Abstract
This study extends a previous research concerning intervertebral motion registration by means of 2D dynamic fluoroscopy to obtain a more comprehensive 3D description of vertebral kinematics. The problem of estimating the 3D rigid pose of a CT volume of a vertebra from its 2D X-ray fluoroscopy projection is addressed. 2D-3D registration is obtained maximising a measure of similarity between Digitally Reconstructed Radiographs (obtained from the CT volume) and real fluoroscopic projection. X-ray energy correction was performed. To assess the method a calibration model was realised a sheep dry vertebra was rigidly fixed to a frame of reference including metallic markers. Accurate measurement of 3D orientation was obtained via single-camera calibration of the markers and held as true 3D vertebra position; then, vertebra 3D pose was estimated and results compared. Error analysis revealed accuracy of the order of 0.1 degree for the rotation angles of about 1 mm for displacements parallel to the fluoroscopic plane, and of order of 10 mm for the orthogonal displacement.
Similar content being viewed by others
1. Introduction
Intervertebral kinematics closely relates to the functionality of spinal segments and can provide useful diagnostic information. Direct measurement of the intervertebral kinematics in vivo is very problematic due to its intrinsic inaccessibility. The use of a fluoroscopic device can provide a continuous 2D screening of a specific spinal tract (e.g., cervical, lumbar) during spontaneous motion of the patient, with an acceptable, low X-ray dose. 2D kinematics can be extrapolated from fluoroscopic sequences. Most of the previous works [1–8] were confined to the estimation of planar motion (most on sagittal plane) and are based on the assumption of absence of out-of-plane coupled motion (e.g., axial rotation). Coupled motion can be neglected in sagittal (flexion-extension) motion (mainly due to anatomic symmetry), but in lateral bending, where a coupled axial rotation is certainly present [9], this approximation is no longer valid.
The knowledge of 3D positioning (pose) of vertebrae with time can lead to full 3D kinematics analysis, or at least to evaluate the presence of out-of-plane motion (rotation). External skin markers do not provide accurate intervertebral motion description [10, 11], and invasive positioning of markers inserted in the vertebrae is not generally viable. In order to allow clinical application, 3D kinematics analysis should be performed by means of readily available, and minimally invasive, instrumentation, combined with an appropriate image processing technique.
In this study, a method for 3D pose estimation of vertebrae based on single plane-projection (e.g., Digital Video Fluoroscopy, DVF) combined with available CT-data [12–17] is proposed. By processing common CT slices it is possible to extract a 3D model of a vertebra, and by subsequent processing using ray-casting techniques it is possible to produce Digitally Reconstructed Radiographs (DRRs), simulating the 3D radiograph formation process. Comparing the DRRs with the real fluoroscopic image it is possible to estimate the real 3D orientation of the vertebra when screened by fluoroscopy (Figure 1).
General sketch of the proposed method. A 3D CT vertebra model is available (the vertebra's 3D rendering is shown at centre). A DRR can be reconstructed from any orientation and distance. DRRs can be matched with a real DVF radiographic projection using a similarity index. The DRR that maximises the similarity with the real image is searched for. This procedure provides the vertebral 3D pose estimation.
To assess the accuracy and the repeatability of the method invitro, a calibration model consisting of a sheep dry vertebra rigidly fixed to an X-raytransparent frame of reference was designed in order to independently evaluate its 3D pose by means of a single camera calibration procedure. The errors with respect to the estimate provided by the calibration procedure were evaluated.
It is anticipated that such a method will also be helpful in a number of other contexts such as Computer Assisted Surgery (CAS) [18–23], Radiotherapy Planning (RTP) and functional evaluation of implanted prosthesis [24–26].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Summary of the Methodology
In this study an in vitro assessment is performed of a method for 3D pose estimation of a vertebra with respect to a fluoroscopic imaging system, based upon the comparison between Digital Video Fluoroscopy (DVF) images and DRRs. The 3D pose estimation is a first step in a full 3D motion analysis [12, 13, 24–26].
