Abstract
Background
Previous studies of gene amplification in Escherichia coli have suggested that it occurs in two steps: duplication and expansion. Expansion is thought to result from homologous recombination between the repeated segments created by duplication. To explore the mechanism of expansion, a 7 kbp duplication in the chromosome containing a leaky mutant version of the lac operon was constructed, and its expansion into an amplified array was studied.
Results
Under selection for lac function, colonies bearing multiple copies of the mutant lac operon appeared at a constant rate of approximately 4 to 5 per million cells plated per day, on days two through seven after plating. Expansion was not seen in a recA strain; null mutations in recBCD and ruvC reduced the rate 100- and 10-fold, respectively; a ruvC recG double mutant reduced the rate 1000-fold. Expansion occurred at an increased rate in cells lacking dam, polA, rnhA, or uvrD functions. Null mutations of various other cellular recombination, repair, and stress response genes had little effect upon expansion. The red recombination genes of phage lambda could substitute for recBCD in mediating expansion. In the red-substituted cells, expansion was only partially dependent upon recA function.
Conclusion
These observations are consistent with the idea that the expansion step of gene amplification is closely related, mechanistically, to interchromosomal homologous recombination events. They additionally provide support for recently described models of RecA-independent Red-mediated recombination at replication forks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Expression of a chromosomal gene in Escherichia coli can be elevated by gene amplification. The mechanism of this amplification is thought to consist of two steps, duplication and expansion. Duplication is rare, largely recA-independent, and occurs between microhomologies in the chromosome as a replication accident. Expansion is frequent, recA-dependent, and thought to result from unequal crossing-over events between the duplicated segments [1–3].
Recent investigations of gene amplification in E. coli have focused on amplification of plasmid-borne genes. A phenotypically leaky F'-borne mutation, ϕ(lacIX13-lacZ), gives rise to Lac+ revertants bearing amplified arrays of 40–80 copies of the lac region [4]. Lac+ revertants of F'lac bearing the +1 frameshift allele ϕ(lacI33-lacZ), extensively employed in studies of adaptive mutation, consist mainly of one-base deletions in runs of iterated bases [5, 6], but clones bearing amplified arrays appear at a lower rate as well [7, 8]. Properties of lac amplification have generally supported the duplication-expansion model. (i) An engineered duplication of the frameshift mutant lac locus amplifies at a greatly elevated frequency [9], as predicted by the idea that duplication is the rate-limiting step (and as had been seen in the case of chromosomal ampC [2]). (ii) Amplification is dependent upon recBCD and ruvABC, as well as recA, indicating an important role for homologous recombination [10].
Expansion of a pre-existing repeat has also been studied primarily on plasmids. In one study, a pBR322 derivative was constructed with two directly repeated tetA genes, each bearing an inactivating mutation, but arranged in such a way that a single unequal crossover would generate an array of three copies, one of which was a functioning gene. In this system, expansion was reduced only five-fold in a recA mutant; expansion was elevated in strains bearing mutations in dnaQ, dnaE, dnaB, or dnaN [11].
Expansion of a pre-existing duplication was compared with amplification of a single copy of F'-borne ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) in another study [10]. Expansion was found to be increased in a polA mutant, and unaffected by overexpression of xonA, while amplification from a single copy was inhibited by both of these conditions. It was concluded that the amplification defects caused by the polA mutant and by xonA overproduction were in duplication, not expansion.
This study was undertaken to characterize expansion of a repeated sequence in the bacterial chromosome. A duplication of chromosomal ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) was constructed (Fig. 1). As expected, it expands at a high rate under selection for function. The effects of mutations in various recombination, replication, DNA repair, and stress response genes on expansion of the duplication were tested. The findings support the idea that expansion occurs via homologous recombination, and suggest as well that many of the recombination events leading to expansion take place at replication forks.
