Abstract
Background
Among semi-aquatic species of the legume genus Aeschynomene, some have the unique property of being root and stem-nodulated by photosynthetic Bradyrhizobium lacking the nodABC genes necessary for the production of Nod factors. These species provide an excellent biological system with which to explore the evolution of nodulation in legumes. Among them, Aeschynomene evenia has emerged as a model legume to undertake the genetic dissection of the so-called Nod-independent symbiosis. In addition to the genetic analysis of nodulation on a reference line, natural variation in a germplasm collection could also be surveyed to uncover genetic determinants of nodulation. To this aim, we investigated the patterns of genetic diversity in a collection of 226 Nod-independent Aeschynomene accessions.
Results
A combination of phylogenetic analyses, comprising ITS and low-copy nuclear genes, along with cytogenetic experiments and artificial hybridizations revealed the richness of the Nod-independent Aeschynomene group with the identification of 13 diploid and 6 polyploid well-differentiated taxa. A set of 54 SSRs was used to further delineate taxon boundaries and to identify different genotypes. Patterns of microsatellite diversity also illuminated the genetic basis of the Aeschynomene taxa that were all found to be predominantly autogamous and with a predicted simple disomic inheritance, two attributes favorable for genetics. In addition, taxa displaying a pronounced genetic diversity, notably A. evenia, A. indica and A. sensitiva, were characterized by a clear geographically-based genetic structure and variations in root and stem nodulation.
Conclusion
A well-characterized germplasm collection now exists as a major genetic resource to thoroughly explore the natural variation of nodulation in response to different bradyrhizobial strains. Symbiotic polymorphisms are expected to be found notably in the induction of nodulation, in nitrogen fixation and also in stem nodulation. Subsequent genetic analysis and locus mapping will pave the way for the identification of the underlying genes through forward or reverse genetics. Such discoveries will significantly contribute to our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underpinning how some Aeschynomene species can be efficiently nodulated in a Nod-independent fashion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
The legume family (Leguminosae) accounts for ~ 27% of the world’s primary crop production and is second only to cereals in economic and nutritional value. It includes many crops of agronomic importance for grain production, pasture and agroforestry. Many legumes are pioneers plants improving soil fertility and moderating harsh environments. Such economic and ecological success of the legume family is, in large part, due to the ability of the vast majority of its 20,000 species to develop symbiotic interactions with nitrogen-fixing bacteria collectively referred as rhizobia [1]. In this symbiosis, the rhizobia produce signal molecules, the Nod factors, whose specific recognition by the host plant is necessary to activate the formation of root nodules that correspond to symbiotic organs where the rhizobia are hosted. Inside the nodules, the rhizobia reduce atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonium (NH4+), a form of nitrogen that is usable by the plant for its development. Historically, two model legumes, Medicago truncatula and Lotus japonicus, have been used to genetically investigate this nodulation process. Such studies have resulted in the identification and elucidation of the role of many genes that are essential for the different steps of nodule development and its infection by the symbiont [2,3,4]. To broaden our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the nitrogen-fixing symbiosis, there has arisen a fast growing interest in uncovering the diversity of nodulation processes that are found in other legume species [5, 6].
In this line, the mainly tropical legume genus Aeschynomene represents a group of prime interest as it contains several original symbiotic features. The genus Aeschynomene was originally known for the ability of different species to develop stem nodules in addition to the typical root nodules. Stem nodulation is uncommon in legumes, being shared with a very few hydrophytic species of the genera Sesbania, Neptunia and Discolobium, but it is widespread among the semi-aquatic Aeschynomene species [7,8,9]. In addition, some bradyrhizobia isolated from Aeschynomene stem nodules exhibit a photosynthetic activity that was shown to play a key role in stem nodules by directly furnishing energy to the bacterium that can be used for biological nitrogen fixation [10, 11]. Even more outstanding was the discovery that some of these photosynthetic bradyrhizobia lack both the canonical nodABC genes required for the synthesis of the key Nod factors and a type III secretion system (T3SS) that is known in other rhizobia to activate or modulate nodulation [12,13,14]. This led to a new paradigm in nodulation studies in which an alternative symbiotic process between rhizobia and legumes efficiently triggers nodule formation in a Nod (factor)-independent fashion.
Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeschynomene revealed that all the species endowed with a Nod-independent nodulation process cluster in a single clade where no species using a Nod-dependent symbiotic process are found [8]. A taxonomic revision of American Aeschynomene was published in 1955 by Rudd [15], but it predated phylogenetic studies in plants and included no species native outside the Neotropics. First molecular studies of Aeschynomene pointed to new cryptic taxa differing by their ploidy levels [16, 17]. The knowledge gained from the study of the Nod-independent clade was also used to select Aeschynomene evenia as a new model legume for the purpose of deciphering the molecular mechanisms of the Nod-independent symbiosis [16, 18]. Key attributes of this species include its small, diploid genome (2n = 20, 415 Mb/1C), its selfing nature and its prolific seed production. Several tools have been developed including artificial hybridization and the Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated root transformation, rendering this species ideal for molecular genetic studies. First insights were obtained from RNAseq analysis and reverse genetics by revealing that some symbiotic determinants identified in Medicago and Lotus are recruited in the Nod-independent process but several key genes involved in bacterial recognition, symbiotic infection and nodule functioning were found not to be expressed during root nodulation [9, 19,20,21].
Forward genetics are now expected to allow the identification of the specific molecular determinants of the Nod-independent process in A. evenia. To optimize research effort, a reference line was inbred and successfully used to generate an SSR-based genetic map of A. evenia [9]. This genetic map uncovered the genome structure and the distribution of symbiotic genes. It also provides a basis for a genome sequencing project and paves the way of the genetic dissection of nodulation in this reference line. This does not exclude exploring the naturally occurring variations in nodulation, as a complementary genetic approach, in order to increase our understanding of symbiotic gene functions and of the genetic control of symbiosis as successfully performed in other legumes such as Medicago, Lotus and soybean [22]. But exploiting genetic diversity requires prior knowledge of the extent and structure of the variations occurring in the species of interest. Although the genetic relationships among the Nod-independent Aeschynomene species have been analysed using molecular markers, only two studies have included a small set of accessions for the diploid A. evenia and the related polyploid A. indica [17, 18]. As a consequence, the variations within and among the species of the Nod-independent clade remain largely uncharacterized.
To enable an efficient use of the natural variation in genetic studies of nodulation, we surveyed the genetic diversity occurring in a collection of 226 Nod-independent Aeschynomene accessions spanning the whole distributional range of this clade. As a first step, genetic relationships and differentiation between Nod-independent Aeschynomene taxa were established using a combination of molecular phylogenies, cytogenetics and hybridization experiments. This information then served as supportive data for the analysis of genotype data obtained for the germplasm collection using a set of 54 SSR markers. Patterns of microsatellite diversity illuminated the genetic basis of the Aeschynomene taxa and uncovered their genetic differentiation. The presence of an underlying genetic structure was then compared with geographical distribution data.