Previous studies [4, 6, 14, 27] showed that fluoroscopy is well-suited to in vivo spine kinematics analysis because of the capability of screening patients during free motion with an acceptably low X-ray dosage and because of the wide availability of fluoroscopes in the clinical environment. However, this technique is limited to planar motion analysis and this assumption is valid only for pure flexion-extension movements. More information is needed in order to estimate 3D motion. Segmented CT volumes can provide an accurate model of a 3D vertebral shape and different X-ray attenuation of its features. Such a 3D vertebral model can be used to compute DRRs.
To estimate the 3D pose of a vertebra, the true DVF image is compared to an opportune set of differently oriented DRRs; the 3D parameters belonging to the DRR which maximise a predefined similarity index, are held as the vertebra 3D pose estimation. The similarity index employed in this study is the image zero-mean, cross-correlation coefficient. Zero-mean Normalized Cross-Correlation (ZNCC) is a widely used similarity function in template matching as well as in motion analysis. Let  be the image under examination, of size
be the image under examination, of size  by
by  pixels,
pixels,  the template, of size
the template, of size  by
by  pixels, and
pixels, and  (
( ) be the subimage of
) be the subimage of  at position (
at position ( ) having the same size as the template
) having the same size as the template  , and let 〈
, and let 〈 〉 and 〈
〉 and 〈 〉 be the computed mean of
〉 be the computed mean of  and of
and of  (
( ) respectively. The Normalized Zero-mean Normalized Cross-Correlation between the template
) respectively. The Normalized Zero-mean Normalized Cross-Correlation between the template  and the image
and the image  at position (
at position ( ) is defined as
) is defined as

The DRR that best matches the real DVF image is searched by means of an iterative, gradient-driven procedure.
In this work the in vivo accuracy and repeatability of the method was assessed using a calibration object. The results of the registrations between the DVF images and the CT volume were compared to an accurate 3D pose estimation obtained by means of fiducial markers embedded in the calibration object.
2.2. Reconstruction of Digital Radiographs
A number of techniques to compute DRRs have been proposed in the literature (see [28]. In this study, DRRs are computed from CT data using a ray-casting algorithm [29, 30]. This technique simulates the radiographic image formation process (see Figure 2).
Algorithm for the simulation of the radiographic process. X-rays are modelled as straight lines (generic X-ray beam) through matter. The radiographic DDR image plane and X-rays are sampled. X-ray attenuation values of the CT 3D model are integrated together with a generic ray in order to obtain the grey-level of the corresponding pixel of the DRR.
A few simplifications are involved: X-ray is monochromatic radiation, traversing as straight lines throughout the matter (scattering effects are neglected); x-rays source (focus) is small (ideally a point) and is positioned at a finite distance from the radiographic plane; the attenuation through the body is described by the following equation for monochromatic radiation [31]:

where  is the intensity of the X-ray radiation at the radiographic plane,
is the intensity of the X-ray radiation at the radiographic plane,  is the intensity of X-ray radiation at the source,
is the intensity of X-ray radiation at the source,  is the linear attenuation coefficient of the voxel at
is the linear attenuation coefficient of the voxel at  whose width is
whose width is  (notice that the effect of beam-hardening [32] is not considered). The relationship between CT-data (represented as Hounsfield Units, HU) and the corresponding attenuation coefficient
(notice that the effect of beam-hardening [32] is not considered). The relationship between CT-data (represented as Hounsfield Units, HU) and the corresponding attenuation coefficient  is represented by the equation [31]:
is represented by the equation [31]:

where  is approximately 0.2
is approximately 0.2  for an X-ray source at 120 kVp.
for an X-ray source at 120 kVp.
