Abstract
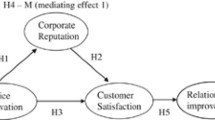
The study has been undertaken with following aims; first, to establish the plausibility of a positive relationship between service innovation and corporate reputation and their effect together on cross-buying intention of customers of telecommunication industry in India. Second, empirically examine the mediating and moderating effect of corporate reputation between service innovation and cross-buying intention. The descriptive approach was applied and tested by adopting a survey method where the sample units comprised of customers from various telecommunication service providers. Convenience sampling method was used based on which 256 customers of major service providers in southern part of India were approached for their opinion on the constructs. Smart—partial least square (hereinafter PLS) software tool was used to test the conceptual framework. On analyzing the result, it was observed that corporate reputation explained the relationship between service innovation and cross-buying intention; further corporate reputation also strengthens the effect of service innovation on cross-buying intention. The survey results indicate that decision makers/managers of telecommunication service firms need to understand that building reputation is one of the key aspects that would strengthen their initiatives of bringing service innovation frequently, as well as make their customers to cross-buy other services. The study fills the gap by analyzing the combined effect of service innovation and corporate reputation and cross-buying intention. Further, the study estimates the mediating and the moderating effect of corporate reputation between service innovation and cross-buying intention in telecommunication service settings which was not attempted earlier.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas, T.H., and P.E. Pedersen. 2011. The impact of service innovation on firm-level financial performance. The Service Industries Journal 31 (13): 2071–2090.
Anderson, E.W., C. Fornell, and D.R. Lehmann. 1994. Customer satisfaction, market share, and profitability: Findings from Sweden. The Journal of Marketing 58 (3): 53–66.
Anderson, J.C., and D.W. Gerbing. 1991. Predicting the performance of measures in a confirmatory factor analysis with pre-test assessment of their substantive validities. Journal of Applied Psychology 76 (5): 732–740.
Anderton, B. 1999. Innovation, product quality, variety, and trade performance: an empirical analysis of Germany and the UK. Oxford Economic Papers 51 (1): 152–167.
Andreassen, T.W., and S. Streukens. 2009. Service innovation and electronic word-of-mouth: is it worth listening to? Managing Service Quality: An International Journal 19 (3): 249–265.
Avlonitis, G.J., P.G. Papastathaopoulou, and S.P. Gounaris. 2001. An empirically-based typology of product innovativeness for new financial services: Success and failure scenarios. Journal of Product Innovation Management 18 (5): 324–342.
Baron, R.M., and D.A. Kenny. 1986. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 51 (6): 1173–1182.
Barras, R. 1986. Towards a theory of innovation in services. Research Policy 15 (4): 161–173.
Bettencourt, L.A. 2004. Change-oriented organizational citizenship behaviors: The direct and moderating influence of goal orientation. Journal of Retailing 80 (3): 165–180.
Blazevic, V., and A. Lievens. 2004. Learning during the new financial service innovation process: antecedents and performance effects. Journal of Business Research 57 (4): 374–391.
Bossink, B.A.G. 2002. The strategic function of quality in the management of innovation. Total Quality Management 13 (2): 195–205.
Bowling, A. 2002. Research Methods in Health: Investigating Health and Health Services, 2nd ed. Buckingham: Biddies Limited, University Press.
Brignall, S., and J. Ballantine. 1996. Performance measurement in service businesses revisited. International Journal of Service Industry Management 7 (1): 6–31.
Bromley, D.B. 2001. Relationships between personal and corporate reputation. European Journal of Marketing 35 (3/4): 316–334.
Burns, N., and S.K. Grove. 1993. The Practice of Nursing Research. Conduct, Critique, and Utilization. Philadelphia: Saunders.
Butera, A. 2000. Cross-selling: capitalizing on the opportunities. Hoosier Bank 87 (7): 14–16.
Carrigan, M., and A. Attalla. 2001. The myth of the ethical consumer–do ethics matter in purchase behavior? Journal of consumer marketing 18 (7): 560–578.
Caruana, A. 1997. Corporate reputation: concept and measurement. Journal of Product and Brand Management 6 (2): 109–118.
Caruana, A., and M.T. Ewing. 2010. How corporate reputation, quality, and value influence on online loyalty. Journal of Business Research 63 (9): 1103–1110.