Results
Species identification and relationships
A collection of 233 accessions was developed to investigate the phylogenetic relationships and the genetic differentiation in the Nod-independent Aeschynomene clade (Additional file 1: Table S1). It included all the known species included in the clade and aimed to cover their distributional range [15, 23, 24]. The nuclear ribosomal ITS region was used as a marker of the species identity and served to reconstruct a phylogeny of the whole group based on the Neighbor Joining (NJ) method (Additional files 2 and 3: Tables S2 and S3). To simplify the resulting tree, accessions showing less than 1% of divergence in their sequence were grouped in the same clade (Fig. 1a, Additional file 4: Doc. S1). The ITS tree was composed of four lineages: one grouping A. filosa, A. rostrata and A. tambacoundensis, a monospecific one with A. deamii, a third one comprising A. evenia and its sister species, and a fourth one containing A. sensitiva and related species (Fig. 1a).
Phylogenetic and genetic relationships in the Nod-independent Aeschynomene clade. Phylogenetic reconstructions were obtained using the Neighbor Joining method. a ITS phylogeny. Accessions with ITS sequence divergence < 1% were clustered together. Numbers of accessions per taxon are indicated in brackets. b Phylogeny based on 5 concatenated low-copy nuclear gene fragments: CYP1, eiF1α, SUI1, SuSy and a gene homolog to Glyma.07G136800 and Glyma.18G187300. -A, -B and -C indicate the different copies found in polyploid species. The four gene pools are identified with a circled number and the A. evenia and A. sensitiva groups are framed in a box bordered with a dashed red line. Diploid taxa are in black and polyploid taxa in blue with ploidy level indicated. Numbers at nodes represent bootstrap values (% of 1000 replicates)
In this phylogenetic tree, a number of putative species displayed the same ITS sequence. In particular, two rare species, A. magna and A. pluriarticulata, tightly clustered with two widespread species, A. denticulata and A. evenia, respectively (Fig. 1a). Similarly, A. evenia and A. indica shared the same ITS signature but they were previously shown to form a species complex containing three cytotypes (2×, 4× and 6×) [17]. To sort these, accessions of this species complex were genotyped with SSR markers that are indicators of their genome constitution [17]. This led to the additional discovery that the A. indica 6× accessions of African and Australian origin displayed different SSR profiles, justifying their distinction in the phylogenic tree (Fig. 1a, data not shown). It is also noteworthy that two accessions did not fit well with the description of any known Aeschynomene species and so we refer to these as Aeschynomene sp. (328) and A. sp. (353) (Fig. 1a, Additional file 1: Table S1). To clarify the genetic status of these putative new taxa, they were both included in a flow cytometry analysis and a chromosome count (Additional file 1: Table S1, Additional file 5: Figure S1). Cytogenetic data were mapped onto the phylogeny, showing that Aeschynomene sp. (328) represented a new 2× taxon while A. sp. (353) was a 4× taxon, similar to the closely related A. virginica, and confirming the hexaploid status of the Australian A. indica 6× (Fig. 1a).
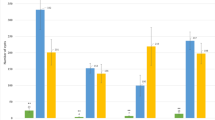
To further uncover genetic relationships between taxa, five low copy nuclear genes -CYP1 (Cyclophilin 1), eiF1α (eukaryotic translation initiation factor α), SUI1 (translation factor), SuSy (Sucrose Synthase) and a gene homolog to Glyma.07G136800 and Glyma.18G187300 identified in Glycine max - were cloned and sequenced in selected accessions (Additional file 2: Table S2). For diploid species, single sequences were obtained, while for polyploid species homeologous sequences were isolated for almost all genes (Additional file 3: Table S3). The five genes treated separately gave similar NJ trees where the homeologous sequences for polyploid taxa could be differentiated based on the differential clustering with the sequences of diploid taxa (not shown). To provide a unique and well-resolved NJ phylogeny, the gene sequences were concatenated together (Fig. 1b). In the resulting tree, the topology of the branches containing the diploid species was similar to that of the ITS tree, corroborating the distinctness of A. sp. (328) from other known Aeschynomene species (Fig. 1a,b). For the polyploid taxa, the different genome components were scattered different part of the phylogeny, revealing that the two taxa A. sp. (353) and A. virginica, and the African and Australian A. indica 6× had the same or a similar genomic constitution (Fig. 1b). To assess the genetic differentiation of these related taxa, they were manually crossed: A. sp. (353) with A. virginica, the African A. indica 6× with the Australian A. indica 6× and A. indica 4× with A. indica 6× for comparison (Fig. 2). In all cases, hybrid plants were obtained but they greatly differed in their fertility compared to their respective parental accessions, as seen by a drastic reduction of both the number of developed pods per flowering axis and of seeds per pod. As a result, these data suggest that the tested taxa are truly different Aeschynomene species.
Hybridization experiments between related taxa. Manual crosses were performed between A. virginica and A. sp (353), A. indica 4× and A. indica 6× -Africa-, A. indica 6× -Africa- and A. indica 6× -Australia. Plant fertility was evaluated for the parental taxa and two independently obtained F1 hybrids based on the number of seeds produced per pod and the number of developed pods per flowering axis. Error bars represent s.d. (n = 30)
Genetic patterns and behaviours
To determine the genetic structure of the genomes of different taxa, we conducted a SSR genotyping of the collection of Aeschynomene accessions. For this, we tested the set of 500 SSRs previously used when developing a genetic map for A. evenia [9]. These markers were screened for polymorphism in four samples that are genetically different: two accessions of A. evenia 2× (the reference line CIAT 22838 and the mapping parent CIAT 8232), one accession of A. indica 4× (PI 196206) and one of A. indica 6× (LSTM19). Of these, 64 markers were selected using two main criteria: (1) the requirement to be polymorphic between the two A. evenia accessions so as to avoid the use of invariant SSRs, (2) to amplify a single allele in the 2× accessions, 2 and 3 alleles in the 4× and 6× accessions, respectively, with the assumption that the distinct alleles came from the different genomic components of the polyploid species (Additional files 6, 7 and 8: Figure S2, Tables S4 and S5). Forty nine out of the 64 selected markers were previously positioned on different A. evenia linkage groups, with their distribution representing a reasonable coverage of the A. evenia genetic map (Additional file 7: Table S4).