To reconstruct a radiograph, the radiographic plane (DRR image plane in Figure 2) is subdivided into a number of pixels, each pixel is ideally connected by a straight line with the X-ray source, and absorption coefficients in the CT volume are summated along this line (generic X-ray beam in Figure 2). Therefore the summation provides the brightness value of the radiographic pixel under examination. Three-linear interpolation [33] of CT data was used to estimate X-ray absorption at a generic point within the CT volume.
2.3. CT and DVF X-Rays Energy Equalisation
Typical CT scanners operate at a peak voltage of about 120 kVp. In fluoroscopy, peak voltages of 40–80 kVp are used. The energy of the X-ray photons, and therefore the  values, are influenced by the peak voltage. The energy dependency of the attenuation coefficients is highly nonlinear [32]. The energy corresponding to the peak of the spectrum has the strongest effect on the attenuation coefficients: we use this energy to perform the correction. The wavelength at the peak (
values, are influenced by the peak voltage. The energy dependency of the attenuation coefficients is highly nonlinear [32]. The energy corresponding to the peak of the spectrum has the strongest effect on the attenuation coefficients: we use this energy to perform the correction. The wavelength at the peak ( ) is approximately given by [34]:
) is approximately given by [34]:  , where
, where  is the peak voltage expressed in kVp and
is the peak voltage expressed in kVp and  is expressed in nm. The corresponding energy can be calculated using the following formula [32]:
is expressed in nm. The corresponding energy can be calculated using the following formula [32]:  , where E is expressed in keV. Before reconstruction of DRRs, CT data must be corrected by multiplication of a correction factor
, where E is expressed in keV. Before reconstruction of DRRs, CT data must be corrected by multiplication of a correction factor  , computed using the following formula:
, computed using the following formula:

where  and
and  indicate the
indicate the  of the material at DVF and at CT energy respectively; the ratio between
of the material at DVF and at CT energy respectively; the ratio between  and the
and the  (density of the material) is called the mass attenuation coefficient. Notice that the lower the peak voltage, the larger the difference between the correction factors for bone and for the other tissues. So the peak voltage is a parameter that determines the contrast between the bone and the other tissues on DVF images. Tabled mass attenuation coefficients versus x-ray energy, for several materials, can be found in Johns and Cunningham [32]; mass attenuation coefficients corresponding to the voltages of the actual devices used in this work are not reported in the table, and were therefore obtained by linear interpolation. To perform energy correction, two thresholds are fixed, in order to separate high density (compact) bone and low density (cancellous) bone within the CT volume: for each voxel whose Hounsfield Unit lies in the predefined range the corresponding correction factor is computed.
(density of the material) is called the mass attenuation coefficient. Notice that the lower the peak voltage, the larger the difference between the correction factors for bone and for the other tissues. So the peak voltage is a parameter that determines the contrast between the bone and the other tissues on DVF images. Tabled mass attenuation coefficients versus x-ray energy, for several materials, can be found in Johns and Cunningham [32]; mass attenuation coefficients corresponding to the voltages of the actual devices used in this work are not reported in the table, and were therefore obtained by linear interpolation. To perform energy correction, two thresholds are fixed, in order to separate high density (compact) bone and low density (cancellous) bone within the CT volume: for each voxel whose Hounsfield Unit lies in the predefined range the corresponding correction factor is computed.
2.4. Estimation of the 3D Pose by Maximising the Cross-Correlation Index
A rigid body in space has 6 degrees of freedom. The pose is determined by the 3D coordinates of the focus (X-ray source) and the Euler angles of the fluoroscopic image plane, which are both expressed in the frame of reference of the CT volume (see Figure 3).
