Abstract
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) is caused due to the disturbance of imprinted genes at chromosome 11p15. The molecular confirmation of this syndrome is possible in approximately 85% of the cases, whereas in the remaining 15% of the cases, the underlying defect remains unclear. The goal of our research was to identify new epigenetic loci related to BWS. We studied a group of 25 patients clinically diagnosed with BWS but without molecular conformation after DNA diagnostics and performed a whole genome methylation analysis using the HumanMethylation450 Array (Illumina).
We found hypermethylation throughout the methylome in two BWS patients. The hypermethylated sites in these patients overlapped and included both non-imprinted and imprinted regions. This finding was not previously described in any BWS-diagnosed patient.
Furthermore, one BWS patient exhibited aberrant methylation in four maternally methylated regions—IGF1R, NHP2L1, L3MBTL, and ZDBF2—that overlapped with the differentially methylated regions found in BWS patients with multi-locus imprinting disturbance (MLID). This finding suggests that the BWS phenotype can result from MLID without detectable methylation defects in the primarily disease-associated loci (11p15). Another patient manifested small but significant aberrant methylation in disease-associated loci at 11p near H19, possibly confirming the diagnosis in this patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS) (OMIM 130650) is an overgrowth disorder with predisposition to embryonal tumor development. Its clinical symptoms include macrosomia, macroglossia, and abdominal wall defects, whereas minor features include ear pits, hypoglycemia, nephromegaly, and hemihypertrophy. BWS is clinically heterogeneous, and the major features may not manifest immediately after birth but appear in the first month of life [1].
Most cases (about 85%) of BWS result from various genetic and epigenetic aberrations in the imprinted region on chromosome 11p15.5. This region contains two imprinting centers: H19 TSS DMR (transcription start site differentially methylated region) and KCNQ1OT1 TSS DMR. The former regulates the transcription of genes IGF2 and H19, whereas the latter regulates, among others, KCNQ10T1 and KCNQ1 [2] in a tissue-dependent manner. About 50% of these cases are caused by a loss of methylation at KCNQ1OT1 TSS DMR on the maternal chromosome and 20% by paternal uniparental disomy (UPD) of 11p15.5. Up to 5% have a gain of methylation on the maternal chromosome at H19 TSS DMR. Between 5% and 10% of the cases are caused by a mutation in the maternal copy of CDKN1C. Finally, some cases are caused by chromosomal aberrations on chromosome 11, for example, microdeletions (< 1%), translocations (< 1%), inversions (< 1%), or duplications (< 1%) within the imprinted region of 11p15 (2). Furthermore, hypomethylation in a large number of imprinting disorders (IDs) occurs not only at a single locus but also at other imprinted loci. This phenomenon is known as multi-locus imprinting disturbance (MLID) and can be seen in about 30% of BWS with hypomethylation at KCNQ1OT1 [3]. In about 15% of BWS, no (epi)genetic cause can be found (Fig. 1) [4].
The aim of this study was to identify new BWS-related epigenetic loci in a group of patients with unknown (epi)genetic cause. We searched for regions with altered methylation in known imprinted genes in each patient and regions with altered methylation shared between patients in the whole methylome.
Methods
DNA was isolated from whole blood samples using Gentra Chemicals (Qiagen).
Patient population
BWS patients
Twenty-five BWS patients (BWS1–BWS25) were devoid of any methylation defect in the imprinted region on chromosome 11p15.5 and a mutation in CDKN1C, as determined in the genome diagnostics department of the Academic Medical Center (the Netherlands). The imprinting defect at 11p15.5 was excluded using high resolution melting analysis (HRMA) [5] and/or methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MS-MLPA). For both the methods, the limit of detection was 10% of alteration of methylation in comparison to negative controls. Maternally inherited mutations in CDKN1C were excluded using Sanger sequencing (see Additional file 1).