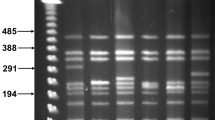
Expansion of a chromosomal duplication. A. Chromosomal (lacI33-lacZ)-lacY [38] was duplicated by phage λ Red-mediated recombination with a linear DNA bearing homology-flanked antibiotic resistance marker Ab. A hypothetical mechanism by which the duplication could be generated, involving crossovers between the linear DNA and both copies of the replicating chromosomal target, is diagrammed [9]. The duplication was constructed with a tetracycline resistance element, which was later replaced with cat. Under selection for Lac function, the (lacIZ33Y)2-cat duplication expands into multiple copies. L and R – chromosomal sequences flanking lac. E – EcoR1 restriction sites. B. Multiple copies of the repeated sequence are seen as bands produced by EcoR1 digestion of cellular DNA. Tests of two Lac+ revertants, one without (-), and one with (+) an expanded lac array, are shown as examples.
Results
An E. coli strain bearing a chromosomal duplication of the leaky ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) allele, when plated on minimal medium containing lactose as the only available carbon source, gives rise to approximately 1000-fold more colonies, over the course of a week, than an otherwise isogenic strain bearing a single copy. As shown in Fig. 2, the colonies start appearing two days after plating, and accumulate at an average rate of approximately 4–5 per million viable duplication-bearing cells plated per day, two to seven days after plating. Daily colony counts vary widely between independent cultures, as well as day-to-day on the same plate. This variation is considerably greater than that observed in experiments with single copy F'-borne ϕ(lacI33-lacZ), in which the appearance of colonies after day two fits a Poisson distribution, implying that the mutations occurred after plating [12]. In contrast, the variation in colony counts seen in experiments with the chromosomal duplication strain indicate that most of the variation between cultures exists prior to plating (unpublished data). This observation is consistent with the hypothesis that each culture contains copy number variants which arise during growth, and that the probability of colony formation varies with copy number at the time of plating. Despite this variability, if 12 or more independent cultures are plated, and daily colony counts are averaged, the rate of accumulation is seen to be nearly constant, as reflected in the close fit of the data points to a straight line.
Kinetics of Lac+ colony formation. Cultures of TP1004, an MG1655 derivative bearing the (lacIZ33Y)2-cat duplication, were plated on lactose minimal agar. Data points represent mean daily colony counts from 19 independent cultures. Error bars represent 1 standard deviation. A least-squares linear regression curve is shown; its slope is 4.71 colonies per million viable chloramphenicol-resistant cells plated per day.
The Lac+ colonies appearing in these experiments can arise either by expansion or by mutation. A strain bearing even a single chromosomal copy of the un-frameshifted lacI-lacZ fusion grows well on lactose minimal medium. However, most or all of the excess Lac+ colonies produced by the duplication-bearing strain contain expanded arrays of the structure diagrammed in Fig. 1. The amplified sequences in these clones are readily visualized as specific bands in restriction enzyme digests of total cellular DNA [4]. In tests of 28 Lac+ revertants from 22 cultures bearing the duplication, including four colonies which appeared on day two, all had expanded; none of 10 single-copy revertants contained amplified arrays (Table 1). Quantitation of total DNA, and DNA in the amplified bands, as described in the methods section, from 10 Lac+ clones, indicated a mean lac copy number of 72, with a standard deviation of 17. Expansion of this magnitude would be expected to result in β-galactosidase production comparable to a single-copy un-frameshifted gene, as the frameshift mutation reduces β-galactosidase production 100-fold [12]. The modest variability of lac copy number in the Lac+ clones presumably reflects a sort of optimum or equilibrium, in which the benefit of more β-galactosidase is balanced by the cost of extra DNA in the chromosome (70 copies of the repeat make the chromosome roughly 10% larger). Cultures of the expanded-array variants contain unknown numbers of point-revertant lac genes. Under continued selection for lac function, it is possible that the population would eventually be taken over by revertants which, bearing a single good copy of lac, have the benefit of sufficient β-galactosidase without the cost of more DNA. However, it is likely that such a changeover would take many generations because the Lac+ revertant has, if anything, only a small selective advantage – it does not have a noticeably faster growth rate on lactose minimal medium, for example. Hastings et al. [8] tested this idea, and found that amplified ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) clones kept under selection for lac function do not form revertants readily.