Different frame of references employed in the study of the 3D pose estimation of the vertebral model. The main frame of reference (OXYZ) is related to CT slices and patient. The other frame of reference ( ) is fixed to the DVF device: where F is the X-ray focal spot,
) is fixed to the DVF device: where F is the X-ray focal spot,  and
and  axes describe the orientation of the image plane and the
axes describe the orientation of the image plane and the  axis represents the direction connecting
axis represents the direction connecting  with the radiographic image centre (focal length). Orientation of the DVF frame of reference is described by a translation vector (e.g.,
with the radiographic image centre (focal length). Orientation of the DVF frame of reference is described by a translation vector (e.g.,  in Table 1, which represent the X-ray focal spot coordinates with respect to the CT frame of reference) and the Euler angles (
in Table 1, which represent the X-ray focal spot coordinates with respect to the CT frame of reference) and the Euler angles ( rotation angles about the axes
rotation angles about the axes  and
and  ).
).
In order to estimate the 3D pose of the vertebra, a set of DRRs using different positioning is generated. The actual radiograph is compared to a set of DRRs by means of a cross-correlation index. The DRR that maximises the cross-correlation is found using a procedure that adopts an iterative step-refinement approach. In the first steps of the iterative procedure the space of the focus coordinates and of the Euler angles is sampled at a low resolution (10 mm, 5 degrees resp.). The DRRs are reconstructed using an initial resolution of approximately 2 mm/pixel; the true DVF is resampled using the same resolution to allow calculation of the cross-correlation. The time required to compute a low-resolution DRR is short and it is possible to screen a wide region of the cross-correlation function to avoid being trapped in local maxima. In the subsequent steps of the iterative procedure the sampling resolution of the space and of the Euler angles is progressively increased (5 mm, 1 mm; 1 degree, 0.1 degrees). In principle, it is possible to increase the resolution further but at high resolutions the data (CT and DVF) sampling errors become predominant. The flow-chart (Figure 4) presents the main stages of the algorithm.
CT volume of the vertebra, actual 2D fluoroscopic projection and information about CT and DVF device (e.g., DVF focal distance, pixels and voxel dimensions, X-ray KVp, etc. ) are the input data. A preliminary step to correct the CT Hounsfield numbers was performed (see the CT and DVF X-rays energy equalisation paragraph). To start the search for vertebra orientation parameters an initial range of search with a low accuracy for the 6 degrees of freedom parameters ( ) was chosen. A set of differently oriented DRR are then computed (for the DRR procedure refer to the Reconstruction of digital radiographs paragraph). Each DRR is then cross-correlated with the actual DVF image and a likelihood map (function of the 6 parameters) is generated. The maximum of the likelihood map is searched and the corresponding 6 parameters are considered the current best estimate of vertebra pose and orientation. The process is iterated, by refining the range of search and by increasing the accuracy of the parameters, until a desired accuracy is reached. Since the DRR algorithm is particularly time consuming, the multiscale approach (increasing accuracy) and the gradient-driven maximum search helps to reduce the total computation time.
) was chosen. A set of differently oriented DRR are then computed (for the DRR procedure refer to the Reconstruction of digital radiographs paragraph). Each DRR is then cross-correlated with the actual DVF image and a likelihood map (function of the 6 parameters) is generated. The maximum of the likelihood map is searched and the corresponding 6 parameters are considered the current best estimate of vertebra pose and orientation. The process is iterated, by refining the range of search and by increasing the accuracy of the parameters, until a desired accuracy is reached. Since the DRR algorithm is particularly time consuming, the multiscale approach (increasing accuracy) and the gradient-driven maximum search helps to reduce the total computation time.
2.5. The Calibration Model
In a previous study the feasibility of the method was evaluated by means of a computer simulation [35, 36]. In this work, in order to perform an in vitro assessment of the method, a calibration model was designed. It was realised with a dried sheep vertebra fixed to a radiographically transparent block (72 by 40 by 34 mm in Perspex) in which eight fiducial markers (3 mm diameter metallic spheres) were inserted (see Figure 5). Fiducial markers were used to perform an accurate 3D pose estimation of the calibration object, these results were held as reference. CT data and DVF images of the calibration model were acquired.