All the patients fulfilled the BWS criteria of DeBaun, displaying at least two of the five most common BWS features, including macrosomia, macroglossia, abdominal wall defects, ear creases/pits, and hypoglycemia [6, 7].
Positive controls (MLID-BWS)
We used five DNA samples from MLID-BWS patients with known hypomethylation at KCNQ1OT1 TSS DMR and other imprinted loci as a positive control group to determine the robustness of this test. Hypomethylation in these patients was previously determined and described by Bliek et al. in 2008 [8]. The additional hypomethylated loci in these patients were as follows:
-
MLID-BWS1: MEST, GNAS_AS1;
-
MLID-BWS2: GNAS_AS1;
-
MLID-BWS3: GNAS_AS1, DIRAS3;
-
MLID-BWS4: MEST; and
-
MLID-BWS5: GBR10A, GNAS_AS1, SNRPN.
Control group
Twenty-six DNA samples from healthy anonymous individuals were used as a normal control group.
HumanMethylation450 array
The HumanMethylation450 array (Illumina, San Diego, USA) was used to obtain genome-wide methylation levels. This array comprises 485,000 CpG sites throughout the genome and covers 99% of RefSeq genes and 96% of CpG islands. In order to reduce technical bias, patients and controls were randomly divided over the analysis. DNA was bisulfite converted using the EZ DNA methylation kit of ZYMO® and subsequently submitted for analysis on the HumanMethylation450 array, outsourced to GenomeScan, Leiden, The Netherlands (ISO/IEC 17025 approved). The quality of raw methylation data was assessed using the MethylAid script in R (GenomeScan’s Guidelines for Successful Methylation Experiments Using the Illumina Infinium® HumanMethylation BeadChip). All the samples met the quality criteria. To analyze our data, we used a statistical method for single-sample analysis described by Rezwan et al. [9] adapted to a MINFI package in R (based on the Crawford-Howell t test). Prior to this analysis, all probes known to involve polymorphic sites (minor allele frequency, MAF > 0.01), cross-hybridization probes, and probes located on sex chromosomes were removed from the dataset. The workflow and QC details are depicted in the Additional file 1. The 450 k data was normalized with the function preprocessFunnorm of MINFI [10].
Differentially methylated positions (DMP) with assigned adjusted P value for M-values smaller than 0.05 were considered as significant (adjusted according to the false discovery rate; FDR).
Searching for DMRs at imprinted loci
Next, we determined whether significant DMPs were located in the imprinted regions. To correctly identify imprinted regions in our data, we used chromosomal locations for imprinted DMRs published by the European Network for Human Congenital Imprinting Disorder. These regions will be referred to as COST regions. (standardized nomenclature for imprinted loci/DMR; http://www.imprinting-disorders.eu/?page_id=3154). Note that COST regions in imprinted loci are differentially methylated alleles. (GenomicRanges version 1.28; R-software).
We calculated the percentage of significant DMPs that were located in COST regions for each patient. Further, to avoid false-positive results, only COST regions with two or more significant DMPs were considered as potential aberrantly methylated regions.
Searching for new DMRs shared between BWS patients
To test whether significant DMPs occurred in two or more BWS patients, we carried out a comparative analysis: (1) first, we selected significant DMPs based on the adj.Pvalue_M < 0.05 per patient, taking into account the direction of aberration (hypomethylated; hypermethylated); (2) then, we compared selected DMPs between patients and filtered out DMPs that occurred in more than one BWS patient; (3) the last filter step involved a selection of at least two significant DMPs within the region (based on the gene name and index number of CpG sites). MLID-BWS patients were included in this analysis.
The implementation of these filter steps allowed for the identification of DMPs showing recurrent altered methylation in BWS patients rather than the biggest effect of size and/or the smallest P value.
