Abstract
Background
Breast cancer is the most common cause of cancer death among women. Several studies have investigated the relationship between the C3435T polymorphism of ABCB1 gene and risk of breast cancer; but the results are conflicting. In the present study, we sought to assess the relationship between the C3435T polymorphism in ABCB1 gene and the risk of breast cancer in a sample of the Moroccan population.
Methods
A case control study was performed on 60 breast cancer patients and 68 healthy women. The ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism was analyzed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) assay. Furthermore, a meta-analysis including 16 studies with 6094 cases of breast cancer and 8646 controls was performed.
Results
Genotype frequencies were 50 % for CC, 33.3 % for CT and 16.7 % for TT in patients and 41.2 % for CC, 48.5 % for CT and 10.3 % for TT respectively in the control group. This difference was not statistically significant. The same trend as observed in the allele distribution between patients and controls (P = 0.84). Findings from the meta-analysis showed that the ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism was not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer in the dominant model (OR = 0.907; 95 % CI = 0.767–1.073; P = 0.25) as well as in the recessive model (OR = 1.181; 95 % CI = 0.973–1.434; P = 0.093) and in the allele contrast model (OR = 1.098; 95 % CI = 0.972–1.240; P = 0.133). However, the stratification of studies on ethnic basis showed that the TT genotype was associated with the risk of breast cancer in Asians (OR = 1.405; 95 % CI = 1.145–1.725; P = 0.001), Caucasians (OR = 1.093; 95 % CI = 1.001–1.194; P = 0.048) and North African (OR = 2.028; 95 % CI = 1.220–3.371; P = 0.006).
Conclusions
We have noted that the implication of C3435T variant on the risk of breast cancer was ethnicity-dependent. However, there is no evidence that ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism could play a role in susceptibility to breast cancer in Morocco. Further studies with a larger sample size, extended to other polymorphisms are needed to understand the influence of ABCB1 genetic variants on the risk of breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Breast cancer is the most common cause of cancer death among women and the most frequently diagnosed female cancer [1]. In Morocco, the cancer registries implemented in Rabat and Casablanca have reported a standardized incidence of 39.9 and 49.2 per 100,000 women respectively [2, 3].
The etiology of this disease is not fully understood, although many risk factors have been identified, such as hormonal, environmental and lifestyle factors. In addition, some molecular markers have been found to be associated with the risk of breast cancer. The human multidrug resistance gene 1 (MDR1/ABCB1), localized to chromosome region 7q21, encodes P-glycoprotein (P-gp) a transmembrane transport protein of 170 kDa that acts as an adenosine triphosphate-dependent efflux transporter pump [4]. This protein is expressed in most human tissues such as intestine, liver, bile, kidney, adrenal gland, placenta, brain and breast. It allows the cells to eliminate hydrophobic substrates and anti-cancer drugs [5–7].
To date, thousands of SNPs have been identified in the ABCB1 gene. One of the most important ABCB1 gene polymorphism is 3435C > T (rs1045642) in exon 26, a synonymous polymorphism witch alters gene expression, protein activity and substrate specificity [8–10]. Indeed, subjects with the TT genotype showed a decreased intestinal P-gp expression compared to CC genotype carriers [11].
Several studies have investigated the relationship between the C3435T polymorphism in ABCB1 gene and the risk of breast cancer in different populations, however the results are inconsistent and the relevance of this polymorphism remains confusing [12–26].
To the best of our knowledge, the relationship between the C3435T polymorphism of ABCB1 gene and the risk of breast cancer has not been examined in the Moroccan population. In this manuscript we evaluated the possible influence of ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism on the susceptibility of breast cancer as well as its correlation with the clinical features of Moroccan patients with breast cancer. Secondly, we carried out a meta-analysis on 16 studies involving 6,094 cases of breast cancer and 8,646 controls in order to widely estimate the relationship between this polymorphism and breast cancer risk.
Methods
Study population
The present study was performed on 60 unrelated patients with histologically confirmed breast cancer treated between 2009 and 2010 at Mohammed VI Center for Cancer Treatment, Ibn Rochd University Hospital of Casablanca, Morocco. The control group consisted of 68 healthy women without a history of breast or other cancers. The general characteristics of the patients, including age of menarche, age of first pregnancy, number of pregnancies, breastfeeding, oral contraceptives use, the number of abortions, menopause status, smoking status, body mass index (BMI) and family history of breast cancer were collected through structured survey forms. Clinical and pathological features including age at diagnosis, histology type, tumor size, Scarff-Bloom-Richardson (SBR) grade, lymph nodes status and hormone receptor status were obtained from medical records.