CT data were acquired by means of a spiral CT scanner (GE 16-slice) set to 120 kVp, 100 mAs with an image resolution 0.5 mm/pixel, 0.75 mm slice thickness. The DVF image was acquired by means of a 9 inch, digital video-fluoroscopy system(GE Advantx) set to 50 kVp, 1 mAs with an image resolution of 0.3 mm/pixel. An accurate estimate of the 3D pose of the calibration model with respect to the fluoroscopic system was obtained with a single camera calibration procedure, using the eight fiducial markers [37, 38].
An intensity-weighted method was used to find the coordinates of the centroid of the fiducial markers both in the CT scan and in the DVF image [39, 40]. The markers were previously segmented using a threshold-based algorithm. For each marker the 2D coordinates of the centroid of its projection on the DVF image were measured. The centroid was calculated as the intensity-weighted average of the coordinates of the pixels belonging to the marker. Measurement error was estimated by repeating measures using various thresholds. In the CT data each marker occupied three-to-four slices. The 3D coordinates of a marker centroid were measured as an intensity-weighted average of the pixel coordinates on each slice in which the marker was visible. In order to evaluate the precision of the single camera calibration, a Monte Carlo simulation was performed adding random noise (standard deviation equal to estimated noise on measured markers of 2 mm) to measured marker coordinates and recalculating the 3D pose of the model.
3. Results
Table 1 presents an example of the 3D pose parameters of the calibration model, independently estimated by means of the single camera, Monte Carlo simulation, calibration procedure using the radiographically transparent frame. The mean values resemble the positioning of the DVF frame of reference with respect to the CT as shown in Figure 3. These results were used as a reference from which to compute the final errors in estimated pose parameters. As example, Figure 6 shows a real DVF of the calibration object beside its correspondent DRR obtained by the CT 3D vertebra model.
To evaluate the accuracy and the precision of the method for 3D pose estimation, presented in the previous section, a set of trials was carefully designed.
It is assumed that an accurate simulation of the radiographic process should produce the best results in 3D pose estimation. However, the more accurate the simulation process, the larger is the computing time required. With this in mind, 4 cases were considered in order to evaluate the influence of the simulation process on the accuracy and precision of 3D pose estimation.
Preprocessing of CT data (segmentation and X-ray energy correction) was performed in the Matlab environment. To speed up DRR computation, all the software required was developed in C++.
In order to evaluate the influence of these various factors, the 4 trials were performed:
-
(a)
using CT data with no corrections at all;
-
(b)
performing only exponential correction in (1) but not the
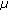 correction;
correction; -
(c)
performing only attenuation coefficient
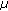 correction (energy) of CT data;
correction (energy) of CT data; -
(d)
performing both corrections.
For each trial, 70 registrations were accomplished within a total of 280 registrations. Errors with respect to the "true pose" registration (obtained via the metallic marker camera calibration) were computed. The results of the 4 trials are presented in Table 2. For each trial the mean errors of the  coordinates (in mm) and in Euler angles (in degrees) are reported. The standard deviations (SD) of errors are also reported.
coordinates (in mm) and in Euler angles (in degrees) are reported. The standard deviations (SD) of errors are also reported.
The results show that, for each trial, the mean error is of approximately 0.1 degree for Euler angles and about 2 mm for coordinates parallel to the radiographic plane. The co-ordinate perpendicular to the radiographic plane, instead, is subjected to a more significant error (about 15 mm). In general errors decrease by applying the described corrections.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
This paper has described an automatic method for 3D pose estimation of a vertebra by means of CT and digital video-fluoroscopy and an in vitro assessment using a calibration object was performed.
The method is based upon a comparison (by means of cross-correlation) between DVF images and DRRs obtained using the CT 3D vertebral model. The DRR is obtained by simulating the radiographic process in an accurate manner, taking into account the effect of the difference of X-ray energy between CT and DVF imaging modalities. The algorithm for the reconstruction of digital radiographs is based on a ray-casting approach.