Preliminary genotyping experiments revealed that the SSRs developed from A. evenia sequences had a transferability rate qualified as (i) modest with A. deamii and A. tambacoundensis, (ii) good with A. sensitiva and A. pratensis and (iii) high with A. denticulata and A. scabra. These data were in accordance with the phylogenetic distance of the different gene pools relative to A. evenia (Fig. 1), but this prompted us to restrict our analysis to the A. evenia and A. sensitiva groups. The corresponding accessions were then subjected to high-throughput SSR genotyping by capillary sequencing (Additional file 9: Figure S3). The absence of amplification for some of them in the A. sensitiva group was compensated by the use of an additional set of SSR markers. Of the 64 SSR markers, 54 generated clearly interpretable allele profiles in at least one of the two groups, 38 SSR markers for the A. evenia group and 46 SSR markers for the A. sensitiva group, with 30 of them in common (Additional file 6: Figure S2). Allelic diversity, estimated by the number of alleles Na, varied importantly among the SSR markers used with an average of 12.8 alleles per locus in the A. evenia group (n = 186 accessions) and 4.21 in the A. sensitiva group (n = 40 accession) (Additional file 10: Table S6). Observed heterozygosities were very low for each SSR (Ho < 0.1 with one exception at 0.2), indicating that they amplified at single locus for diploid accessions and homeologous loci for polyploid accessions (Additional file 10: Table S6).
These results supported the appropriateness of these SSRs for investigating the genetic properties of species. Therefore they were analysed in a second step to characterize the taxa. Transferability level of the SSR markers from A. evenia, ranged from 92 to 100% for other taxa of the A. evenia group and from 72 to 78% for those of the A. sensitiva group (Table 1, Additional file 11: Table S7). Analysing the Na parameter revealed different levels of genetic variation among the Aeschynomene taxa, one of the highest being found in A. evenia (mean 5.2 alleles per SSR) (Table 1, Additional file 10: Table S6). These values reflected the genetic diversity of the taxa, but they were likely to have been influenced by the marked variation in sample sizes and by the non-random selection of the SSR markers. The mean number of alleles detected for the SSR markers in each taxon were congruent with their ploidy levels, with (i) 1.00 to 1.06 alleles observed for diploid taxa, (ii) 1.42 to 1.92 alleles for tetraploid taxa and (iii) 2.63 to 2.84 alleles for hexaploid taxa (Table 1, Additional file 12: Table S8). Accessions displaying more alleles than expected from their ploidy level were considered as heterozygous (Additional files 1 and 13: Tables S1, S9). Selfing rates based on the observed heterozygosities, ranged from 94.5% to 100%, with an average 98.7% score for A. evenia (Table 1, Additional file 13: Table S9). This provided genetic support for previous observations that the Nod-independent Aeschynomene species are preferentially autogamous [17, 18].
Genetic diversity and genotype delineation
Based on the geographical distributions of the accessions making up the different Nod-independent Aeschynomene taxa, most of their genetic diversity and structure were expected to be uncovered. Therefore, the genotyping data obtained for the A. evenia and A. sensitiva groups were combined and used to estimate pair-wise distances between all accessions and thereby generate a dissimilarity matrix in DARwin v5 [25]. From this, NJ trees were calculated for the 2×, 4×, 6× ploidy levels separately. Indeed, alleles of the genomic components of polyploid accessions cannot be analysed separately and so their inclusion in the analysis of the diploid accessions would result in their grouping with only one of the potential progenitors. Considering the 2× NJ tree, well-separated clades were evident and corresponded to the known species A. evenia, A. ciliata, A. denticulata, A. rudis, A. scabra, A. serrulata, A. selloi and A. sensitiva, as well as the newly identified A. sp. (328) (Fig. 3a,Additional file 9: Figure S3). Interestingly, A. pluriarticulata was found to be nested within the A. evenia accessions and the accession of A. magna tightly clustered with accessions of A. denticulata. This information together with the phylogenetic and genetic relationships makes their taxonomic distinctness uncertain. Conversely, the tree topology showed a clear separation of the two A. evenia subspecies, evenia and serrulata, and several 2× taxa (A. denticulata, A. evenia ssp. evenia, A. evenia ssp. serrulata and A. sensitiva) could be subdivided in different clusters delineating genotypes (Fig. 3a,Additional file 9: Figure S3). Among these, genetic diversity and differentiation was the highest for A. evenia ssp. evenia (here after A. evenia s.s. in the text), with 7 genotypes identified. Regarding the 4× tree, A. virginica and A. sp (353) were found to form sister lineages and contrasted patterns of genetic differentiation were observed with a very low genetic variability noted for A. pratensis whereas A. indica 4× was composed of several well-diverged clusters (Fig. 3b,Additional file 9: Figure S3). In the 6× tree, the African and Australian A. indica 6× were genetically distant with the African set subdivided in two homogenous genotypes while the Australian set contained three genotypes that formed far more diverse assemblages, indicative of distinct evolutions (Fig. 3c, Additional file 9: Figure S3).
NJ trees representing the genetic diversity among the Nod-independent Aeschynomene accessions. The trees were developed separately in DARWIN using the allelic data of 54 SSRs for the 2× (a), 4× (b) and 6× (c) taxa. Well-differentiated taxa are distinctly coloured and identified genotypes are numbered. Species suspected to be morphological variants are marked with an asterisk
In a search for other relationships, a Factorial Analysis (FA) was also carried out in DARwin v5 [25]. This approach is more informative regarding distances among different groups and it also allows comparison of accessions of different ploidy levels. We focused on A. evenia and A. sensitiva to get a more detailed view of the genetic relatedness between the 2× genotypes and the derived polyploid taxa. FA clearly distinguished A. sensitiva and A. pratensis when using the factorial axes 1 and 2 (Fig. 4a). Factorial axes 2 and 3 separated the four A. sensitiva genotypes and but the central position of A. pratensis was interpreted has an absence of a preferential relationship with any of the A. sensitiva genotypes (Fig. 4b). Therefore, either the parental A. sensitiva genotype that contributed to the polyploid genome of A. pratensis was missing or A. pratensis was formed before the intraspecific differentiation of A. sensitiva as suggested by the sequence divergence of the nuclear genes (Fig. 1b). For A. evenia s.s., the FA separated the 7 identified genotypes but grouped the three A. indica taxa together when using factorial axes 1 and 2 (Fig. 4c). These polyploid taxa could be separated along factorial axis 4 and showed preferential affinity with the two unseparated genotypes (1) and (2) of A. evenia along factorial axis 2 (Fig. 4d). These observations suggested a common origin of the three A. indica taxa that would derive from the same A. evenia genome donor, this latter being potentially ancestral to the genotypes 1 and 2.
Factorial analysis of Nod-independent Aeschynomene taxa. (a) and (b) for the A. evenia-A. indica species complex, (c) and (d) for the A. sensitiva-A. pratensis species complex. Two pairss of factorial axes (with the percentage of variation they account for indicated in parenthesis) are used for each species complex so as to show genetic distinctness and relationships. Taxon colours and genotype numbers are the same as in Fig. 3
Geographical structure of the Aeschynomene species
The Nod-independent Aeschynomene clade is mainly a tropical/subtropical group, but the species show distinct geographical distributions [15, 23, 24]. Out of the 19 taxa considered here (Table 1), 13 are strictly American, while three taxa (A. evenia, A. indica 4× and A. sensitiva) have a wider distribution; two are African (A. indica 6× - Africa- and A. tambacoundensis) and one Australian (A. indica 6× - Australia-). This confirmed previous conclusions that America is the centre of origin and diversification of this clade but that several outliers have subsequently evolved in other continents [8]. Because some species showed a pronounced genetic differentiation and are part of polyploid species complexes, we investigated to what extent the corresponding cytotypes and genotypes are geographically structured. In the A. sensitiva-A. pratensis species complex, A. sensitiva has a transatlantic distribution. When mapping accessions globally, a clear geographical separation of the four A. sensitiva genotypes was observed. One occupies the Caribbean region, one found in Colombia, another one the central area of South America and, more noticeably a fourth one being present both in coastal East Brazil and in Africa, suggesting a recent dispersal event (Fig. 5a, Additional file 9: Figure S3, Additional file 1: Table S1). In contrast to A. sensitiva, the low genetic diversity observed in A. pratensis 4× revealed no consistent geographical pattern (Fig. 5A, Additional file 9: Figure S3, Additional file 1: Table S1).