Results
HumanMethylation450 array
In order to test the ability of the HumanMehylation450 array to detect alterations of methylation in BWS, we tested five MLID-BWS patients with known epimutations. Significant DMPs were seen in all known aberrantly methylated regions (KCNQ1OT1, DIRAS3, GNAS-AS1, MEST, GRB10, and SNRPN), indicating that this platform can detect methylation defects in BWS. Moreover, by using this method, we identified hypomethylation in 18 other imprinted loci (DIRAS3_Ex2, IGF1R, GNAS-XL, WRB, FAM50B, FANCC, GNAS-A/B, NHP2L1, ERLIN2, MAGEL2, MCTS2P, PPIEL, PEG10, RB1, NDN, SNRPN_5′DMR4, SNRPN_variant4, and L3MBTL1) and hypermethylation in two imprinted loci (ZDBF2 and GNAS-NESP), which were not known to be aberrantly methylated in these five MLID-BWS patients (Table 1).
We performed a single-sample analysis for each patient in our BWS cohort. The number of significantly hypomethylated DMPs per patient ranged from 184 (BWS3) to 967 (BWS24) while that of significantly hypermethylated DMPs ranged from 148 (BWS16) to 12,931 (BWS24) (Table 2).
In two patients, BWS24 and BWS25, we found hypermethylation throughout the methylome. We identified almost 13,000 hypermethylated DMPs in BWS24, which is more than 3% of all the informative probes included in the analysis. In BWS25, hypermethylated DMPs, significantly, accounted almost for 2% of all the informative probes. The percentage of hypermethylated DMPs in other patients did not exceed 0.44%.
BWS24 and BWS25 also exhibited a slightly increased number of hypomethylated DMPs in comparison to other BWS patients but not different from MLID-BWS patients. Significantly, hypomethylated DMPs accounted for 0.23% in BWS24 and 0.15% in BWS25 of all the informative probes included in the analysis. In MLID-BWS patients, this percentage ranged from 0.11% to 0.21%.
The analysis of genomic distributions of significant DMPs of these two patients showed their similarity (Fig. 2). Hypermethylated significant DMPs were overrepresented in 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR), body, OpenSea, and enhancers while hypomethylated significant DMPs were overrepresented in Islands, DNase I hypersensitivity site (DHS), and Promoter_Associated.
Genomic distribution of significant DMPs in patients BWS24 and BWS25. The plots compare the percentage of genomic distribution (genomic annotations of HumanMethylation450k array, Illumina) of all the informative probes included in our data and the percentage of genomic distribution of significant DMPs detected in patients BWS24 and BWS25. We compared the distribution of UCSC_RefGene_Group (1st exon, TSS200, TSS1500, 5′UTR, body, 3′UTR), Relation_to_UCSC_CpG_Island (Shore, Shelf, N, S), differentially methylated regions (DMR; CDMR, cancer-specific differentially methylated region; RDMR, reprogramming-specific differentially methylated region), overlapping enhancers loci, Regulatory_Feature_Group (Gene_Associated, Gene_Associated_Cell_type_specific, Promoter_Associated, Promoter_Associated_Cell_type_specific, Unclassified, Unclassified_Cell_type_specific), and DNase I hypersensitivity site (DHS). The number above each bar represents percentage. a The comparison of genomic distribution of hypermethylated DMPS in BWS24. b The comparison of genomic distribution of hypomethylated DMPs in BWS24. c The comparison of genomic distribution of hypermethylated DMPs in BWS25. d The comparison of hypomethylated DMPs in BWS25
To exclude the fact that these methylation patterns in these two patients are caused by cell type skewing, we estimated the distribution of cell types (function: estimateCellCounts, R package: FlowSorted.Blood.450k). Both the patients manifested comparable cell type profiles to the other patients in this group.
All significant DMPs per patient are listed in Additional file 2: Table S1 and Additional file 3: Table S2.
The estimation of the distribution of cell types and calculated P values are listed in Additional file 4: Table S3 and Additional file 5: Table S4.
Searching for DMRs at imprinted loci
We calculated the percentage of total significant DMPs located in COST regions for each patient and for further analysis considered only COST regions with two or more significant DMPs as significantly aberrant (to avoid false-positive results).