Cellular Operators Association of India- COAI, 2015. GSM Subscriber Figure Report—2015, http://www.coai.com/Statistics/GSM-Subscriber-Figure-Report. 19 March, 2015.
Chen, Y.S. 2008. The driver of green innovation and green image–green core competence. Journal of Business Ethics 81 (3): 531–543.
Chin, W.W., B.L. Marcolin, and P.R. Newsted. 2003. A partial least squares latent variable modeling approach for measuring interaction effects: Results from a Monte Carlo simulation study and an electronic-mail emotion/adoption study. Information Systems Research 14 (2): 189–217.
Churchill, G.A., and P.J. Peter. 1984. Research design effects on the reliability of rating scales: a meta-analysis. Journal of Marketing Research 21 (4): 360–375.
Coombs, R., and I. Miles. 2000. Innovation, Measurement and Services: The New Problematique. In Innovation Systems in the Service Economy, ed. J.S. Metcalfe, and I. Miles, 85–103. Boston, MA: Springer.
Corkindale, D., and M. Belder. 2009. Corporate brand reputation and the adoption of innovation. Journal of Product and Brand Management 18 (4): 242–250.
Cravens, K., E. Goad Oliver, and S. Ramamoorti. 2003. The reputation index: Measuring and managing corporate reputation. European Management Journal 21 (2): 201–212.
Cretu, A.E., and R.J. Brodie. 2007. The influence of brand image and company reputation where manufacturers market to small firms: A customer value perspective. Industrial Marketing Management 36 (2): 230–240.
Damanpour, F., R.M. Walker, and C.N. Avellaneda. 2009. Combinative effects of innovation types and organizational performance: A longitudinal study of service organizations. Journal of Management Studies 46 (4): 650–675.
Datta, A. 2011. An integrative model to explain the ability to commercialize innovations: Linking networks, absorptive capacity, ambidexterity and environmental factors. Journal of Management & Strategy 2 (2): 2–22.
Davies, G., R. Chun, R.V. da Silva, and S. Roper. 2001. The personification metaphor as a measurement approach for corporate reputation. Corporate Reputation Review 4 (2): 113–127.
Davis, F.D., R. Bagozzi, and P.R. Warshaw. 1989. User acceptance of computer technology: a comparison of two theoretical models. Management Science 35 (8): 982–1003.
De Brentani, U., and R.G. Cooper. 1992. Developing successful new financial services for businesses. Industrial Marketing Management 21 (3): 231–241.
De Ruyter, K., M. Wetzels, and M. Kleijnen. 2001. Customer adoption of e-service: an experimental study. International Journal of Service Industry Management 12 (2): 184–207.
Dean, D.H. 2003. Consumer perception of corporate donations effects of company reputation for social responsibility and type of donation. Journal of Advertising 32 (4): 91–102.
Deshpande, R., J.U. Farley, and F.E. Webster Jr. 1993. Corporate culture customer orientation and innovativeness in Japanese firms: A quadrad analysis. Journal of Marketing 57 (1): 23–37.
Dortok, A. 2006. A managerial look at the interaction between internal communication and corporate reputation. Corporate Reputation Review 8 (4): 322–338.
Edvardsson, B. 1997. Quality in new service development: key concepts and a frame of reference. International Journal of Production Economics 52 (1): 31–46.
Edvardsson, B., and J. Olsson. 1996. Key concepts for new service development. Service Industries Journal 16 (2): 140–164.
Fitzgerald, L., R. Johnston, T.J. Brignall, R. Silvestro, and C. Voss. 1991. Performance Measurement in Service Businesses. London: CIMA.
Flynn, L.R., and R.E. Goldsmith. 1993. A validation of the Goldsmith and Hofacker innovativeness scale. Educational and Psychological Measurement 53 (4): 1105–1116.
Fogelman, K., and C. Comber. 2002. Surveys and sampling. Research Methods in Educational Leadership and Management 2: 93–107.
Fombrun, C. 1996. Reputation. Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
Fombrun, C.J., N.A. Gardberg, and J.M. Sever. 2000. The reputation quotient: A multi-stakeholder measure of corporate reputation. Journal of Brand Management 7 (4): 241–255.
Fombrun, C.J. 2007. List of lists: A compilation of international corporate reputation ratings. Corporate Reputation Review 10 (2): 144–153.
Fornell, C., and F.L. Bookstein. 1982. Two structural equation models: LISREL and PLS applied to consumer exit-voice theory. Journal of Marketing Research 19 (4): 440–452.