The clones appearing as Lac+ colonies acquire their ability to grow on lactose while under selection. Colonies re-streaked on lactose minimal plates form colonies visible to the unaided eye in 24 hours or less, regardless of whether they were picked on day 2 or day 7. Reversion and amplification of F'-borne ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) are adaptive, in that they occur only in the presence of lactose, not when the bacteria are simply starved [8, 13]. The leakiness of the mutant allele is critical for adaptive mutation: residual lactose metabolism is enough to power the replication/recombination/repair processes involved, though not enough for cell division [12]. The experiment graphed in Fig. 3 shows that expansion of a chromosomal ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) is similarly adaptive. Cultures were plated on minimal medium containing no available carbon source. Lactose was added after two or four days by injection under the agar slab. There was no sudden burst of colonies appearing two or three days later, as would be expected if expanded lac arrays had accumulated during starvation. Rather, the kinetics of appearance of Lac+ colonies resembled that seen in the cells initially plated on lactose, with a delay of either two or four days, and at declining rates, suggesting that the starving cells gradually lost their potential to expand.
Adaptive nature of the expansion. Cultures of TP1004, an MG1655 derivative bearing the (lacIZ33Y)2-cat duplication, were plated on minimal agar in which lactose was made available as the only available carbon source, either at the time of plating (circles), or after two (triangles) or four (squares) days of incubation. Data points represent mean daily colony counts from 12 independent cultures. Error bars are omitted for clarity; as in Fig. 2, the standard deviations are comparable in magnitude to the means.
Strains combining the duplication with mutations in DNA transaction genes were tested for Lac+ colony formation (Fig. 4). A null mutation in recA reduced the rate nearly 1000-fold, nearly down to that of a strain bearing a single copy of ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) (labeled "sc" near the bottom of Fig. 4). The recA mutation had no significant effect in the single copy background. The strong recA dependence of expansion in this experiment contrasts with the weak recA dependence seen in a previous study of expansion of a plasmid-borne duplication [11], but is not surprising, for two reasons: (i) The duplicated segment in this study was much larger, and recA dependence tends to increase with increasing homology lengths [14, 15]. (ii) The assay employed in the previous study required only a single recombination event, whereas becoming strongly Lac+ by expansion of a chromosomal ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) duplication probably involves more than one recombination event.
Roles of replication, repair, and recombination functions in expansion. Multiple independent cultures of the indicated genotype were plated on lactose minimal medium. Strains are all MG1655 derivatives. All except the ones labeled "sc" (for single copy) bear the the (lacIZ33Y)2-cat duplication. Strains labeled "red+" bear the phage λ red recombination genes, which replace the recC-ptr-recB-recD gene cluster in the E. coli chromosome. Except for the red substitution, the lexA alleles, and the recAo281 operator mutation, all the alleles are nulls made by substituting an antibiotic resistance element for the coding sequence of the gene.
Null mutations in recBCD and ruvC reduced Lac+ colony formation 100-fold and 10-fold, respectively. Other mutations eliminating single recombination functions, recF, recG, recN, recQ, recR, and ruvAB, had little overall effect. A ruvC recG double mutant was also tested. Like the recA mutation, and as in other homologous recombination events [16], it generated Lac+ colonies approximately 1000-fold less efficiently than wild type.
A disruption of the E. coli yfgL gene was reported to confer a strong recombination/repair deficiency phenotype [17]. As shown in Fig. 4, however, a yfgL null mutation constructed for this study has little or no effect on expansion. It also confers no UV-sensitivity or transductional recombination phenotype, in either an MG1655 or an AB1157 strain background (not shown); others have found no recombination/repair phenotype associated with a yfgL null as well [18].