The study was approved by the local ethics committee and written informed consent was obtained from each participant.
Genotyping
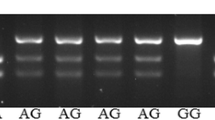
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood using the salting out method [27]. The ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism was analyzed by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) assay using the primer sequences 5′-TTGATGGCAAAGAAATAAAGC-3′ and 5′-CTTACATTAGGCAGTGACTCG-3′. The PCR reaction was performed in a total volume of 25 μl containing 100 ng of genomic DNA, 1× of 5× GoTaq Flexi Buffer (Promega), 1.25 mM MgCl2, 0.2 mM of each dNTP, 0.625 mM of each primer and 0.5U Go Taq DNA polymerase (Promega). PCR program consisted of an initial denaturation at 94 °C for 5 min followed by 35 cycles of 95 °C for 90 s, 55 °C for 60 s, 72 °C for 90 s, and a final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. Controls with known genotypes (homozygous wild-type, homozygous mutant, and heterozygous) were included in each PCR as a reference. PCR products were digested with 10 units of Mbo I restriction enzyme for 16 h. The digested products were separated by 3 % agarose gel electrophoresis after ethidium bromide staining and observed under UV light. The resulting fragments were 130 bp and 76 bp for the Wild-type homozygote CC, 206 bp, 130 bp and 76 bp for the heterozygote CT and 206 bp for Homozygote mutant variant TT.
Meta-analysis
A literature search of online databases (PubMed, Embase, Scopus, EBSCO…) was conducted until April 1, 2016 using appropriate keywords: “MDR1”, “ABCB1”, “C3435T polymorphism” and “breast cancer”. All languages were searched initially, but only English language studies were selected.
The following criteria were used to select the eligible studies: (a) a case-control study on the association between ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and breast cancer risk, (2) have an available genotype or allele frequency, and odds ratio (OR) with 95 % confidence interval (CI). Major exclusion criteria were (a) case-only study and review articles and (b) studies without raw data of the C3435T ABCB1 genotypes.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 19.0 software. The chi-squared (χ2) test was used to assess the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in genotype distribution. OR with 95 % CI was used to assess the strength of the association between ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and breast cancer risk. Student’s t-test and Fisher exact test were used to evaluate the correlation between the studied polymorphism and the clinicopathological parameters. All tests were two-sided and a p value less than 0.05 were considered as statistically significant.
The meta-analysis was performed by MedCalc v.11.6.1.0 software. OR with 95 % CI was used to assess the association between the ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and breast cancer risk. Genetic heterogeneity was tested by Cochran’s (Q) test [28]. Random-effects model was used when the P value of heterogeneity test is less than 0.05; otherwise, fix-effects model was used.
Results
The general characteristics of breast cancer patients without any history of smoking are summarized in Table 1. The mean age at diagnosis was 41.5 ± 10.4 years. Mean of BMI was 26.2 kg/m2 (range 16.6–43.6 kg/m2). The mean age of menarche was 13.5 years old (range 10–18 years) and the mean age of menopause was 48.5 ± 4.9 years old (range 40–59 years). 63.3 % of patients had descendants (2.9 ± 1.6 children), 79.5 % of them breastfeed (22.6 months, range 1–72). Finally, 48.3 % of patients presented a family history of breast cancer. The hormone replacement therapy has not been used by post-menopausal women.
Allele and genotype frequencies of ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism in breast cancer patients and controls are summarized in Table 2. In breast cancer patients, the CC genotype was found in 50 %, CT genotype was found in 33.3 % and TT genotype was found in 16.7 %. In the control group, the frequencies of genotypes were 41.2 % for CC, 48.5 % for CT and 10.3 % for TT. This difference was not statistically significant. The genotype distributions among cases and controls were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (χ2 = 3.75, P = 0.05 for patients and χ2 = 0.36, P = 0.55 for controls). The allele frequencies in breast cancer patients and healthy controls were 66.7 and 65.4 % for C allele, and 33.3 and 34.6 % for T allele, respectively (OR = 0.95; 95 % CI = 0.56–1.59; P = 0.84). The ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism was not significantly associated with increased risk of breast cancer in the additive, dominant and recessive models.