Fornell, C., and D.F. Larcker. 1981. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research 18 (1): 39–50.
Fryxell, G.E., and J. Wang. 1994. The fortune corporate reputation index: Reputation for what? Journal of Management 20 (1): 1–14.
Gadrey, J., F. Gallouj, and O. Weinstein. 1995. New modes of innovation: how services benefit industry. International Journal of Service Industry Management 6 (3): 4–16.
Ganesan, P., and M. Sridhar. 2016. Service Innovation and Customer Performance of Telecommunication Service Provider: A Study on Mediation Effect of Corporate Reputation. Corporate Reputation Review 19 (1): 77–101.
Ghozali, I. 2006. Analisis Multivariate lanjutan dengan program SPSS. Semarang: Badan Penerbit Universitas Diponegoro.
Gonzalez Mieres, C., J. Angel Lopez Sanchez, and M. Leticia Santos Vijande. 2012. Internal marketing, innovation and performance in business services firms: The role of organizational unlearning. International Journal of Management 29 (4): 403–429.
Goodhue, D.L., W. Lewis, and R. Thompson. 2012. Does PLS have advantages for small sample size or non-normal data? MIS Quarterly 36 (3): 891–1001.
Hair, J.F., C.M. Ringle, and M. Sarstedt. 2011. PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. Journal of Marketing theory and Practice 19 (2): 139–152.
Hair Jr., J.F., M. Sarstedt, L. Hopkins, and V.G. Kuppelwieser. 2014. Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM): An emerging tool in business research. European Business Review 26 (2): 106–121.
Harris, F., and L. De Chernatony. 2001. Corporate branding and corporate brand performance. European Journal of Marketing 35 (3/4): 441–456.
Helm, S., and C. Klode. 2011. Challenges in Measuring Corporate Reputation. Reputation Management, 99–110. Berlin: Springer.
Helm, S., A. Eggert, and I. Garnefeld. 2010. Modeling the impact of corporate reputation on customer satisfaction and loyalty using partial least squares. In Handbook of Partial Least Squares, ed. V. Vinzi, 515–534. Berlin: Springer.
Helm, S., I. Garnefeld, and J. Tolsdorf. 2009. Perceived corporate reputation and consumer satisfaction–an experimental exploration of causal relationships. Australasian Marketing Journal 17 (2): 69–74.
Henard, D.H., and P.A. Dacin. 2010. Reputation for product innovation: Its impact on consumers. Journal of Product Innovation Management 27 (3): 321–335.
Hillenbrand, C., and K. Money. 2007. Corporate responsibility and corporate reputation: Two separate concepts or two sides of the same coin? Corporate Reputation Review 10 (4): 261–277.
Holak, S.L., and D.R. Lehmann. 1990. Purchase intentions and the dimensions of innovation: an exploratory model. Journal of Product Innovation Management 7 (1): 59–73.
Hong, S.Y., and S.U. Yang. 2009. Effects of reputation, relational satisfaction, and customer–company identification on positive word-of-mouth intentions. Journal of Public Relations Research 21 (4): 381–403.
Hu, M.L.M., J.S. Horng, and Y.H.C. Sun. 2009. Hospitality teams: Knowledge sharing and service innovation performance. Tourism Management 30 (1): 41–50.
Iacobucci, D., and A. Duhachek. 2003. Advancing alpha: Measuring reliability with confidence. Journal of Consumer Psychology 13 (4): 478–487.
Iyer, G.R., P.J. LaPlaca, and A. Sharma. 2006. Innovation and new product introductions in emerging markets: Strategic recommendations for the Indian market. Industrial Marketing Management 35 (3): 373–382.
James, L.R., and J.M. Brett. 1984. Mediators, moderators, and tests for mediation. Journal of Applied Psychology 69 (2): 307–321.
Janssens, A.C.J., Y.S. Aulchenko, S. Elefante, G.J. Borsboom, E.W. Steyerberg, and C.M. Van Duijn. 2006. Predictive testing for complex diseases using multiple genes: fact or fiction? Genetics in Medicine 8 (7): 395–400.
Jeng, S.P. 2008. Effects of corporate reputations, relationships and competing suppliers marketing programmes on customers cross-buying intentions. The Service Industries Journal 28 (1): 15–26.