To test the hypothesis that the deficiencies of recA, recBCD, ruvC, and ruvC recG mutants in Lac+ colony formation are due to their inability to expand the duplication, two alternative explanations were considered and ruled out. (i) Lac+ revertants of these mutants could grow much more slowly than Lac+ revertants of wild type. Lac+ colonies were restreaked on minimal lactose plates on the days they arose. In the cases of wild type, recA, recBCD, and ruvC, all of the Lac+ clones formed colonies visible to the unaided eye by 24 hours after restreaking, independent of the day on which they arose. In the case of the ruvC recG double mutant, none of the 8 tested Lac+ revertants formed visible colonies by 24 hours, but all did so by 48 hours. However, counting the ruvC recG colonies after 8 days instead of 7 only increased the median from 0.029 to 0.056 colonies per million viable cells plated (data not shown). Thus, slow growth of revertants can account for only a small part of the deficiencies of the recombination mutants in forming Lac+ colonies. (ii) The mutants could be proficient at expansion, but deficient at survival on the selection plates. Survival of the mutants on lactose minimal medium was tested as described in the methods section. The results (Table 1) indicate that none of the mutants has a substantial survival defect relative to wild type.
The Lac+ revertants of the deficient mutants consist of varying populations of expanded and mutated clones (Table 1). In the case of recA, none of 10 tested clones had an expanded lac array. The frequency of expanded arrays among recBCD revertants was 9 out of 10; ruvC was 10 out of 10, recG was 18 out of 18, and ruvC recG was 6 out of 14.
The Lac+ reversion phenotype of a recG null mutant is more complex than the data in Fig. 4 suggest. The mutant strain's rate of colony formation tends to increase sharply late in the experiment, with the new colonies tending to appear as satellites of older colonies (not shown). Factors influencing the timing and extent of this satellite-based population explosion include plating density, but are otherwise unknown. The recG mutant data shown in Fig. 4 are from selected experiments, in which the plating density was low, and satellitism was not as strongly evident as in other experiments. Satellitism of this sort suggests that something produced by the older colonies on the plate stimulates recombination, perhaps via a genotoxic effect. It is consistent with the finding that overexpression of recG protects E. coli against weak organic acids [19].
The effects on expansion of varying RecA activity were tested by plating mutants affecting recA expression. The uninducible lexA3 mutation has been reported to reduce the frequency of a number of different homologous recombination events [20]; it also reduced Lac+ colony formation approximately five-fold. The SOS-constitutive lexA71::Tn5 mutation (in a sulA null background, to suppress its lethality) had no significant effect; neither did the recAo281 operator constitutive allele.
A number of replication genes were tested for roles in expansion. A null mutation in polA increased the rate of expansion 5-fold; null mutations in the other non-essential DNA polymerase-encoding genes polB, dinB, and umuDC, had little or no effect. Loss of the replication restart function priA caused a small decrease in expansion efficiency, while loss of rnhA caused a nearly 7-fold increase.
A strain lacking dam function exhibited a 35-fold elevated rate of Lac+ colony formation. Apparently, part of this elevated rate is due to the double-strand breaks which occur as the result of mis-directed mismatch repair in dam mutants [21, 22]. As shown in Fig. 4, a dam mutH double mutant exhibited an intermediate rate between those of wild type and the dam single mutant. The mutH null allele by itself had little or no effect.
Other DNA repair functions were tested for effects on expansion as well. A uvrD null mutant formed Lac+ colonies at a 10-fold elevated rate, while mutM, mutY, a mutM mutY double, and an ada null mutation had no significant effects.
The question of whether expansion of a chromosomal repeat occurs as part of a stress response, like amplification starting from a single episomal copy [23], was explored by testing null mutations in rpoS and relA. As shown in Fig. 4, these mutations had little or no effect on Lac+ colony formation.
Expansion mediated by the Red recombination system of phage λ was studied in a series of strains in which the phage red genes replace the recC-ptr-recB-recD gene cluster in the E. coli chromosome (designated "red+" in Fig. 4). Replacing RecBCD with Red has no effect on the rate of Lac+ colony formation, but it changes the extent to which expansion is dependent upon other recombination functions. In the red-substituted background, a recA null mutation reduces Lac+ colony formation only 35-fold. Among the recA revertants, 8 of 10 that were tested contained expanded lac arrays (Table 1), showing that Red, unlike RecBCD, can promote expansion in the absence of RecA. Red-mediated expansion is reduced by a recF null mutation, and elevated slightly by a recG null; these mutant effects are seen in Red-mediated gene replacement events as well [24]. The rnhA null mutation has a stronger effect in the red-substituted background than in wild type, elevating the rate of expansion 45-fold.