The 3D parameters belonging to the DRR that maximises the cross-correlation were considered as the estimators of the 3D pose of the vertebra. An iterative (gradient driven), step-refinement, multiscale approach was used to reliably estimate the absolute maxima of the cross-correlation function described by variables representing the 6 degrees of freedom of a rigid body (vertebra).
To perform an assessment of the method, a calibration model, with embedded fiducial markers, was designed in order to allow an accurate estimate of the 3D pose as a baseline. An appropriate set of trials was designed to investigate the possibility of not simulating accurately the radiographic process.
From the results it can be inferred that accuracy and precision of the 3D pose estimation increases when the simulation becomes more accurate, in particular, taking into account the effect of X-ray energies and the exponential attenuation of X-ray through matter.
The method presents satisfactory results in the computation of Euler angles and of focus coordinates parallel to the radiographic plane. However, the coordinates orthogonal to the radiographic plane are subjected to more significant errors. Nevertheless, in practical cases, this information is known via positioning of the patient with respect to the DVF device.
To explain this fact it should be observed that a displacement in the direction perpendicular to the radiographic plane causes a "zoom effect". This "zoom" is clearly visible only if the displacement is of the order of 10–15 mm. Therefore the cross-correlation index is not able to distinguish between 2 DVF images obtained with orthogonal coordinates differing less than 10–15 mm.
It is worth mentioning that by using the calibration model, the effect of soft tissue and adjacent vertebrae has been neglected. Therefore the presented results reasonably represent an upper limit for the accuracy and precision achievable in real applications. However, recent further study involving the analysis of the cervical spine motion in human patients seems to confirm the applicability of such a methodology [41]. Current work aims to evaluate the use of first derivatives of DVF images to improve and speed up the template matching process [42].
References
Dimnet J, Fischer LP, Gonon G, Carret JP: Radiographic studies of lateral flexion in the lumbar spine. Journal of Biomechanics 1978, 11(3):143-150. 10.1016/0021-9290(78)90006-4
Stokes IAF, Wilder DG, Frymoyer JW, Pope MH: Assessment of patients with low-back pain by biplanar radiographic measurement of intervertebral motion. Spine 1981, 6(3):233-240. 10.1097/00007632-198105000-00005
Breen AC, Allen R, Morris A: Spine kinematics: a digital videofluoroscopic technique. Journal of Biomedical Engineering 1989, 11(3):224-228. 10.1016/0141-5425(89)90146-5
von Mameren H, Drukker J, Sanches H, Beursgens J: Cervical spine motion in the sagittal plane (I) range of motion of actually performed movements, an X-ray cinematographic study. European Journal of Morphology 1990, 28(1):47-68.
van Mameren H, Sanches H, Beursgens J, Drukker J: Cervical spine motion in the sagittal plane II: position of segmental averaged instantaneous centers of rotation—a cineradiographic study. Spine 1992, 17(5):467-474. 10.1097/00007632-199205000-00001
Muggleton JM, Allen R: Automatic location of vertebrae in digitized videofluoroscopic images of the lumbar spine. Medical Engineering and Physics 1997, 19(1):77-89. 10.1016/S1350-4533(96)00050-1
Bifulco P, Cesarelli M, Allen R, Muggleton J, Bracale M: Automatic vertebrae recognition throughout a videofluoroscopic sequence for intervertebral kinematics study. In Time Varying Image Processing and Moving Object Recognition. Volume 4. Edited by: Cappellini. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands; 1996:213-218.