Jin, B., J. Yong Park, and J. Kim. 2008. Cross-cultural examination of the relationships among firm reputation, e-satisfaction, e-trust, and e-loyalty. International Marketing Review 25 (3): 324–337.
Kamakura, W.A., B.S. Kossar, and M. Wedel. 2004. Identifying innovators for the cross-selling of new products. Management Science 50 (8): 1120–1133.
Keh, H.T., and Y. Xie. 2009. Corporate reputation and customer behavioral intentions: The roles of trust, identification and commitment. Industrial Marketing Management 38 (7): 732–742.
Kerlinger, F.N. 1986. Foundations of Behavioral Research, 3rd ed. New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston.
Kim, J.B., and C.J. Choi. 2003. Reputation and product tampering in service industries. The Service Industries Journal 23 (4): 3–11.
Kline, R.B. 2005. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. Methodology in the Social Sciences, 3rd ed. New York: The Guilford Press.
Kostopoulos, K., A. Papalexandris, M. Papachroni, and G. Ioannou. 2011. Absorptive capacity, innovation, and financial performance. Journal of Business Research 64 (12): 1335–1343.
Lai, C.S., C.J. Chiu, C.F. Yang, and D.C. Pai. 2010. The effects of corporate social responsibility on brand performance: The mediating effect of industrial brand equity and corporate reputation. Journal of Business Ethics 95 (3): 457–469.
Lin, Lei. 2012. The impact of service innovation on firm performance: Evidence from the Chinese tourism sector. The Service Industries Journal 33 (15/16): 1–34.
Lieberman, M.B., and D.B. Montgomery. 1988. First-mover advantages. Strategic Management Journal 9 (S1): 41–58.
Lippman, S.A., and K.F. McCardle. 1987. Does cheaper, faster, or better imply sooner in the timing of innovation decisions? Management Science 33 (8): 1058–1064.
Little, T.D., N.A. Card, J.A. Bovaird, K.J. Preacher, and C.S. Crandall. 2007. Structural Equation Modeling of Mediation and Moderation with Contextual Factors. Modeling Contextual Effects in Longitudinal Studies, (chapter -9), vol. 1, 207–230. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Liu, T.C., and L.W. Wu. 2007. Customer retention and cross-buying in the banking industry: An integration of service attributes, satisfaction and trust. Journal of Financial Services Marketing 12 (2): 132–145.
Lovelock, C., and E. Gummesson. 2004. Whither services marketing? In search of a new paradigm and fresh perspectives. Journal of service research 7 (1): 20–41.
Lowry, P.B., and J. Gaskin. 2014. Partial least squares (PLS) structural equation modeling (SEM) for building and testing behavioral causal theory: When to choose it and how to use it. IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication 57 (2): 123–146.
Lu, H.P., and P.Y.J. Su. 2009. Factors affecting purchase intention on mobile shopping web sites. Internet Research 19 (4): 442–458.
Luoma-aho, V. 2007. Neutral reputation and public sector organizations. Corporate Reputation Review 10 (2): 124–143.
Matthing, J., B. Sandén, and B. Edvardsson. 2004. New service development: Learning from and with customers. International Journal of Service Industry Management 15 (5): 479–498.
McAdam, R., and G. Armstrong. 2001. A symbiosis of quality and innovation in SMEs: A multiple case study analysis. Managerial Auditing Journal 16 (7): 394–399.
Menor, Larry J., Mohan V. Tatikonda, and Scott E. Sampson. 2002. New service development: Areas for exploitation and exploration. Journal of Operations Managements 20 (2): 135–157.
Meyer, A.D., and J.B. Goes. 1988. Organizational assimilation of innovations: A multilevel contextual analysis. Academy of Management Journal 31 (4): 897–923.
Michaelis, M., D.M. Woisetschläger, C. Backhaus, and D. Ahlert. 2008. The effects of country of origin and corporate reputation on initial trust: An experimental evaluation of the perception of Polish consumers. International Marketing Review 25 (4): 404–422.
Miles, M.P., and J.G. Covin. 2000. Environmental marketing: a source of reputational, competitive, and financial advantage. Journal of Business Ethics 23 (3): 299–311.
Ngobo, P.V. 2004. Drivers of customers cross-buying intentions. European Journal of Marketing 38 (9/10): 1129–1157.