Geographical distribution of Nod-independent Aeschynomene taxa. (a) for the A. sensitiva-A. pratensis species complex and (b) for the A. evenia-A. indica species complex. Accessions with no geographical information are not shown; details of the accession origins are provided in Additional files 1 and 14: Table S1 and Figure S4. Taxon colours and genotype numbers are the same as in Fig. 3
In the pantropically distributed A. evenia-A. indica species complex, a prominent geographical division between the different taxa was observed. A. evenia s.s. (2×) grows both in America and Africa, A. indica 4× is widespread in Asia, including India, and it is also present in North Eastern America, while the two A. indica 6× taxa distinctly occur in Africa and Australia (Fig. 5b). At the intraspecific level, the identified genotypes were found to represent geographically defined groups. A. evenia displayed a high level of genetic structure with 5 American and 2 African genotypes. As far as phylogenetic relationships can be inferred from an SSR-based NJ tree, the African genotypes appeared to have diverged after a recent transatlantic migration from the Neotropics (Fig. 5b, Additional file 9: Figure S3, Additional file 1: Table S1). A. indica 4× contained 3 distinct Indian lineages, one genotype spanning Eastern Asia and the North Eastern America, a second widespread in Northern Australia but also occurring in Asia, and a third throughout South Asia and extending to the Pacific (Fig. 5b). The Australian A. indica 6× was found to have a wide distribution extending from Eastern to Western Australia. Missing collection data limited the analysis of the three 6× genotypes but they did not overlap in distributional area with A. indica 4× (Fig. 5b, Additional file 9: Figure S3, Additional file 1: Table S1). In contrast, distribution of the African A. indica 6× was restricted to the Subsahelian zone and the two identified genotypes clearly could be distinguished based on their location, one in the western part of the zone, the other one with a more central position (Fig. 5b, Additional file 9: Figure S3, Additional file 1: Table S1). Noteworthy, at a macroscale, there exists an overlap in distribution of African A. indica 6× with A. evenia s.s, but the latter was more widespread in Africa.
To test whether this genetic diversity could support polymorphism in nodulation traits, a number of accessions of A. evenia s.s. and A. indica were submitted to root or stem inoculation with two photosynthetic nodABC gene-lacking Bradyrhizobium strains, ORS278 and BTAi1. A high variation in stem nodule development was observed in A. evenia when it was inoculated with ORS278 (Fig. 6a). Conversely, root nodulation was more homogenous but plant defense reactions characterized by the accumulation of brown compounds, most probably of polyphenol nature as already described for incompatible interactions [26], were obvious in nodules of A. indica 6× -Africa- inoculated with BTAi1 (Fig. 6b, Additional file 14: Figure S4a). This incompatibility was accompanied by a low nitrogen-fixing activity and an overall reduction in plant development (Fig. 6c, Additional file 14: Figure S4b).
Variation of nodulation traits observed in accessions of A. evenia and A. indica. (a)
Stem nodulation observed in various accessions of A. evenia, 3 weeks post inoculation with ORS278. (b) Root nodule development in accessions of A. evenia and A. indica following inoculation with Bradyrhizobium ORS278 and BTAi1. 14-dpi nodules were cut to observe the leghemoglobin color and reaction defense (arrow). (c) Comparison of plant growth (aerial part) after inoculation with Bradyrhizobium ORS278 and BTAi1, at 14 dpi. Scale bar in (a): 5 mm, in (b): 1 mm
Discussion
This in-depth characterization of a Nod-independent Aeschynomene germplasm collection identified four main lineages and uncovered genetic diversity and structure at different scales: cytotypes, species and genotypes (as summarised in Table 1). Interestingly, this group of Aeschynomene is composed of mainly diploid taxa (13 out of 19), including the model legume A. evenia, which are expected to be the easiest to handle at a genetic standpoint. For the polyploid taxa (4 tetraploids and 2 hexaploids), low-copy nuclear genes and SSR analysis supported an allopolyploid origin and several genome donors could be identified [17; this study]. This must facilitate the identification and distinction of the different subgenomic components of the polyploid genomes and this indicated that these polyploid taxa must behave genetically as diploids. Segregation of molecular markers, however, has not been performed to date at a genome-wide scale and we therefore cannot exclude that they might behave as segmental allopolyploids just as recently reported for peanut and chrysanthemum [27, 28]. Such dual structure may be found notably in A. pratensis for which the two expected homeologous versions of the tested low-copy nuclear genes were not always detected.
In addition to shedding light on the genetic basis of the different Aeschynomene species, our analyses were used to identify different taxa and to delimit their taxonomic boundaries. Indeed, the approach of genotyping a germplasm collection already has shown to be a powerful tool resolving taxonomic issues and providing the basis of a good taxonomic classification in the legume genus Lens that includes the cultivated lentil [29]. Here, the rare species Aeschynomene pluriarticulata and A. magna were found to have ITS and low-copy nuclear gene sequences very similar to those of A. evenia and A. denticulata, respectively (Fig. 1). The NJ SSR trees further revealed that these two pairs of taxa clustered closely together. This strongly suggested that A. pluriarticulata and A. magna are more likely morphological variants of A. evenia and A. denticulata than distinct species (Fig. 3). But for A. magna, living material is now necessary to confirm this. Conversely, A. evenia ssp. evenia and A. evenia ssp. serrulata were found to form sister clades in the ITS and low-copy nuclear gene phylogenies (in accordance with their current grouping into a single species) but are clearly distinct entities in the SSR tree (Figs. 1,3). Concordant with this strong genetic differentiation, the two subspecies of A. evenia previously were demonstrated not to be cross-compatible [18]. Similarly, A. virginica and A. sp. 353, along with the African and Australian 6× A. indica taxa, formed separate groups in the SSR tree and their hybridization generated F1 hybrids with a marked reduction in fertility (Figs. 2,3). This raises the question of whether these taxa should be treated at the subspecies level or as separate species. On the other hand, the situation was clear for Aeschynomene sp. (328); this taxon was consistently found to be divergent in the ITS, low-copy nuclear gene and the SSR trees (Figs. 1,3). Therefore, it can be reliably considered as a new species belonging to the A. sensitiva group, notwithstanding that this conclusion is based on a single accession of what is apparently a rare taxon.