MLID-BWS patients showed the highest percentage of significant DMPs assigned to COST regions, ranging from 3.73% to 17.97%, as expected (Table 3). In BWS24 and BWS25, the percentage of total significant DMPs located in COST regions was slightly high but lower than that in MLID-BWS patients. This percentage was 0.55% in BWS24 and 1.19% in BWS25. In contrast to MLID-BWS, BWS24 and BWS25 displayed hypermethylation in COST regions. However, the number of significant DMPs in these regions was relatively small, and the DMPs were non-consecutive. Both the patients displayed hypermethylation in H19 TSS DMR (BWS24—8 DMPs, BWS25—26 DMPs), BWS24 additionally near IGF2_3′UTR (3 DMPs).
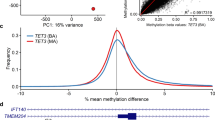
In BWS7, we detected three hypomethylated DMRs (near NHP2L1, IGF1R, and L3MBTL) and one hypermethylated DMR (near ZDBF2) with two or more significant DMPs overlapping with COST regions in MLID-BWS patients (Fig. 3, Additional file 6: Table S5).
In BWS4, we detected alteration of methylation in the primary BWS-associated locus on 11p. In KCNQ1OT1, two consecutive hypomethylated DMPs were annotated with delta differences of − 0.37 and − 0.45. These two DMPs exhibited a stable methylation status in control with an adequate beta mean of 0.56 and 0.51 and standard deviation (SD) 0.03 and 0.04, respectively. Hypomethylation in this locus was not detected with standard diagnostics (see Additional file 1). Additional sequencing of this region (Sanger sequencing) showed the presence of SNP (rs190535862; minor allele frequency (MAF), A = 0.005; G > A) in one of the two hypomethylated CpGs positions in this patient, explaining the detected hypomethylation.
BWS22 displayed hypermethylation in H19 TSS DMR in three nonconsecutive probes. The absolute delta difference in only one of these three DMPs was larger than 10%. However, all of them had a significant adj.P-value_M (all delta differences and adj.P-values assigned to each DMP per patient are listed in Additional file 1). The methylation status of all three DMPs in control was stable with SD 0.02, 0.01, and 0.02, respectively. Sanger sequencing did not show the presence of a SNP in this region. Moreover, we detected hypermethylation in this patient in two other imprinted loci assigned to MEST and PEG13 (two significant DMPs in each).
The genomic locations of COST regions and the complete COST region analysis are listed in the Additional file 7: Table S6, Additional file 8: Table S7, and Additional file 9: Table S8.
Searching for DMRs shared between BWS patients in the methylome
We compared significant DMPs between patients, including MLID-BWS patients.
Regarding hypermethylation comparative analysis, we detected 6613 significant DMPs shared between a minimum of two BWS patients. A majority of them were shared between BWS24 and BWS25 in whom we detected hypermethylation throughout the methylome. We observed an increased number of hypermethylated DMPs annotated to the protocadherin gamma gene cluster located on chromosome 5. Thirty DMPs assigned to this cluster displayed hypermethylation in three MLID-BWS patients and BWS7. Further inspection of the 130 healthy individuals previously collected in our lab for diverse genome-wide methylation studies did not reveal any abnormal methylation in this region suggesting that alteration of methylation of this locus is specific for these patients (Table 4). Moreover, unsupervised hierarchical clustering of this region showed that the DNA pattern of BWS7 and three MLID-BWS patients fell in the same cluster (Fig. 4b).
The heat maps of altered methylated probes from the comparative analysis. The blue beam represents healthy individuals from three different cohorts, and the red beam represents BWS patients. Normal controls come from three different batches that are visible on the plots. a Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of the beta values of the significantly hypomethylated probes annotated to the DUSP22 detected in the current study. b Unsupervised hierarchical clustering of the beta values of the significantly hypermethylated probes annotated to the protocadherin gamma gene cluster detected in the current study
We detected 1521 significantly hypomethylated DMPs shared between a minimum of two patients. More than 20% were annotated to imprinted loci (as reported above in the COST regions analysis) and shared between MLID-BWS patients. A majority of these shared probes represented single DMPs.