McCane B, King TI, Abbott JH: Calculating the 2D motion of lumbar vertebrae using splines. Journal of Biomechanics 2006, 39(14):2703-2708. 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.09.015
White AA III, Panjabi MM: The basic kinematics of the human spine: a review of past and current knowledge. Spine 1978, 3(1):12-20. 10.1097/00007632-197803000-00003
Zhang X, Xiong J: Model-guided derivation of lumbar vertebral kinematics in vivo reveals the difference between external marker-defined and internal segmental rotations. Journal of Biomechanics 2003, 36(1):9-17. 10.1016/S0021-9290(02)00323-8
Cerveri P, Pedotti A, Ferrigno G: Kinematical models to reduce the effect of skin artifacts on marker-based human motion estimation. Journal of Biomechanics 2005, 38(11):2228-2236. 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.09.032
Bifulco P, Cesarelli M, Roccasalva Firenze M, Verso E, Sansone M, Bracale M: Estimation of the 3D positioning of anatomic structures from radiographic projection and volume knowledge. Proceedings of the 8th Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing (MEDICON '98), 1998 CD-ROM: 2.5
Bifulco P, Cesarelli M, Verso E, Roccasalva Firenze M, Sansone M, Bracale M: Simulation of the radiography formation process from CT patient volume. Proceedings of the 8th Mediterranean Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing (MEDICON '98), 1998 CD-ROM: 2.5
Bifulco P, Cesarelli M, Allen R, Sansone M, Bracale M: Automatic recognition of vertebral landmarks in fluoroscopic sequences for analysis of intervertebral kinematics. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 2001, 39(1):65-75. 10.1007/BF02345268
Birkfellner W, Wirth J, Burgstaller W, et al.: A faster method for 3D/2D medical image registration—a simulation study. Physics in Medicine and Biology 2003, 48(16):2665-2679. 10.1088/0031-9155/48/16/307
Rohlfing T, Russakoff DB, Denzler J, Mori K, Maurer CR Jr.: Progressive attenuation fields: fast 2D-3D image registration without precomputation. Medical Physics 2005, 32(9):2870-2880. 10.1118/1.1997367
Russakoff DB, Rohlfing T, Adler JR Jr., Maurer CR Jr.: Intensity-based 2D-3D spine image registration incorporating a single fiducial marker. Academic Radiology 2005, 12(1):37-50. 10.1016/j.acra.2004.09.013
Hamadeh A, Lavallee S, Cinquin P: Automated 3-dimensional computed tomographic and fluoroscopic image registration. Computer Aided Surgery 1998, 3(1):11-19. 10.3109/10929089809148123
Mac-Thiong J-M, Aubin CE, Dansereau J, de Guise JA, Brodeur P, Labelle H: Registration and geometric modelling of the spine during scoliosis surgery: a comparison study of different pre-operative reconstruction techniques and intra-operative tracking systems. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 1999, 37(4):445-450. 10.1007/BF02513328
Weese J, Gocke R, Penney GP, Desmedt P, Buzug TM, Schumann H: Fast voxel-based 2D/3D registration algorithm using a volume rendering method based on the shear-warp factorization. Medical Imaging 1999: Image Processing, 1999, Proceedings of SPIE 3661: 802-810.
Lavallee S, Szeliski R: Recovering the position and orientation of free-form objects from image contours using 3D distance maps. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1995, 17(4):378-390. 10.1109/34.385980
Lavalle S, Szeliski R, Bruniee L: Anatomy based registration of three-dimensional medical images, range images, X-ray projections, and three-dimensional models using octree-splines. In Computer Integrated Surgery: Technology and Clinical Applications. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass, USA; 1995.
Hurvitz A, Joskowicz L: Registration of a CT-like atlas to fluoroscopic X-ray images using intensity correspondences. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery 2008, 3(6):493-504. 10.1007/s11548-008-0264-z
Banks SA, Hodge WA: Accurate measurement of three-dimensional knee replacement kinematics using single-plane fluoroscopy. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 1996, 43(6):638-649. 10.1109/10.495283
Zuffi S, Leardini A, Catani F, Fantozzi S, Cappello A: A model-based method for the reconstruction of total knee replacement kinematics. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 1999, 18(10):981-991. 10.1109/42.811310
Hirokawa S, Abrar Hossain M, Kihara Y, Ariyoshi S: A 3D kinematic estimation of knee prosthesis using X-ray projection images: clinical assessment of the improved algorithm for fluoroscopy images. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing 2008, 46(12):1253-1262. 10.1007/s11517-008-0398-8
Bifulco P, Cesarelli M, Sansone M, Allen R, Bracale M: Fluoroscopic analysis of inter-vertebral lumbar motion: a rigid model fitting technique. Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, 1997 714.