Discussion and conclusion
The genetic requirements of homologous recombination in E. coli vary with the particular event examined, but some features of chromosomal events are nearly general: dependence on recA and recBCD, and mild or no dependence upon a variety of other recombination functions whose roles are revealed mainly in the absence of recBCD function [14]. Expansion by duplicated chromosomal ϕ(lacI33-lacZ) fits this general pattern. Similarly, mutations with known hyper-rec phenotypes – polA, dam, uvrD, and rnhA [20, 25, 26] – also cause an elevated rate of expansion. These observations support the idea that expansion is best understood as a homologous recombination event or series of events.
The Red recombination system of phage λ promotes RecA-independent recombination between chromosomes if at least one of the chromosomes is replicating, and RecA-dependent recombination between non-replicating chromosomes [27–30]. The RecA-independent expansion seen in red-substituted bacteria suggests that at least some of the Red-mediated recombination events involved in expansion take place at replication forks [30, 31].
The involvement of replication in recombination events leading to expansion is additionally suggested by the increased rates of expansion of the rnhA and dam mutants. Replication in both these mutants escapes cell cycle regulation. In an rnhA mutant, unsynchronized DNA replication initiates at multiple sites in the chromosome [32]. In a dam mutant, initiation is confined to oriC but is not regulated [33]. Elevated recombination frequencies in both of these mutants may be due, at least in part, to an increased occurrence of double strand breaks. Both exhibit greatly reduced viability in the absence of RecBCD function, possibly because RecBCD is needed to repair the excess double strand breaks [34, 35]. Eliminating the mismatch repair endonuclease MutH in a dam mutant prevents the double strand breaks which result from mis-directed mismatch repair, but does not bring expansion down to the wild type level; unregulated replication itself is a possible cause of the residual excess expansion in the dam mutH double mutant. The mechanism by which improperly regulated replication forks provoke more recombination events than normally regulated replication forks is unknown, but there are a number of possible explanations. They might be more prone to breaking down or to running into each other, or just more numerous in the cell.
Methods
Duplication of ϕ(lacI33-lacZ)-lacY
Plasmid pTP1029 [36] is a vector containing the tetRA genes from Tn10 and the pir-dependent replication origin R6Korigamma. pTP1060 was made by ligating a synthetic DNA made from two oligodeoxyribonucleotides, GATCCAGGTTCTTTGAGCTCTTTGGCGGCCGC and GATCGCGGCCGCCAAAGAGCTCAAAGAACCTG, into the Bam HI site of pTP1029. pTP1016 [36] contains E. coli sequences which normally flank the lacI and lacY genes; in the plasmid, they flank the cat gene. pTP1027 [36] and pTP1049 [37] contain the same flank sequences as pTP1016, with wild type lacIZY and ϕ(lacI33-lacZ)-lacY, respectively, between them. pTP1061 was made by ligating the cat-with-lac-flanks cassette of pTP1016 into the NotI site of pTP1060. A strain bearing a duplication of the chromosomal segment containing ϕ(lacI33-lacZ)-lacY was constructed by electroporating strain TP890 with Bsr G1- and Sph 1-digested plasmid pTP1061, and selecting for tetracycline resistance (see Fig. 1). The tet-origamma insert between the duplicated lac copies was replaced by cat via recombination with a linear DNA generated by PCR with a Tn9-containing strain as template, and primers GATCCCGCGGAATAACATCATTTGGTGACGAAATAACTAAATGAGACGTTGATCGGCACG and CCACGATGCGTCCGGCGTAGAGGATCTGAAGATCAGCAGTATTCAGGCGTAGCACCAGGC. The presence of duplicated segments in bacterial chromosomes was verified by the use of PCR with divergent primers, as described [36]. Other strain construction details are given in Tables 2 and 3.