The most often altered methylated region was annotated to DUSP22. Ten DMPs located in this region shared hypomethylation between seven patients: MLID-BWS1, BWS1, BWS2, BWS3, BWS11, BWS19, and BWS22. The visualization of 130 healthy individuals showed variability in this specific region for healthy individuals (Fig. 4a), strongly suggesting that the hypomethylation of DMPs located near DUSP22 detected in the current study is not specific for BWS.
The complete comparative analysis is listed in Additional file 10: Table S9.
Discussion
We analyzed the methylation status of DNA in the cohort of 25 BWS patients devoid of any known (epi)genetic cause. We also included five MLID-BWS patients with known hypomethylated regions. Besides the known loci, we identified 18 other significantly hypomethylated and two hypermethylated imprinted regions. The percentage of significant DMPs in the COST regions was found to be higher in MLID-BWS than in other patients, indicating that the disruption of methylation is enriched in imprinted genes in MLID rather than genome-wide loss of methylation.
In patients BWS24 and BWS25, we detected hypermethylation throughout the methylome. BWS24 displayed hypermethylation in 3% and BWS25 in almost 2% of all the informative probes. This percentage is very high compared to that of other patients in whom hypermethylated DMPs did not exceed 0.44%. Both these patients also displayed hypermethylation in imprinted loci among others in H19 TSS and additionally in IGF2_3′UTR in BWS24. However, the changes in methylation in these regions are subtle and do not clearly explain the development of BWS phenotype in these patients. The number of significant DMPs located in the COST regions was lower than that found in MLID-BWS patients, indicating aberrant methylation is not specific for imprinted regions, which suggests a different underlying mechanism to that in MLID patients. It has been shown recently that mutations in chromatin modifying genes cause aberrant methylation patterns throughout the genome. Possibly the methylation profile in our patients is caused by a mutation in such a gene [11].
In patient BWS7, we detected several hypomethylated imprinted loci that overlapped with MLID-BWS patients (NHP2L1, IGF1R, L3MBTL, and ZDBF2). All detected regions were previously described not only in MLID-BWS patients but also in other imprinting disorders showing MLID. For example, Docherty et al. described hypomethylation in the NHP2LI locus in Silver-Russell syndrome with MLID [12], and Rochtus et al. described hypomethylation in the IGF1R locus in patients with pseudohypoparathyroidism [13].
The most interesting of these four loci seems to be a locus situated near IGF1R. IGF1R is a receptor for IGF1 and IGF2. IGF2 is overexpressed in BWS cases with a gain of methylation at H19 TSS DMR. IGF1R is normally a biallelic expression. However, Howard et al. reported a BWS case with monoallelic expression of the maternal IGF1R in a normal kidney, in Wilms tumor, and in lymphocytes. It is worth mentioning here that BWS patients with the gain of methylation in H19 TSS DMR have a risk of Wilms tumor development [14]. In addition, many publications demonstrate that IGF1R affects birth weight and postnatal growth. This applies to both the overgrowth and the growth retardation. Okubo et al. reported two children with an abnormal growth were related to IGF1R. The first child with a growth retardation and hypoglycemia had only one copy of IGF1R while the second with overgrowth showed three copies of IGF1R. This suggests that loss of expression of IGF1R leads to growth retardation and over expression leads to overgrowth [15]. In BWS7, MLID-BWS3, MLID-BWS4, and MLID-BWS5, we detected a significant hypomethylation in the locus near IGF1R. The major feature of BWS is overgrowth, and we can speculate that hypomethylation of the IGF1R locus may lead to the over-expression of this gene and cause overgrowth in our patients. However, additional studies are necessary to ascertain this causal relationship.