Given their high variability, the SSR markers are a powerful tool to highlight putative subdivisions in different Aeschynomene species that served to define genotypes. Striking is that these genotypes, delineated solely on the basis of marker data, corresponded to geographically based subgroups. Thus, the genetic structure of the Aeschynomene taxa appeared to mirror the eco-geographic distribution of the associated genotypes, a situation also described for other plants including lentil, tomato, pigeonpea and switchgrass [30,31,32,33]. Although not a major aim of this study, such genetic structure can help to understand the origin and the migration of some populations. This is notably the case for A. indica whose natural distribution range is obscure. The identified genetic clusters, which most prominently corresponded with geographical distribution patterns, likely reflected real differences within each species. Among the species studied, A. evenia s.s. had the highest genetic diversity with 7 genotypes, some of them previously being shown to be fully cross-compatible [18]. It is also noteworthy that the different Aeschynomene taxa displayed very high selfing rates. Using lines that tend to be mostly homozygous facilitates artificial hybridizations and analysis of confidently segregation patterns in the progeny in order to investigate the genetic determinism underlying the nodulation traits.
All these data taken together make our germplasm collection a valuable genetic resource for the Nod-independent Aeschynomene group. So how best to further exploit it? To decipher the molecular mechanisms underlying the different original nodulation properties found in the Nod-independent symbiosis, A. evenia was recently selected as a model species [16, 18]. The species is currently being subjected to full genome sequence analysis and an ongoing mutagenesis project is predicted to identify new symbiotic genetic determinants in the near future. Such approaches applied to the historical model legumes M. truncatula and L. japonicus led to major advances in the study of the nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with the identification of a set of symbiotic genes involved in the recognition of rhizobial signals, transduction, infection and nodule organogenesis [2, 4]. But mutants are usually screened for the loss of their ability to establish a symbiosis, due to the disruption of gene function, and they are developed in the frame of the study of a single plant line-rhizobial strain system. Conversely, the screening of natural populations with multiple rhizobial strains can reveal some symbiotic phenotypes that depend on both the host genetic background and the rhizobial strain. In fact, studying natural variation approach has been shown to be a powerful tool for gaining insights into the genetic basis underlying the specificity of the symbiotic interaction in three legumes, Medicago, Lotus or soybean. The identified symbiotic polymorphisms were mostly of two types: some plant-rhizobial strain combinations resulted in non-nodulating phenotypes (Nod−), others in the production of small white infected nodules proved to be defective in nitrogen fixation (Fix−) [34,35,36,37,38]. This indicated that the control of host-rhizobial strain compatibility occurred at two different levels in the symbiotic process.
It is noteworthy that the genetic analysis of natural variation shed light on the function of some key symbiotic genes. The LysM-RLK receptors, which were identified using the mutant approach to be the probable Nod factor receptors, represent a well-known example. Indeed, a synteny-based positional cloning identified LYK3 in Medicago as corresponding to the SYM2 gene that controls the symbiotic infection in a Nod factor structure dependent manner in the pea ‘Afghanistan’ ecotype [34, 38]. The diversity information has also been exploited in Lotus to further substantiate that the LysM-RLK receptors mediate specific recognition of Nod factors [39]. More recently, our current understanding of the symbiotic mechanisms has been challenged for the supposed role of NCR peptides that were initially shown as important effectors of endosymbiont’s differentiation to nitrogen-fixing bacteroids. Making use of the differential ability of Sinorhizobium meliloti Rm41 to form functional or non-nitrogen fixing nodules depending on the Medicago accession used, two genes, NFS1 and NFS2, were identified and shown to code for NCR peptides [36,37,38,39,40]. This broadened the role of the NCR peptides in the fixation stage by revealing that some of them also control discrimination against incompatible microsymbionts. A thorough survey of naturally occurring variation also provided ground for the discovery of new genetic determinants of nodulation. This was notably the case in soybean where this approach led to the identification of two dominant genes that restrict nodulation in a strain-specific manner, Rj2/Rfg1 encoding a TIR-NBS-LRR resistance (R) gene and Rj4 that codes for a thaumatin-like protein [41, 42]. This revealed that some host genotypes are able to trigger gene-for-gene resistance, which is found in plant-pathogen interactions, to selectively interact with certain symbiotic strains but to exclude others.
These illuminating examples show that there is a mileage to be gained from exploring the natural variation in nodulation in the Nod-independent Aeschynomene group. To screen our germplasm collection, many Bradyrhizobium strains are available, including photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic ones [14, 43, 44]. A recent report revealed important variations in the ability of different Nod-independent Aeschynomene species to be nodulated in a T3SS-dependent fashion by the non-photosynthetic Bradyrhizobium strains STM6978 and USDA61 [14]. Such marked variations were also observed between different accessions of A. evenia s.s., providing the basis for a genetic analysis of this differential susceptibility. Variations in symbiotic traits with naturally-nodulating photosynthetic Bradyrhizobium strains have not been thoroughly surveyed yet, but the observations made in the present study using the strains ORS278 and BTAi1 yield promising preliminary results. By evaluating different genotype-rhizobial combinations, we predict that symbiotic polymorphisms will be found, notably in the induction of nodulation, nitrogen fixation and also in stem nodulation. Crossable accessions exhibiting polymorphic symbiotic phenotypes can then be selected for hybridization experiments, subsequent genetic analysis and locus mapping. This will pave the way for the identification of the genes underpinning these symbiotic responses through forward or reverse genetics. To assist in these studies, genomic and genetic data, together with a number of molecular tools, are being accumulated for the model species A. evenia and it thus represents the easiest system to work with [16, 20]. Despite the high genetic diversity observed in A. evenia, the number of available germplasm samples remains relatively modest since it has not been as extensively sampled as other legumes of interest [22]. Therefore, the accessions of other Nod-independent taxa in the same gene pool or in the related one containing A. sensitiva, represent a good complement. In addition, the expected high level of microsynteny with A. evenia will facilitate a synteny-based positional approach, as has been successfully performed between Pea and Medicago to identify the gene underlying the SYM2 locus [34, 45]. As a result, genetic resources developed for the Nod-independent Aeschynomene clade can be fully exploited for the search of natural variation in nodulation with Bradyrhizobium.
Conclusions
With the goal of discovering natural variation in the Nod-independent Aeschynomene legumes, we developed a large collection of 226 accessions that spans the geographical distribution of the different taxa in this group, including the model species A. evenia. These accessions were subjected to combined analyses of gene sequencing, cytogenetics, hybridization experiments and SSR genotyping. This work resulted in the delineation of taxon boundaries and in the discovery of new genotypes. Taxa displaying a significant genetic diversity were characterized by a clear geographically-based genetic structure. In addition, low-copy nuclear genes and patterns of microsatellite diversity illuminated the genetic basis of the Aeschynomene diploid and polyploid taxa that are all predominantly autogamous and have a predicted simple disomic inheritance, two attributes favorable for genetics. Such a well-characterized collection of accessions constitutes a major genetic resource for exploring the natural variation of nodulation in response to different Bradyrhizobia strains and for searching for their underlying genetic determinants. Discoveries of alternative functions in symbiotic genes identified in other model legumes or of new genes involved in the recognition of the still unknown non-Nod bacterial signal, nodule functioning and in the restriction of compatibility would add a new dimension to our understanding of the genetic control of nodulation in the Nod-independent symbiosis.