Plating methods
Strains to be tested for reversion to Lac+ were grown to saturation in M9 0.1% glycerol minimal medium at 37°C, and plated on M9 0.1% lactose plates at 37°C. M9 minimal media, supplemented with thiamine at 5 μg/ml, were as described [7]. In most cases, viable duplication-positive titers were determined by plating on LB agar supplemented with chloramphenicol at 10 μg/ml, which permits colony formation only by bacteria retaining the cat gene between the duplicated segments. Strains with poor viability in rich media (ruvC recG, polA, priA) were titered on M9 glucose plates; retention of the duplication in these cases was assessed by testing the chloramphenicol resistance of individual colonies from the titer plates. Lactose minimal plates were inoculated with 1–2 × 109 cells, either of the strain to be tested by itself, or, in most cases, of the strain to be tested plus a non-reverting, lac deletion-bearing scavenger strain [13]. The rates of appearance of Lac+ colonies shown in Figures 2, 3, and 4 are calculated as Lac+ colonies per million chloramphenicol-resistant viable cells plated (or per million viable cells, in the cases of the single copy strains).
Expansion test
Revertant colonies appearing on the M9 lactose plates were streaked on M9 lactose plates, which were incubated at 37°C until visible colonies formed. Heavy inocula constituting the bulk of the growth from the streaks were then scraped from the plate and grown to saturation in 5 ml M9 0.1% lactose minimal medium at 37°C. (Some of the revertant colonies tested, in the wild type background only, were inoculated directly from the selection plates into liquid lactose minimal medium; but all revertants in the wild type background tested positive for expanded arrays, regardless of the variation in culture methods). DNA was extracted by the use of a procedure involving freezing and thawing, lysozyme digestion, extraction with a phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol mixture, extraction with ether, and precipitation with ethanol [30]. Portions were digested with EcoR1 and RNase, and subjected to electrophoresis in an agarose gel, followed by ethidium bromide staining. For quantitation of the repeat-specific bands, standards consisting of HindIII-digested phage lambda DNA of known concentration were included in the gel, in separate lanes. Total DNA in the sample was quantitated by spotting RNase-treated samples on an agarose slab containing ethidium bromide at 1 μg/ml, along with standards of known concentration. Band and spot intensities were measured by the use of digital photography and Kodak 1D software.
Survival test
Mutations to be tested for their effects on survival on lactose minimal medium were crossed into a strain bearing a deletion of the lac operon. Cultures were grown to saturation in M9 0.1% glycerol as in the Lac+ reversion test, and deposited on the surfaces of 0.6 ml M9 lactose agar plugs at the bottom of 12 × 75 mm plastic tubes, at approximately the same plating density (relative to volume of medium) as the bacteria in the Lac+ reversion test. The tubes were incubated at 37°C. Cells were suspended by vortexing in 2 ml of buffer, and titered on M9 glucose plates, on days 0 and 7. The ratio of titer on day 7 to titer on day 0 for the wild type control was 0.83 ± 0.12 (mean ± standard error from six measurements).
Abbreviations
- Kbp:
-
kilobasepair.
References
Edlund T, Normark S: Recombination between short DNA homologies causes tandem duplication. Nature. 1981, 292: 269-271. 10.1038/292269a0
Edlund T, Grundstrom T, Bjork GR, Normark S: Tandem duplication induced by an unusual ampA1-, ampC-transducing lambda phage: a probe to initiate gene amplification. Mol Gen Genetics. 1980, 180: 249-257. 10.1007/BF00425836.
Andersson RP, Roth JR: Tandem genetic duplication in phage and bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977, 31: 473-505. 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.002353
Tlsty TD, Albertini AM, Miller JH: Gene amplification in the lac region of E. coli. Cell. 1984, 37: 217-224. 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90317-9
Rosenberg SM, Longerich S, Gee P, Harris RS: Adaptive mutation by deletions in small mononucleotide repeats. Science. 1994, 265: 405-407. 10.1126/science.8023163
Foster PL, Trimarchi JM: Adaptive reversion of a frameshift mutation in Escherichia coli by simple base deletions in homopolymeric runs. Science. 1994, 265: 407-409. 10.1126/science.8023164
Foster PL: Population dynamics of a Lac- strain of Escherichia coli during selection for lactose utilization. Genetics. 1994, 138: 253-261.