In BWS4, we observed hypomethylation in two consecutive DMPs located in imprinted locus KCNQ1OT1, primarily associated with BWS. A SNP was present at the hybridization site of the probes of both CpGs. Knowledge of the fact that the existence of a SNP in the examined CpG can have an impact on methylation readouts [16], we believe that hypomethylation of the other DMP is a result of the cross-reaction between the two probes. This led to the conclusion that this finding is probably not the cause of BWS in this patient, and one should consider the presence of a SNP when only one or two nearby CpGs show hypomethylation.
BWS22 displayed gain of methylation in three nonconsecutive DMPs in the imprinted H19 locus, and only one DMP had a delta difference larger than 10%. Although significant, it is not clear whether such a small number of aberrant DMPs can be causative for BWS. It may be that, due to tissue mosaicism, other tissues in this patient are more affected and aberrant methylation covers a larger region. Alders et al. reported three BWS patients with epigenetic changes in tongue and buccal swab but with normal methylation status in the blood [17]. The tissue mosaicism may also be a cause of BWS in other patients in our cohort.
We observed enriched hypermethylation in 30 DMPs annotated to the protocadherin gamma gene cluster located on chromosome 5 in three of five MLID-BWS patients and BWS7. The additional visualization of methylation patterns in healthy individuals showed that hypermethylation in this locus was specific for these three patients. Interestingly, BWS7 showed disturbed methylation in imprinted regions overlapping with MLID-BWS cases as well. This strengthens our hypothesis that BWS7 has MLID and led us to the conclusion that MLID patients display similar methylation patterns not only in imprinted but also in non-imprinted regions.
One region near the DUSP22 gene showed profound hypomethylation in seven BWS patients, involving ten DMPs. A similar hypomethylation pattern was observed in 27 of 130 healthy individuals, indicating hypomethylation in this locus is not specific for BWS. The differential methylation in this gene has been so far reported in several methylation studies [18,19,20]. We observed aberrant methylation in this gene in other cohorts (data not published) as well. Steegenga et al. described changes in methylation in DUSP22 in an age-related study and showed that changes in methylation in this gene do not influence gene expression and aberrant methylation may be due to interindividual variation [21]. Our results are in agreement with this hypothesis.
In summary, in our cohort of 25 BWS patients without a molecular conformation, we identified one patient with MLID, two patients with genome-wide hypermethylation, and one patient with only very subtle hypermethylation at the H19 locus. The results described here suggest that the HumanMethylation array is highly sensitive and can even detect a small alteration of methylation, which is helpful in confirming the diagnosis.
Conclusions
BWS diagnosis cannot always be confirmed by routine diagnostic tests.
The results of our study indicate that the BWS phenotype may result from different epi(genetic) aberrations, and these aberrations do not necessarily have to be in the primarily disease-associated locus on 11p15. Additionally, we showed that the HumanMethylation450 array may be used to extend BWS diagnostics. This study points to unknown epi(genetic) mechanisms and paves the way for development of new diagnostics tests for BWS.
Limitations
Our study was limited to lymphocytes, and we were not able to determine the methylation status in the imprinted region on chromosome 11p in other tissues and thereby excluded tissue mosaicism.
Moreover, the single case method does not include a correction for blood cell distribution, which may influence the results.
Abbreviations
- BWS:
-
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
- DHS :
-
DNase I hypersensitivity site
- DMP :
-
Differentially methylated position
- DMR :
-
Differentially methylated region
- FDR :
-
False discovery rate
- HRMA :
-
High resolution melting analysis
- IDs :
-
Imprinting disorders
- MAF :
-
Minor allele frequency
- MLID :
-
Multi-locus imprinting disturbance
- MS-MLPA :
-
Methylation-specific multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification
- QC :
-
Quality control
- SNP :
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- TSS :
-
Transcription start site
References
Pandita A, Gupta S, Gupta G, et al. Beckwith-Weidemann syndrome with IC2 (KvDMR1) hypomethylation defect: a novel mutation. Case Rep. 2018;2018:bcr-2017–222419.