Table 3 shows the potential association between the C3435T genetic variant and risk factors of breast cancer in patients. There was no evidence of a significant association between this polymorphism and risk factors of breast cancer (P > 0.05).
Clinical and pathological characteristics of breast cancer patients, according to ABCB1 genotypes are shown in Table 4. Our data suggest that there is no significant association between the ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and age at diagnosis, menopausal status, histology type, tumor size, SBR grade, lymph node status and hormone receptor status (P > 0.05).
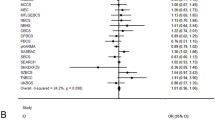
Concerning the meta-analysis, the characteristics of the selected studies are summarized in Table 5. Our findings showed no significant association between C3435T polymorphism of ABCB1 and the risk of breast cancer in the dominant model (OR = 0.907; 95 % CI = 0.767–1.073; P = 0.25) as well as the recessive model (OR = 1.181; 95 % CI = 0.973–1.434; P = 0.093), and the allele contrast model (OR = 1.098; 95 % CI = 0.972–1.240; P = 0.133) (Table 6; Fig. 1).
Forest plot of the relationship between ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and breast cancer risk (T vs. C). The black squares correspond to the odds ratios of the individual studies. The areas of squares are proportional to the study weight. The horizontal lines represent 95 % confidence intervals. The diamonds represent the pooled odd ratios with 95 % confidence intervals
A significant correlation was observed between breast cancer risk and C3435T polymorphism in the recessive model (P = 0.008) and in the allele contrast model (P = 0.017) under the fixed-effects model. However, we observed heterogeneity among the total studies in the recessive model (I2 = 62.01 %; P = 0.0005), in the dominant model (I2 = 57.35 %; P = 0.0023) and in the allele contrast model (I2 = 69.04 %; P < 0.0001). This explains the use of the random effects model in all these cases.
To identify the potential source of the significant heterogeneity observed in the overall population, we performed a subgroup analysis based on ethnicity. The results showed an increased risk of breast cancer among Asians (OR = 1.405; 95 % CI = 1.145–1.725; P = 0.001), Caucasians (OR = 1.093; 95 % CI = 1.001–1.194; P = 0.048) and North African (OR = 2.028; 95 % CI = 1.220–3.371; P = 0.006) with the TT genotype under the recessive model. Nevertheless, no significant association was found in mixed populations. We noted a significant association with breast cancer risk in the homozygote and allele contrast models for North Africans and Asians populations carrying the TT genotype and T allele (Table 7).
Discussion
ABCB1 gene is a member of the ABC family that encodes P-gp protein, which is an ATP-dependent efflux pump that allows the cells to eliminate toxins and carcinogenic substances [6]. Some reports suggested that this polymorphism may influence the risk of a number of cancers, especially breast carcinoma [29]. Indeed, this synonymous mutation (Ile1145Ile) influences protein stability [30] and causes cellular damage or apoptosis alteration witch play an important role in cancer development due to an accumulation of metabolites within the cell [31, 32].
In the present study, we have evaluated the association between the genetic polymorphism C3435T of ABCB1 gene and the risk of breast cancer among Moroccan patients. In agreement with a number of previous reports [16, 18, 21, 23, 24], our findings revealed no significant association between this polymorphism and breast cancer development. Otherwise, Gutierrez-Rubio et al. [24] did not find differences in the distribution of C3435T polymorphism between breast cancer patients and controls. However, when they have examined the association between this polymorphism and breast cancer risk, according to the menopausal status of patients, they found that premenopausal women with T allele have 2-fold increased risk of breast cancer.
In contrast, other studies have reported different results. Most of these findings reported the association of TT genotype and T allele with high risk of breast cancer. Turgut et al. [13] revealed a 1.5-fold increased risk for the development of breast cancer in T allele carriers. Similarly, Cizmarikova et al. [17] and George et al. [15] have found a significantly higher prevalence of T allele and TT genotype in breast cancer patients when compared to controls (P = 0.019 and P = 0.025 respectively). Furthermore, Wu et al. [20] conducted a large study with 1,173 breast cancer women and 1,244 controls and reported a significant increase in the frequency of the TT genotype (TT vs. CC: OR = 1.386; 95 % CI = 1.091–1.761; P = 0.008) and T allele (OR = 1.281; 95 % CI = 1.021–1.285; P = 0.020) in patients with breast cancer. More recently, Fawzy et al. [22] studied 190 Egyptian females with breast cancer and showed that the frequency of the TT genotype (OR = 1.45; 95 % CI = 1.09–1.94; P = 0.01) and T allele (OR = 2.41; 95 % CI = 1.27–4.56; P = 0.0006) were significantly higher in breast cancer patients compared to healthy controls.