Hastings PJ, Bull HJ, Klump JR, Rosenberg SM: Adaptive amplification: an inducible chromosomal instability mechanism. Cell. 2000, 103: 723-731. 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00176-8
Slechta ES, Bunny KL, Kugelberg E, Kofoid E, Andersson DI, Roth JR: Adaptive mutation: general mutagenesis is not a programmed response to stress but results from rare coamplification of dinB with lac. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003, 100: 12847-12852. 10.1073/pnas.1735464100
Slack A, Thornton PC, Magner DB, Rosenberg SM, Hastings PJ: On the mechanism of gene amplification induced under stress in Escherichia coli. PLOS Genetics. 2006, 2: e48- 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020048
Morag AS, Saveson CJ, Lovett ST: Expansion of DNA repeats in Escherichia coli : effects of recombination and replication functions. J Mol Biol. 1999, 289: 21-27. 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2763
Foster PL: Adaptive mutation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2004, 186: 4846-4852. 10.1128/JB.186.15.4846-4852.2004
Cairns J, Foster PL: Adaptive reversion of a frameshift mutation in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1991, 128: 695-701.
Lloyd RG, Low KB: Homologous recombination. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology. Edited by: Neidhardt FC. 1996, 2236-2255. ASM Press, 2
Dutra BE, Sutera VA, Lovett ST: RecA-independent recombination is efficient but limited by exonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007, 104: 216-221. 10.1073/pnas.0608293104
Lloyd RG: Conjugational recombination in resolvase-deficient ruvC mutants of Escherichia coli K-12 depends on recG. J Bacteriol. 1991, 173: 5414-5418.
Khairnar NP, Kamble VA, Mangoli SH, Apte SK, Misra HS: Involvement of a periplasmic protein kinase in DNA strand break repair and homologous recombination in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 2007, 65: 294-304. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05779.x
Vuong P, Bennion D, Mantei J, Frost D, Misra R: Analysis of YfgL and YaeT interactions through bioinformatics, mutagenesis, and biochemistry. J Bacteriol. 2008, 190: 1507-1517. 10.1128/JB.01477-07
Steiner P, Sauer U: Overexpression of the ATP-dependent helicase RecG improves resistance to weak organic acids in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2003, 63: 293-299. 10.1007/s00253-003-1405-5
Zieg J, Maples VR, Kushner SR: Recombination levels of Escherichia coli K-12 mutants deficient in various replication, recombination, or repair genes. J Bacteriol. 1978, 134: 958-966.
Wang TV, Smith KC: Inviability of dam recB cells of Escherichia coli is correlated with their inability to repair DNA double-strand breaks produced by mismatch repair. J Bacteriol. 1986, 165: 1023-1025.
Nowosielska A, Marinus MG: Cisplatin induces DNA double-strand break formation in Escherichia coli dam mutants. DNA Repair. 2005, 7: 773-781. 10.1016/j.dnarep.2005.03.006.
Lombardo M, Aponyi I, Rosenberg SM: General stress response regulator RpoS in adaptive mutation and amplification in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 2004, 166: 669-680. 10.1534/genetics.166.2.669
Poteete AR, Fenton AC: Genetic requirements of phage λ Red-mediated gene replacement in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 2000, 182: 2336-2340. 10.1128/JB.182.8.2336-2340.2000
Konrad EB: Method for the isolation of Escherichia coli mutants with enhanced recombination between chromosomal duplications. J Bacteriol. 1977, 130: 167-172.
Blakely GW, Murray NE: Control of the endonuclease activity of type I restriction-modification systems is required to maintain chromosome integrity following homologous recombination. Mol Microbiol. 2006, 60: 883-893. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05144.x
Stahl FW, McMilin KD, Stahl MM, Craseman JM, Lam S: The distribution of crossovers along unreplicated lambda bacteriophage chromosomes. Genetics. 1974, 77: 395-408.
Stahl FW, McMilin KD, Stahl MM, Nozu Y: An enhancing role for DNA synthesis in formation of bacteriophage λ recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1972, 69: 3598-3601. 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3598
Stahl MM, Thomason L, Poteete AR, Tarkowski T, Kuzminov A, Stahl FW: Annealing vs. invasion in phage λ recombination. Genetics. 1997, 147: 961-977.