Methods
Plant material
All the accessions of Aeschynomene used in this study, their geographical origin and source data are listed in Additional file 1: Table S1. Seeds were scarified with sulphuric acid for germination and plants were grown in pots filled with compost under greenhouse conditions (temperature: 26-36 °C, relative humidity: 70%-80%, insect-proof screens) as detailed [16]. Interspecific crosses were performed according to the protocol developed earlier and the nature of the resulting hybrids was checked using SSR markers (data not shown) [16]. Fertility of the F1 plants was assessed by recording the number of successfully developed pods per flowering axis and the number of seeds in each pod.
Plant nodulation and ARA
Nodulation tests were carried out using Bradyrhizobium sp. strains ORS278 and BTAi1 [12]. The strains were cultivated for 7 days in yeast-mannitol liquid medium at 34 °C. Root inoculation was performed in an in vitro growth chamber on 7-day-old plants using 1 mL of bacterial culture with an optical density at 600 nm adjusted to 1. Stem inoculation was carried out in a greenhouse by wrapping the stem of 5-week-old plants with a paper soaked with bacterial culture for 24 h. Stem nodules were observed at 21dpi and root nodules at 14dpi. Nitrogen-fixing activity was estimated on the entire plant by measurement of acetylene reducing activity (ARA) and microscopic observations were performed using a stereo-microscope (Nikon AZ100, Champigny-sur-Marne, France) as previously published [46].
Genome size estimation and chromosome counting
Flow cytometry measurement was performed on leaf material to estimate genome sizes of various accessions as already explained [16]. These estimates were based on the measurements of three plants per accession using Lycopersicum esculentum (Solanaceae) cv “Roma” (2C = 1.99 pg) as the internal standard. For chromosome number counts, metaphasic chromosomes were prepared from root-tips, spread on slides and stained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). Chromosomes were counted from images obtained with a fluorescent microscope as previously described [16].
Plant DNA extraction
Genomic DNA was extracted from fresh leaves using the CTAB (Cetyl Trimethyl Ammonium Bromide) method improved by the addition of β-mercaptoethanol 2% and PVPP 2%. For herbarium material, a protocol adapted for fragmented DNA was used, with increased length of the incubation (90 min), centrifugation (20 min) and precipitation (15 min) steps was used. DNA quantity was evaluated by spectrophotometer and DNA samples normalized to a uniform concentration of 10 ng/μL.
Gene sequencing and sequence analysis
The nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer region (ITS: ITS1-5.8S rDNA gene-ITS2) and five low copy nuclear genes CYP1, eiF1α, Sucrose Synthase, SUI1 and a gene homolog to Glyma.07G136800 and Glyma.18G187300 identified in Glycine max were amplified with the primers listed in Additional file 2: Table S2. PCR amplifications, cloning and sequencing of PCR products were performed as already described [17, 18]. The DNA sequences generated in this study were deposited in Genbank (Additional file 3: Table S3) and additional sequences are available in Additional file 4: Doc. S1. For the phylogenetic analyses, the gene sequences were aligned in ClustalX, version 1.81b and the alignments were checked in Genedoc v2.7. Phylogenetic reconstructions were performed with the MEGA v7 program using the Neighbor Joining approach and the Tamura 3-parameter model with a 1000 x bootstrap.
SSR marker selection and genotyping
A total of 500 primer pairs were initially defined to develop SSR markers for genetic mapping in A. evenia (Additional file 7: Table S4) [9]. In the present study, they were again tested on two polymorphic accessions of A. evenia and two cytotypes of A. indica (Additional file 8: Table S5). Forward primers all contained a 5′-end M13 tail (5′-CACGACGTTGTAAAACGAC-3′), enabling the tagging the PCR products during the PCR amplification with 4 M13 primer-fluorescent dyes 6-FAM™, NED®, VIC®, or PET® (Applied Biosystems, CA, USA). Amplicon sizes were analysed using an ABI 3700 automatic capillary sequencer (Applied Biosystems) as previously described [9]. 54 SSR markers were organized in 4-SSR multiplexes and used to genotype the accessions belonging to the A. evenia and the A. sensitiva groups as detailed in Additional file 6: Figure S2. Allele scorings were analysed using GeneMapper 4.0 software (Applied Biosystems) and exported as data tables for two groups of genotyping.
SSR data analysis
Genotyping data files were assembled in a single database that was used to determine genetic relationships among the accessions. For this, a distance-based approach was applied by calculating with a shared allele index a genetic dissimilarity matrix in DARwin v5 software [25]. Then, individual relations were separately analyzed for each ploidy level (2×, 4×, 6×) with a tree construction based on an unweighted Neighbor Joining method while genetic affinities between diploid and polyploid species were investigated by a factorial analysis as implemented in DARwin v5. The genetic diversity was evaluated by computing the number of alleles per locus (Na) and the observed heterozygosities Ho for each SSR locus and for different accession groups (Additional files 12 and 13: Tables S8, S9).
References
Graham PH, Vance CP. Legumes: importance and constraints to greater use. Plant Physiol. 2003;131:872–7.
GED O. Speak, friend, and enter: signaling systems that promote beneficial symbiotic associations in plants. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2013;11:252–63.
Oldroyd GED, Murray JD, Poole PS, Downie JA. The rules of engagement in the legume-Rhizobial Symbiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 2011;45:119–44.
Reid DE, Ferguson BJ, Hayashi S, Lin YH, Gresshoff PM. Molecular mechanisms controlling legume autoregulation of nodulation. Ann Bot. 2011;108(5):789–95.
Sprent JI. Evolving ideas of legume evolution and diversity: a taxonomic perspective on the occurrence of nodulation. New Phytol. 2007;174:11–25.
Sprent JI, James EK. Legume-rhizobial symbiosis: an anorexic model? New Phytol. 2008;179:3–5.
Boivin C, Ndoye I, Molouba F, De Lajudie P, Dupuy N, Dreyfus B. Stem nodulation in legumes: diversity, mechanisms, and unusual characteristics. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1997;16(1):1–30.
Chaintreuil C, Arrighi JF, Giraud E, Miche L, Moulin L, Dreyfus B, Munive-Hernadez J, Villegas-Hernadez M, Béna G. Evolution of symbiosis in the legume genus Aeschynomene. New Phytol. 2013;200:1247–59.