Counterwise, a recent study of Abouhalima et al. [26] among Jordanian women have revealed a higher prevalence of CC genotype in breast cancer patients compared to controls (P < 0.001) and individuals with T allele were 2 times less likely to develop breast cancer (P < 0.0001). It should be noted that in a study of Salem et al., the T allele was more prevalent among Jordanians than the C allele [33]. On the other hand, the authors suggested strong linkage disequilibrium with other polymorphisms in ABCB1 gene and alterations in the post translational pathway which influences the efficacy and stability of P-gp in patients with CC genotype [26]. Similarly, in Kurdish patients the frequency of CC genotype and C allele were higher in patients than in controls; this result was not statistically significant [25].
These conflicting results may be due to the ethnicity and the environment of the studied population, the analysis type and the sample size. Indeed, it was reported that the distribution of C3435T genotypes varies among populations [33–35]. In Caucasians, the C3435T genotype frequency was 22, 50 and 28 % for CC, CT and TT genotypes respectively [36]. In Morocco, genotype frequencies were 39 % for CC, 51 % for CT and 10 % for TT [37].
Besides, we did not find a significant difference in the distribution of breast cancer risk factors among CC, CT and TT genotypes. Similar to our results, Tatari et al. reported an absence of association between C3435T genotypes of ABCB1 gene and the risk factors, including age of disease onset, cancer stage, family history of the cancer, smoking history, age of menarche, age of first pregnancy, number of pregnancies, abortion history, and history of oral contraceptive consumption (P > 0.05) [16]. Also, Wu et al. have reported no statistically significant correlation between genotype distributions and age at diagnosis, menopausal state and family history of breast carcinoma [20].
The correlation between the clinical and pathological features of breast cancer in the present study, according to C3435T polymorphism genotypes revealed no significant association at this level. In this line, Turgut et al. [13], Wu et al. [20] and Macías-Gómezdid et al. [23] have reported similar results. However, Ghafouri et al. have found a significant correlation between ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and clinical grades of breast cancer with higher grade in CC carriers (P = 0.027) [25]. On the other hand, Wu et al. [20] observed that patients with a negative status of ER and PR have more CT + TT genotypes than CC genotype (P = 0.013).
In second place, we tried through the present study to evaluate the association between the ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and breast cancer risk through a meta-analysis involving 16 studies with 6,094 cases of breast cancer and 8,646 controls. Our meta-analysis suggests that the ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism has no effect on breast cancer development. It is noteworthy that a lack of homogeneity between studies was observed regarding the distribution of ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism. This heterogeneity might be explained by ethnicity variability and sample size across the different studies included in the present meta-analysis. Indeed, Wang et al. in a meta-analysis observed significant heterogeneity among the total studies, but not in the small size sample analysis [38].
A number of meta-analysis were undertaken to assess the association between ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and risk of breast cancer [38–41]. The first meta-analysis conducted in 2011 which included 7 studies for ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism did not show any association between this polymorphism and risk of breast cancer [38]. However, it should be noted some errors in C3435T genotypes reported for the study of Nordgard et al. [12] and George et al. [15] which probably would have influenced the study results [42].
A meta-analysis conducted two years later [38], enrolled 10 case-control studies with 5,282 cases and 7,703 controls, indicated that this polymorphism were associated with a significantly increased risk of breast cancer according to the following models TT vs. CC (P = 0.003); TT vs. CT + CC (P = 0.003) and TT + CT vs. CC (P = 0.029). Although our study was based on the same data of the previous meta-analysis [38], we did not find any significant association between the C3435T polymorphism and risk of breast cancer. This can be explained by the fact that we have added the results from other populations with different genetic background, such as North Africa (Morocco, Egypt), Middle East (Jordan) and also mixed populations (Mexico). In Morocco, for example, the frequency of the wild-type 3435CC genotype was found to be higher than that observed in Caucasians and Asians. Conversely, the frequency of the mutated homozygous variant was lower compared to the same populations. However, similar results were reported in Egypt which may be attributed probably to their common ethnic and geographic origins [37].