Shuman C, Beckwith JB, Weksberg R. Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome. 2000 Mar 3 [Updated 2016 Aug 11]. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2019.Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1394/.
Sanchez-Delgado M, Riccio A, Eggermann T, Maher ER, Lapunzina P, Mackay D, Monk D. Causes and consequences of multi-locus imprinting disturbances in humans. Trends Genet. 2016;32(7):444–55.
Weksberg R, Shuman C, Smith AC. Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2005;137C(1):12–23.
Alders M, Bliek J, vd Lip K, vd Bogaard R, Mannens M. Determination of KCNQ1OT1 and H19 methylation levels in BWS and SRS patients using methylation-sensitive high-resolution melting analysis. Eur J Hum Genet. 2009;17(4):467–73.
DeBaun MR, Tucker MA. Risk of cancer during the first four years of life in children from the Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome Registry. J Pediatr. 1998;132(3 Pt 1):398–400.
Ibrahim A, Kirby G, Hardy C, Dias RP, Tee L, Lim D, Berg J, MacDonald F, Nightingale P, Maher ER. Methylation analysis and diagnostics of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome in 1,000 subjects. Clin Epigenetics. 2014;6(1):11.
Bliek J, Verde G, Callaway J, Maas SM, De Crescenzo A, Sparago A, Cerrato F, Russo S, Ferraiuolo S, Rinaldi MM, et al. Hypomethylation at multiple maternally methylated imprinted regions including PLAGL1 and GNAS loci in Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2009;17(5):611–9.
Rezwan FI, Docherty LE, Poole RL, Lockett GA, Arshad SH, Holloway JW, Temple IK, Mackay DJ. A statistical method for single sample analysis of HumanMethylation450 array data: genome-wide methylation analysis of patients with imprinting disorders. Clin Epigenetics. 2015;7:48.
Aryee MJ, Jaffe AE, Corrada-Bravo H, Ladd-Acosta C, Feinberg AP, Hansen KD, Irizarry RA. Minfi: a flexible and comprehensive bioconductor package for the analysis of Infinium DNA methylation microarrays. Bioinformatics. 2014;30(10):1363–9.
Aref-Eshghi E, Rodenhiser DI, Schenkel LC, Lin H, Skinner C, Ainsworth P, Pare G, Hood RL, Bulman DE, Kernohan KD, et al. Genomic DNA methylation signatures enable concurrent diagnosis and clinical genetic variant classification in neurodevelopmental syndromes. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;102(1):156–74.
Docherty LE, Rezwan FI, Poole RL, Jagoe H, Lake H, Lockett GA, Arshad H, Wilson DI, Holloway JW, Temple IK, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of patients with imprinting disorders identifies differentially methylated regions associated with novel candidate imprinted genes. J Med Genet. 2014;51(4):229–38.
Rochtus A, Martin-Trujillo A, Izzi B, Elli F, Garin I, Linglart A, Mantovani G, Perez de Nanclares G, Thiele S, Decallonne B, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of pseudohypoparathyroidism patients with GNAS imprinting defects. Clin Epigenetics. 2016;8:10.
Howard TK, Algar EM, Glatz JA, Reeve AE, Smith PJ. The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor gene is normally biallelically expressed in human juvenile tissue and tumours. Hum Mol Genet. 1993;2(12):2089–92.
Okubo Y, Siddle K, Firth H, O'Rahilly S, Wilson LC, Willatt L, Fukushima T, Takahashi S, Petry CJ, Saukkonen T, et al. Cell proliferation activities on skin fibroblasts from a short child with absence of one copy of the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF1R) gene and a tall child with three copies of the IGF1R gene. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(12):5981–8.