Chaintreuil C, Rivallan R, Bertioli DJ, Klopp C, Gouzy J, Courtois B, et al. A gene-based map of the nod factor-independent Aeschynomene evenia sheds new light on the evolution of nodulation and legume genomes. DNA Res. 2016;23:365–76.
Giraud E, Hannibal L, Fardoux J, Vermeglio A, Dreyfus B. Effect of Bradyrhizobium photosynthesis on stem nodulation of Aeschynomene sensitiva. Proc Nat Acad Sci (U S A). 2000;97(26):14795–800.
Giraud E, Fleischman D. Nitrogen-fixing symbiosis between photosynthetic bacteria and legumes. Photosynth Res. 2002;82:115–30.
Giraud E, Moulin L, Vallenet D, Barbe V, Cytryn E, Avarre JC, et al. Legumes symbioses: absence of nod genes in photosynthetic bradyrhizobia. Science. 2007;316(5829):1307–12.
Okazaki S, Kaneko T, Sato S, Saeki K. Hijacking of leguminous nodulation signaling by the rhizobial type III secretion system. Proc Nat Acad Sci (USA). 2013;110:17131–6.
Okazaki S, Tittabutr P, Teulet A, Thouin J, Fardoux J, Chaintreuil C, et al. Rhizobium-legume symbiosis in the absence of nod factors: two possible scenarios with or without the T3SS. ISME J. 2016;10:64–74.
Rudd VE. The American species of Aeschynomene. Contributions of the United States National Herbarium. 1955;32:1–172.
Arrighi JF, Cartieaux F, Brown SC, Rodier-Goud M, Boursot M, Fardoux J, et al. Aeschynomene evenia, a model Plant for Studying the molecular genetics of the nod-independent rhizobium-legume Symbiosis. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact. 2012;25:851–61.
Arrighi JF, Chaintreuil C, Cartieaux F, Cardi C, Rodier-Goud M, Brown SC, et al. Radiation of the nod-independent Aeschynomene relies on multiple allopolyploid speciation events. New Phytol. 2014;201:1457–68.
Arrighi JF, Cartieaux F, Chaintreuil C, Brown S, Boursot M, Giraud E. Genotype delimitation in the nod-independent model legume Aeschynomene evenia. PLoS One. 2013;8:e63836.
Czernic P, Gully D, Cartieaux F, Moulin L, Guefrachi I, Patrel D, et al. Convergent evolution of endosymbiont differentiation in Dalbergioid and inverted repeat-lacking clade legumes mediated by nodule-specific cysteine-rich peptides. Plant Physiol. 2015;169:1254–65.
Fabre S, Gully D, Poitout A, Patrel D, Arrighi JF, Giraud E, et al. Nod factor-independent nodulation in Aeschynomene evenia required the common plant-microbe symbiotic toolkit. Plant Physiol. 2015;169(4):2654–64.
Nouwen N, Arrighi JF, Cartieaux F, Gully D, Klopp C, Giraud E. The role of rhizobial (NifV) and plant (FEN1) homocitrate synthesis in Aeschynomene - photosynthetic Bradyrhizobium symbiosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:448.
Gentzbittel L, Andersen SU, Ben C, Rickauer M, Stougaard J, Young ND. Naturally occurring diversity helps to reveal genes of adaptive importance in legumes. Front Plant Sci. 2015;6:269.
African Plant Database (version 3.4.0). Conservatoire et Jardin botaniques de la Ville de Genève and South African National Biodiversity Institute, Pretoria, http://www.ville-ge.ch/musinfo/bd/cjb/africa/.
Tropical Forages: an interactive selection tool. Cook, B.G., Pengelly, B.C., Brown, S.D., Donnelly, J.L., Eagles, D.A., Franco, M.A., Hanson, J., Mullen, B.F., Partridge, I.J., Peters, M. and Schultze-Kraft, R. CSIRO, DPI&F(Qld), CIAT and ILRI, Brisbane, Australia. 2005. http://www.tropicalforages.info
Perrier X, Jacquemoud-Collet JP. 2006. DARwin software http://DARwin.cirad.fr/DARwin
Vasse J, de Billy F, Truchet G. Abortion of infection during the rhizobium meliloti-alfalfa symbiotic interaction is accompanied by a hy- persensitive reaction. Plant J. 1993;4:555–66.
Klie M, Schie S, Linde M, Debener T. The type of ploidy of chrysanthemum is not black or white: a comparison of a molecular approach to published cytological methods. Front Plant Sci. 2014;5:479.
Leal-Bertioli S, Shirasawa K, Abernathy B, Moretzsohn M, Chavarro C, Clevenger J, Ozias-Akins P, Jackson S, Bertioli D. Tetrasomic recombination is surprisingly frequent in allotetraploid Arachis. Genetics. 2015;199(4):1093–105.
Wong MM, Gujaria-Verma N, Ramsay L, Yuan HY, Caron C, Diapari M, et al. Classification and characterization of species within the genus lens using genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS). PLoS One. 2015;10(3):e0122025.
Blanca J, Cañizares J, Cordero L, Pascual L, Diez MJ, Nuez F. Variation revealed by SNP genotyping and morphology provides insight into the origin of the tomato. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e48198.
Kassa MT, Penmetsa RV, Carrasquilla-Garcia N, Sarma BK, Datta S, Upadhyaya HD, Varshney RK, von Wettberg EJ, Cook DR. Genetic patterns of domestication in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.) and wild Cajanus relatives. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39563.
Lu F, Lipka AE, Glaubitz J, Elshire R, Cherney JH, Casler MD, Buckler ES, Costich DE. Switchgrass genomic diversity, ploidy, and evolution: novel insights from a network-based SNP discovery protocol. PLoS Genet. 2013;9(1):e1003215.
Khazaei H, Caron CT, Fedoruk M, Diapari M, Vandenberg A, Coyne CJ, et al. Genetic diversity of cultivated lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) and its relation to the World's agro-ecological zones. Front Plant Sci. 2016;7:1093.
Geurts R, Heidstra R, Hadri AE, Downie JA, Franssen H, Van Kammen A, Bisseling T. Sym2 of pea is involved in a nodulation factor-perception mechanism that controls the infection process in the epidermis. Plant Physiol. 1997;115(2):351–9.
Tirichine L, de Billy F, Huguet T. Mtsym6, a gene conditioning Sinorhizobium strain-specific nitrogen fixation in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. 2000;123(3):845–51.
Liu J, Yang S, Zheng Q, Zhu H. Identification of a dominant gene in Medicago truncatula that restricts nodulation by Sinorhizobium meliloti strain Rm41. BMC Plant Biol. 2014;14:167.
Yang S, Wang Q, Fedorova E, Liu J, Qin Q, Zheng Q, et al. Microsymbiont discrimination mediated by a host-secreted peptide in Medicago truncatula. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(26):6848–53.
Limpens E, Franken C, Smit P, Willemse J, Bisseling T, Geurts R. LysM domain receptor kinases regulating rhizobial nod factor-induced infection. Science. 2003;302(5645):630–3.