Poteete AR: Involvement of DNA replication in phage lambda Red-mediated homologous recombination. Mol Microbiol. 2008, 68: 66-74. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06133.x
Court DL, Sawitzke JA, Thomason LC: Genetic engineering using homologous recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 2002, 36: 361-388. 10.1146/annurev.genet.36.061102.093104
deMassy B, Fayet O, Kogoma T: Multiple origin usage for DNA replication in sdrA (rnhA) mutants of Escherichia coli K-12: initiation in the absence of oriC. J Mol Biol. 1984, 178: 227-236. 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90141-4
Boye E, Løbner-Olesen A: The role of dam methyltransferase in the control of DNA replication in E. coli. Cell. 1990, 62: 981-989. 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90272-G
Kogoma T, Hong X, Caldwell GW, Barnard KG, Asai T: Requirement of homologous recombination functions for viability of the Escherichis coli cell that lacks RNase HI and exonuclease V activities. Biochimie. 1993, 75: 89-99. 10.1016/0300-9084(93)90029-R
Marinus MG, Morris NR: Biological function for 6-methyladenine residues in the DNA of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1974, 85: 309-322. 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90366-0
Poteete AR, Fenton AC, Nadkarni A: Chromosomal duplications and cointegrates generated by the bacteriophage lambda Red system in Escherichia coli K-12. BMC Molecular Biology. 2004, 5: 22- 10.1186/1471-2199-5-22
Stumpf JD, Poteete AR, Foster PL: Amplification of lac cannot account for adaptive mutation to Lac+ in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 2007, 189 (6): 2291-2299. 10.1128/JB.01706-06
Rosche WA, Foster PL: The role of transient hypermutators in adaptive mutation in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999, 96: 6862-6867. 10.1073/pnas.96.12.6862
Baba T, Ara T, Hasegawa M, Takai Y, Okumura Y, Baba M, Datsenko KA, Tomita M, Wanner BL, Mori H: Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: the Keio collection. Mol Syst Biol. 2006, 2: 2006.0008- 10.1038/msb4100050
Murphy KC, Campellone KG, Poteete AR: PCR-mediated gene replacement in Escherichia coli. Gene. 2000, 246: 321-330. 10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00071-8
Poteete AR, Fenton AC, Murphy KC: Roles of RuvC and RecG in phage λ Red-mediated recombination. J Bacteriol. 1999, 181: 5402-5408.
Poteete AR, Fenton AC, Wang HR: Recombination-promoting activity of the bacteriophage λ Rap Protein in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 2002, 184: 4626-4629. 10.1128/JB.184.16.4626-4629.2002
Poteete AR: Modulation of DNA repair and recombination by the bacteriophage λ Orf function in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 2004, 186: 2699-2707. 10.1128/JB.186.9.2699-2707.2004
Poteete AR, Rosadini C, Pierre CS: Gentamicin and other cassettes for chromosomal gene replacement in Escherichia coli. Biotechniques. 2006, 41 (3): 261-263. 10.2144/000112242
Murphy KC, Campellone KG: Lambda Red-mediated recombinogenic engineering of enterohemorrhagic and enteropathogenic E. coli. BMC Molecular Biology. 2003, 4: 11- 10.1186/1471-2199-4-11
Uhlin BE, Volkert MR, Clark AJ, Sancar A, Rupp WD: Nucleotide sequence of a recA operator mutation. Mol Gen Genet. 1982, 185: 251-254. 10.1007/BF00330794
Acknowledgements
I thank Patricia Foster, Michael Volkert, Martin Marinus, and Susan Lovett for helpful discussions; Michael Volkert and Martin Marinus for strains; and Rosemary Proff, Dery Miller, Shilpa Nadimpalli, Bach Nguyen, Juliet Zhang, Aiden Galarza, and Matthew Lim for technical assistance. This research was supported by US National Science Foundation grant MCB-0234991, and by a grant from the University of Massachusetts Healey Endowment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Authors’ original submitted files for images
Below are the links to the authors’ original submitted files for images.
Rights and permissions
This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Poteete, A.R. Expansion of a chromosomal repeat in Escherichia coli: roles of replication, repair, and recombination functions. BMC Molecular Biol 10, 14 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-14
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-14