T_2\) are the frequencies of the two signals, and L is the minimum length of the time series. Within this study, we worked with hourly means of observatory data. Therefore, Eq. (17) gives 30 d to separate M2 from S2 or Sq, 55 d to separate M2 from N2, 363 d to separate S2 from K2, and 364 d to separate P1 from K1. In reality, since data often contain noise, reliable separation may require even longer time series.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Guzavina, M., Grayver, A. & Kuvshinov, A. Do ocean tidal signals influence recovery of solar quiet variations?. Earth Planets Space 70, 5 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-017-0769-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-017-0769-1