Alakuijala J, Jaske U-M, Sallinen S, Helminen H, Laitinen J: Reconstruction of digital radiographs by texture mapping, ray casting and splatting. Proceedings of the 18th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, 1996 2: 643-645.
Gottesfeld Brown LM, Boult TE: Registration of planar film radiographs with computed tomography. Proceedings of the Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis (MMBIA '96), 1996 42-51.
Weese J, Penney GP, Desmedt P, Buzug TM, Hill DLG, Hawkes DJ: Voxel-based 2-d/3-d registration of fluoroscopy images and CT scans for image-guided surgery. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine 1997, 1(4):284-293. 10.1109/4233.681173
Cho Z, Jones JP, Singh M: Foundations of Medical Imaging. Wiley Interscience, New York, NY, USA; 1993.
Johns HE, Cunningham JR: The Physics of Radiology. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, Ill, USA; 1983.
Marschner SR, Lobb RJ: An evaluation of reconstruction filters for volume rendering. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Visualization (Visualization '94), 1994, Washington, DC, USA 100-107.
van der Plaats GJ, Vijlbrief P: Medische Rontgentechniek in de Diagostiek. Uitgeversmaatschappij de Tijdstroom; 1978.
Bifulco P, Sansone M, Cesarelli M, Allen R, Bracale M: Estimation of out-of-plane vertebra rotations on radiographic projections using CT data: a simulation study. Medical Engineering and Physics 2002, 24(4):295-300. 10.1016/S1350-4533(02)00021-8
Bifulco P, Sansone M, Cesarelli M, Bracale M: In-vivo evaluation of cervical spine intervertebral kinematics by means of digital fluoroscopy: experimental set-up. Proceedings of the 2nd European Medical & Biological Engineering Conference (EMBEC '02), December 2002, Vienna, Austria
Dapena J, Harman EA, Miller JA: Three-dimensional cinematography with control object of unknown shape. Journal of Biomechanics 1982, 15(1):11-19. 10.1016/0021-9290(82)90030-6
Hatze H: High-precision three-dimensional photogrammetric calibration and object space reconstruction using a modified DLT-approach. Journal of Biomechanics 1988, 21(7):533-538. 10.1016/0021-9290(88)90216-3
Bose CB, Amir I: Design of fiducials for accurate registration using machine vision. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1990, 12(12):1196-1200. 10.1109/34.62609
Chiorboli G, Vecchi GP: Comments on "design of fiducials for accurate registration using machine vision". IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1993, 15(12):1330-1332. 10.1109/34.250850
Sansone M, Bifulco P, Cesarelli M, Bracale M: Evaluation of spine kinematics after surgical intervention: a feasibility study. Proceedings of the Medicon and Health Telematics, July-August 2004, Ischia, Italy
Bifulco P, Cesarelli M, Romano M, Allen R, Cerciello T: Vertebrae tracking through fluoroscopic sequence: a novel approach. Proceedings of the World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering: The Triennial Scientific Meeting of the IUPESM, September 2009, Munich, Germany
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
About this article
Cite this article
Bifulco, P., Cesarelli, M., Allen, R. et al. 2D-3D Registration of CT Vertebra Volume to Fluoroscopy Projection: A Calibration Model Assessment. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2010, 806094 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/806094
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/806094










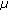 correction;
correction;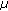 correction (energy) of CT data;
correction (energy) of CT data;