Thereby, we stratified our meta-analysis by ethnicity to get a better idea about the involvement of this polymorphism in breast cancer risk. Our findings indicate that patients with TT genotype had a significantly increased risk of breast cancer in Asians, Caucasians and North African but not among mixed populations. These might be due to the differences in genetic background and lifestyle and seem to confirm that the C3435T polymorphism of ABCB1 gene varies across different populations [43].
Conclusions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study, which examined the association of ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism with the risk of breast cancer in a sample of the Moroccan population. The results of the present study revealed no difference between breast cancer patients and controls for ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism. In addition, we did not find a significant correlation between this polymorphism and clinicopathological features of breast cancer patients. This may be explained by the limited statistical power due to our small sample size. It is also necessary to remember that there are other polymorphisms in the ABCB1 gene implicated in the etiology of breast cancer which also deserve to be studied. Therefore, the results of the present study must be interpreted with caution and cannot be generalized. Larger case-control study, with at least 340 breast cancer patients and 340 healthy controls, including more polymorphisms of ABCB1 with haplotype analysis is needed to approve or not our conclusions and to obtain more clear information about the influence of ABCB1 genetic variants in breast cancer risk in Morocco. Moreover, it would also be interesting to study the association of this polymorphism with chemotherapy resistance in breast cancer in our population. Furthermore, the results obtained from the meta-analysis demonstrated that the implication of C3435T variant on the risk of breast cancer risk was modulated by ethnicity.
Abbreviations
- ABCB1:
-
ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PCR-RFLP:
-
Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism
- PR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- SBR:
-
Scarff-Bloom-Richardson
References
IARC Globocan. International agency for research on cancer. 2012.
RCRC. 2012 Cancers Register of Grand Casablanca 2005-2006-2007.
RCR. 2012 Cancers Register of Rabat 2005
Ueda K, Clark DP, Chen CJ, Roninson IB, Gottesman MM, Pastan I. The human multidrug resistance (mdr1) gene. cDNA cloning and transcription initiation. J Biol Chem. 1987;262(2):505–8.
Ieiri I. Functional significance of genetic polymorphisms in P-glycoprotein (MDR1, ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP, ABCG2). Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2012;27(1):85–105.
Kreile M, Rots D, Piekuse L, Cebura E, Grutupa M, Kovalova Z, Lace B. Lack of association between polymorphisms in genes MTHFR and MDR1 with risk of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(22):9707–11.
Pongstaporn W, Pakakasama S, Chaksangchaichote P, Pongtheerat T, Hongeng S, Permitr S. MDR1 C3435T and C1236T polymorphisms: association with high-risk childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(7):2839–43.
Hemauer SJ, Nanovskaya TN, Abdel-Rahman SZ, Patrikeeva SL, Hankins GD, Ahmed MS. Modulation of human placental P-glycoprotein expression and activity by MDR1 gene polymorphisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;79(6):921–5.
Hutson JR, Koren G, Matthews SG. Placental P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein: influence of polymorphisms on fetal drug exposure and physiology. Placenta. 2010;31:351–7.
Kimch-Sarfaty C, Oh JM, Kim IW, Sauna ZE, Calcagno AM, Ambudkar SV, Gossesman MM. A silent polymorphism in the MDR1 gene changes substrate specificity. Science. 2007;315:525–8.
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmöller J, Johne A, Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Roots I, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U. Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:3473–8.
Nordgard SH, Ritchie MD, Jensrud SD, Motsinger AA, Alnaes GI, Lemmon G, Berg M, Geisler S, Moore JH, Lønning PE, Børresen-Dale AL, Kristensen VN. ABCB1 and GST polymorphisms associatedwith TP53 status in breast cancer. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2007;17(2):127–36.
Turgut S, Yaren A, Kursunluoglu R, Turgut G. MDR1 C3435T polymorphism in patients with breast cancer. Arch Med Res. 2007;38(5):539–44.
Henríquez-Hernández LA, Murias-Rosales A, Hernández González A, Cabrera De León A, Díaz-Chico BN, Mori De Santiago M, Fernández Pérez L. Gene polymorphisms in TYMS, MTHFR, p53 and MDR1 as risk factors for breast cancer: a case–control study. Oncol Rep. 2009;22(6):1425–33.