Daca-Roszak P, Pfeifer A, Zebracka-Gala J, Rusinek D, Szybinska A, Jarzab B, Witt M, Zietkiewicz E. Impact of SNPs on methylation readouts by illumina infinium humanmethylation450 beadchip array: implications for comparative population studies. BMC Genomics. 2015;16:1003.
Alders M, Maas SM, Kadouch DJ, van der Lip K, Bliek J, van der Horst CM, Mannens MM. Methylation analysis in tongue tissue of BWS patients identifies the (EPI) genetic cause in 3 patients with normal methylation levels in blood. Eur J Med Genet. 2014;57(6):293–7.
Lee MJ, Min BJ, Choung HK, Kim N, Kim YA, Khwarg SI. Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles according to Chlamydophila psittaci infection and the response to doxycycline treatment in ocular adnexal lymphoma. Mol Vis. 2014;20:1037–47.
Moleres A, Campion J, Milagro FI, Marcos A, Campoy C, Garagorri JM, Gomez-Martinez S, Martinez JA, Azcona-Sanjulian MC, Marti A, et al. Differential DNA methylation patterns between high and low responders to a weight loss intervention in overweight or obese adolescents: the EVASYON study. FASEB J. 2013;27(6):2504–12.
Ouyang B, Baxter CS, Lam HM, Yeramaneni S, Levin L, Haynes E, Ho SM. Hypomethylation of dual specificity phosphatase 22 promoter correlates with duration of service in firefighters and is inducible by low-dose benzo[a]pyrene. J Occup Environ Med. 2012;54(7):774–80.
Steegenga WT, Boekschoten MV, Lute C, Hooiveld GJ, de Groot PJ, Morris TJ, Teschendorff AE, Butcher LM, Beck S, Muller M. Genome-wide age-related changes in DNA methylation and gene expression in human PBMCs. Age (Dordr). 2014;36(3):9648.
Funding
No funding was obtained.
Availability of data and materials
All HumanMethylation450 data are available on request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA, MM, and JB designed the study. SM diagnosed and selected patients of the study. FR and DM designed the statistical method. IK, MA, PH, and AV performed the statistical analysis. IK, KL, AM, and AV performed the lab experiments. IK, MA, and MM contributed to the manuscript writing and revision. All authors reviewed the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
METC waived (anonymous study, further study in line with clinical question).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Contains additional information about (1) quality control, (2) pre-processing data and statistical methods, (3) estimation of the cell type distribution, (4) standard diagnostics, and (5) additional inspection of primary BWS associated loci at 11p15.5. (DOCX 555 kb)
Additional file 2:
Table S1. Significant hypermethylated DMPs per patient. (XLSX 3887 kb)
Additional file 3:
Table S2. Significant hypomethylated DMPs per patient. (XLSX 1129 kb)
Additional file 4:
Table S3. The estimation of the cell types distribution. (CSV 4 kb)
Additional file 5:
Table S4. The calculation of P values of the cell types distribution per patient. (XLSX 47 kb)
Additional file 6:
Table S5. The summary of identified aberrant CpGs within COST regions. (DOCX 25 kb)
Additional file 7:
Table S6. Genomic locations of imprinted loci—COST regions. (CSV 2 kb)
Additional file 8:
Table S7. Significant hypermethylated DMPs within the COST regions (per patient). BWS patients that did not display aberrant methylation in imprinted COST regions are not included in this table. (XLSX 38 kb)
Additional file 9:
Table S8. Significant hypomethylated DMPs overlapped with COST regions. BWS patients that did not display aberrant methylation in imprinted COST regions are not included in this table. (XLSX 98 kb)
Additional file 10:
Table S9. Results of the comparative analysis. (XLSX 5326 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Krzyzewska, I.M., Alders, M., Maas, S.M. et al. Genome-wide methylation profiling of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome patients without molecular confirmation after routine diagnostics. Clin Epigenet 11, 53 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-019-0649-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-019-0649-6