Radutoiu S, Madsen LH, Madsen EB, Jurkiewicz A, Fukai E, Quistgaard EM, et al. LysM domains mediate lipochitin-oligosaccharide recognition and Nfr genes extend the symbiotic host range. EMBO J. 2007;26(17):3923–35.
Wang Q, Yang S, Liu J, Terecskei K, Ábrahám E, Gombár A, et al. Host-secreted antimicrobial peptide enforces symbiotic selectivity in Medicago truncatula. Proc Nat Acad Sci (USA). 2017;114(26):6854–9.
Yang S, Tang F, Gao M, Krishnan HB, Zhu HR. Gene-controlled host specificity in the legume-rhizobia symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(43):18735–40.
Tang F, Yang S, Liu J, Zhu H. Rj4, a gene controlling nodulation specificity in soybeans, encodes a thaumatin-like protein but not the one previously reported. Plant Physiol. 2016;170(1):26–32.
Molouba F, Lorquin J, Willems A, Hoste B, Giraud E, Dreyfus B, et al. Photosynthetic bradyrhizobia from Aeschynomene spp. are specific to stem-nodulated species and form a separate 16S ribosomal DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism group. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65(7):3084–94.
Miché L, Moulin L, Chaintreuil C, Contreras-Jimenez JL, Munive-Hernandez JA, Del Carmen Villegas-Hernandez M, et al. Diversity analyses of Aeschynomene symbionts in tropical Africa and central America reveal that nod-independent stem nodulation is not restricted to photosynthetic bradyrhizobia. Environ Microbiol. 2010;12(8):2152–64.
Gualtieri G, Kulikova O, Limpens E, Kim DJ, Cook DR, Bisseling T, et al. Microsynteny between pea and Medicago truncatula in the SYM2 region. Plant Mol Biol. 2002;50(2):225–35.
Bonaldi K, Gargani D, Prin Y, Fardoux J, Gully D, Nouwen N, et al. Nodulation of Aeschynomene afraspera and A. indica by photosynthetic Bradyrhizobium sp. strain ORS285: the nod-dependent versus the nod-independent symbiotic interaction. MPMI. 2011;24:1359–71.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the different germplasm banks for provision of seeds: AusPGRIS (Australia), CIAT (Colombia), ILRI (Ethiopia), IRRI (Philippines), Kew Gardens (UK) and USDA (USA). We are also very grateful to the many herbaria and botanists who provided additional relevant plant material that significantly contributed our sampling. The present work has benefited from the facilities and expertise of the cytometry facilities of Imagerie-Gif (http://www.i2bc.paris-saclay.fr/spip.php?rubrique184) and of the molecular cytogenetic facilities of the AGAP laboratory (https://umr-agap.cirad.fr/en/platforms/plateformes/genotyping).
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the French National Research Agency (ANR-AeschyNod-14-CE19-0005-01) that served for the design of the study, experimentation and analysis of the data.
Availability of data and materials
The gene sequences generated in this study have been deposited in GenBank (accession numbers listed in Additional file 3: Table S3) and additional sequences are available in Additional file 4: Doc. S1. All the SSR marker characteristics are included as supplementary information files (Additional files 7, 8, 10, 11, 12 and 13: Table S4-S9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CC was responsible for obtaining the plant material and the SSR genotyping data, and together with LB carried out the gene sequencing. RR and PM participated in the SSR marker development and genotyping. XP, GM, LL and BT performed computational analysis of the SSR genotyping data. MGP and MB carried out cytometry analyses. JF and EG handled the nodulation tests. HV, H. Randriambanona and H. Ramanankierna organized field collection of plant material and contributed to the acquisition and analysis of diversity data. GPL provided expertise in legume taxonomy and biogeography, and together with EG reviewed the manuscript. J.F.A. conceived the study, analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The sources of the Aeschynomene accessions used in this study are indicated in Additional file 1: Table S1. In addition to seedbank and herbaria supply, some accession were collected for purpose of this study in Madagascar (with authorization from the Malagasy Ministry of Scientific Research) and in New-Caledonia (licence n°60,912 from the Northern Province). Collection and identification of these new accessions were performed by Heriniaina Ramanankierana, Herizo Randriambanona, Hervé Vandrot and Jean-François Arrighi.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Additional files
Additional file 1:
Table S1. Accessions used in this study, origin and characteristics. (XLSX 23 kb)
Additional file 2:
Table S2. Nuclear genes used for the phylogenetic analyses. (XLSX 11 kb)
Additional file 3:
Table S3. GenBank numbers for the sequences used in the phylogenetic analyses. (XLSX 12 kb)
Additional file 4:
Doc. S1. ITS sequences obtained for the Nod-independent Aeschynomene accessions. (DOCX 30 kb)
Additional file 5:
Figure S1. Chromosome numbers in new Aeschynomene taxa. Root tip metaphase chromosomes stained in blue with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole). Chromosome numbers are indicated in brackets. Scale bars: 5 μm. (PPTX 1008 kb)
Additional file 6:
Figure S2. Schematic representation of the different steps of the genotyping process from marker selection to data treatment. (PPTX 64 kb)
Additional file 7:
Table S4. Origin, location and primer sequences for the SSR markers used for genotyping. (XLSX 13 kb)
Additional file 8:
Table S5. Repeat motif and allelic amplification profiles of the SSR selected for genotyping. (XLSX 13 kb)
Additional file 9:
Figure S3. Detailed NJ trees representing the genetic diversity among the Nod-independent Aeschynomene accessions. The trees were developed separately in DARWIN using the allelic data of 65 SSRs for the 2× (a), 4× (b) and 6× (c) taxa. Well-differentiated taxa are distinctly colored. Identified genotypes are marked with a red dot and numbered. Accessions are designated with their LSTM code mentioned in Additional file 1: Table S1 followed by their geographical origin. Species suspected to be morphological variants are marked with an asterisk. Taxon colours and genotype numbers are the same as in Fig. 3. (PPTX 187 kb)
Additional file 10:
Table S6. Allelic diversity of the SSR markers (XLSX 22 kb)
Additional file 11:
Table S7. Cross-species transferability of the SSR markers (XLSX 13 kb)
Additional file 12:
Table S8. Scoring of mean allele number per SSR and species (XLSX 15 kb)
Additional file 13:
Table S9. Observed heterozygosity (Ho) in Aeschynomene species (XLSX 14 kb)
Additional file 14:
Figure S4. Comparison of the nodulation properties of A. evenia s.s. and A. indica. Different accessions were root inoculated with Bradyrhizobium ORS278 and BTAi1 and analysed at 14dpi. (a) Number of nodules per accession. (b) Acetylene-reducing activity (ARA). A.U. Arbitrary Unit. Error bars represent s.d. (n = 6). (PPTX 179 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Chaintreuil, C., Perrier, X., Martin, G. et al. Naturally occurring variations in the nod-independent model legume Aeschynomene evenia and relatives: a resource for nodulation genetics. BMC Plant Biol 18, 54 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1260-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1260-2