George J, Dharanipragada K, Krishnamachari S, Chandrasekaran A, Sam SS, Sunder E. A single-nucleotide polymorphism in the MDR1 gene as a predictor of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 2009;9(3):161–5.
Tatari F, Salek R, Mosaffa F, Khedri A, Behravan J. Association of C3435T single-nucleotide polymorphism of MDR1 gene with breast cancer in an Iranian population. DNA Cell Biol. 2009;28(5):259–63.
Cizmarikova M, Wagnerova M, Schonova L, Habalova V, Kohut A, Linkova A, Sarissky M, Mojzis J, Mirossay L, Mirossay A. MDR1 (C3435T) polymorphism: relation to the risk of breast cancer and therapeutic outcome. Pharmacogenomics J. 2010;10(1):62–9.
Taheri M, Mahjoubi F, Omranipour R. Effect of MDR1 polymorphism on multidrug resistance expression in breast cancer patients. Genet Mol Res. 2010;9(1):34–40.
Abbas S, Beckmann L, Chang-Claude J, Hein R, Kropp S, Parthimos M, Dünnebier T, Hamann U, Brors B, Eils R, Zapatka M, Brauch H, Justenhoven C, Flesch-Janys D, Brüning T, Pesch B, Spickenheuer A, Baisch C, Ko YD, Dahmen N, Abbas S, Brauch H, Chang-Claude J, Dünnebier T, Flesch-Janys D, Hamann U, Hein R, Justenhoven C, Salazar R, MARIE-GENICA Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility for Menopausal Hormone Therapy Related Breast Cancer Risk. Polymorphisms in the BRCA1 and ABCB1 genes modulate menopausal hormone therapy associated breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;120(3):727–36.
Wu H, Kang H, Liu Y, Tong W, Liu D, Yang X, Lian M, Yao W, Zhao H, Huang D, Sha X, Wang E, Wei M. Roles of ABCB1 gene polymorphisms and haplotype in susceptibility to breast carcinoma risk and clinical outcomes. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138(9):1449–62.
Rubiś B, Hołysz H, Barczak W, Gryczka R, Łaciński M, Jagielski P, Czernikiewicz A, Półrolniczak A, Wojewoda A, Perz K, Białek P, Morze K, Kanduła Z, Lisiak N, Mrozikiewicz PM, Grodecka-Gazdecka S, Rybczyńska M. Study of ABCB1 polymorphism frequency in breast cancer patients from Poland. Pharmacol Rep. 2012;64(6):1560–6.
Fawzy MS, Awad HA, Ahmad HS, Kamel LM, Tom MM. Multi-drug resistance 1 genetic polymorphisms gene expression and prediction of chemotherapy response in breast cancer Egyptian patients. Egypt J Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;32(1):75–98.
Macías-Gómez NM, Gutiérrez-Angulo M, Leal-Ugarte E, Ramírez-Reyes L, Peregrina-Sandoval J, Meza-Espinoza JP, Ramos Solano F, de la Luz A-MM, Santoyo TF. MDR1 C3435T polymorphism in Mexican patients with breast cancer. Genet Mol Res. 2014;13(3):5018–24.
Gutierrez-Rubio SA, Quintero-Ramos A, Durán-Cárdenas A, Franco-Topete RA, Castro-Cervantes JM, Oceguera-Villanueva A, Jiménez-Pérez LM, Balderas-Peña LM, Morgan-Villela G, Del-Toro-Arreola A, Daneri-Navarro A. 1236 C/T and 3435 C/T polymorphisms of the ABCB1 gene in Mexican breast cancer patients. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(1):1250–9.
Ghafouri H, Ghaderi B, Amini S, Nikkhoo B, Abdi M, Hoseini A. Association of ABCB1 and ABCG2 single nucleotide polymorphisms with clinical findings and response to chemotherapy treatments in Kurdish patients with breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(6):7901–6.
Abuhaliema AM, Yousef AM, El-Madany NN, Bulatova NR, Awwad NM, Yousef MA, Al Majdalawi KZ. Influence of Genotype and Haplotype of MDR1 (C3435T, G2677A/T, C1236T) on the Incidence of Breast Cancer - a Case–control Study in Jordan. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17(1):261–6.
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16:1215.
Handoll HH. Systematic reviews on rehabilitation interventions. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006;87(6):875.
Ikeda M, Tsuji D, Yamamoto K, Kim YI, Daimon T, Iwabe Y, Hatori M, Makuta R, Hayashi H, Inoue K, Nakamichi H, Shiokawa M, Itoh K. Relationship between ABCB1 gene polymorphisms and severe neutropenia in patients with breast cancer treated with doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide chemotherapy. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2015;30:149–53.
Fung KL, Pan J, Ohnuma S, Lund PE, Pixley JN, Kimchi-Sarfaty C, Ambudkar SV, Gottesman MM. MDR1 synonymous polymorphisms alter transporter specificity and protein stability in a stable epithelial monolayer. Cancer Res. 2014;74(2):598–608.
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Smyth MJ. Multiple physiological functions for multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein? Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25:1–6.
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Tainton KM, Smyth MJ. A role for P-glycoprotein in regulating cell death. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000;38(1–2):1–11.
Salem AH, Ali M, Ibrahim A, Ibrahim M. Genotype and Allele Frequencies of MDR-1 Gene Polymorphism in Jordanian and Sudanese Populations. Am J Med Stud. 2014;2(1):19–23.
Ozawa S, Soyama A, Saeki M, Fukushima-Uesaka H, Itoda M, Koyano S, Sai K, Ohno Y, Saito Y, Sawada J. Ethnic differences in genetic polymorphisms of CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP3As and MDR1/ABCB1. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2004;19(2):83–95.
Santos PC, Soares RA, Santos DB, Nascimento RM, Coelho GL, Nicolau JC, Mill JG, Krieger JE, Pereira AC. CYP2C19 and ABCB1 gene polymorphisms are differently distributed according to ethnicity in the Brazilian general population. BMC Med Genet. 2011;12:13.
Hamidovic A, Hahn K, Kolesar J. Clinical significance of ABCB1 genotyping in oncology. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2010;16(1):39–44.
Kassogue Y, Dehbi H, Nassereddine S, Quachouh M, Nadifi S. Genotype variability and haplotype frequency of MDR1 (ABCB1) gene polymorphism in Morocco. DNA Cell Biol. 2013;32(10):582–8.
Wang Z, Wang T, Bian J. Association between MDR1 C3435T polymorphism and risk of breast cancer. Gene. 2013;532(1):94–9.
Lu PH, Wei MX, Yang J, Liu X, Tao GQ, Shen W, Chen MB. Association between two polymorphisms of ABCB1 and breast cancer risk in the current studies: a meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;125(2):537–43.
Sheng X, Zhang L, Tong N, Luo D, Wang M, Xu M, Zhang Z. MDR1 C3435T polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis based on 39 case–control studies. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(7):7237–49.
Wang J, Wang B, Bi J, Li K, Di J. MDR1 gene C3435T polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis of 34 case–control studies. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012;138(6):979–89.
Wang J, Wang B, Bi J. Significant association between ABCB1 gene C3435T polymorphism and breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;126(3):815–7.
Ameyaw MM, Regateiro F, Li T, Liu X, Tariq M, Mobarek A, Thornton N, Folayan GO, Githang’a J, Indalo A, Ofori-Adjei D, Price-Evans DA, McLeod HL. MDR1 pharmacogenetics: frequency of the C3435T mutation in exon 26 is significantly influenced by ethnicity. Pharmacogenetics. 2001;11(3):217–21.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank all the staffs of the Genetics and Molecular Pathology Laboratory and Mohammed VI Cancer Treatment Center for their collaboration. We are extremely grateful to all patients for their participation and cooperation.
Funding
This work was supported by Hassan II University of Casablanca.
Availability of data and material
Data and material request may be sent to the corresponding author.
Authors’ contributions
AT and YK performed the analysis and drafted the manuscript. BD and AT carried out statistical analysis. HJ and AT contributed to patients recruitment and data acquisition. HD participated in controls recruitment. HJ, AB and SN participated in the conception of the study and supervised the work. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects and the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine of Casablanca.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Tazzite, A., Kassogue, Y., Diakité, B. et al. Association between ABCB1 C3435T polymorphism and breast cancer risk: a Moroccan case-control study and meta-analysis. BMC Genet 17, 126 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0434-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-016-0434-x