Nguyen, N., and G. Leblanc. 2001. Corporate image and corporate reputation in customers retention decisions in services. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 8 (4): 227–236.
Nunnally, J.C. 1978. Psychometric Theory. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Parasuraman, A. 2010. Service productivity, quality and innovation: Implications for service-design practice and research. International Journal of Quality and Service Sciences 2 (3): 277–286.
Park, C., and T.M. Lee. 2009. Information direction, website reputation and e-WOM effect: A moderating role of product type. Journal of Business Research 62 (1): 61–67.
Park, J.W., R. Robertson, and C.L. Wu. 2006. Modelling the impact of airline service quality and marketing variables on passengers future behavioral intentions. Transportation Planning and Technology 29 (5): 359–381.
Peterson, R.A. 2000. A meta-analysis of variance accounted for and factor loadings in exploratory factor analysis. Marketing Letters 11 (3): 261–275.
Phelps, J.E., R. Lewis, L. Mobilio, D. Perry, and N. Raman. 2004. Viral marketing or electronic word-of-mouth advertising: Examining consumer responses and motivations to pass along email. Journal of Advertising Research 44 (4): 333–348.
Ping, R. A., 2009. Is there any way to improve average variance extracted (AVE) in a latent variable (LV) X (Revised). http://home.att.net/-rpingjr/ImprovAVE1.doc. Accessed 3 June, 2013.
Price, R., and R.J. Brodie. 2001. Transforming a public service organization from inside out to outside in the case of Auckland City-New Zealand. Journal of Service Research 4 (1): 50–59.
Reichheld, F.P., and W.E. Sasser. 1990. Zero defeciions: Quoliiy comes to services. Harvard Business Review 68 (5): 105–111.
Reinartz, W.J., and V. Kumar. 2003. The impact of customer relationship characteristics on profitable lifetime duration. Journal of Marketing 67 (1): 77–99.
Roberts, P.W., and G.R. Dowling. 2002. Corporate reputation and sustained superior financial performance. Strategic Management Journal 23 (12): 1077–1093.
Rose, C., and S. Thomsen. 2004. The impact of corporate reputation on performance: Some danish evidence. European Management Journal 22 (2): 201–210.
Rosebush, M. 2011. Validations of the Character Mosaic Report. Air Force Academy Colorado Springs Co. Accessed on 4 November, 2014.
Salisbury, W.D., R.A. Pearson, A.W. Pearson, and D.W. Miller. 2001. Perceived security and World Wide Web purchase intention. Industrial Management and Data Systems 101 (4): 165–177.
Schumpeter, J.A. 1934. The theory of economic development: An inquiry into profits, capital, credit, interest, and the business cycle. Transaction Publishers 55: 1–255.
Selnes, F. 1993. An examination of the effect of product performance on brand reputation, satisfaction and loyalty. Journal of Product & Brand Management 2 (4): 45–60.
Sichtmann, C., M.V. Selasinsky, and A. Diamantopoulos. 2011. Service quality and export performance of business-to-business service providers: The role of service employee-and customer-oriented quality control initiatives. Journal of International Marketing 19 (1): 1–22.
Sirilli, G., and R. Evangelista. 1998. Technological innovation in services and manufacturing: Results from Italian surveys. Research Policy 27 (9): 881–899.
Sobel, M. 1982. Asymptotic confidence intervals for indirect effects on structural equation models. In Sociological Methodology, vol. 13, ed. S. Leichardt, 290–312. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Soureli, M., B.R. Lewis, and K.M. Karantinou. 2008. Factors that affect consumers cross-buying intention: a model for financial services. Journal of Financial Services Marketing 13 (1): 5–16.
Staw, B.M., and L.D. Epstein. 2000. What bandwagons bring: Effects of popular management techniques on corporate performance, reputation, and CEO pay? Administrative Science Quarterly 45 (3): 523–556.
Su, C.S. 2011. The role of service innovation and customer experience in ethnic restaurants. The Service Industries Journal 31 (3): 425–440.
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India, TRAI (2017) Telecom Subscription Data as on 28th February—2017, http://www.trai.gov.in/sites/default/files/Press_Release_34_Eng_28_04_2017_0.pdf. Accessed 16 June, 2017.
Vickery, S.K., J. Jayaram, C. Droge, and R. Calantone. 2003. The effects of an integrative supply chain strategy on customer service and financial performance: an analysis of direct versus indirect relationships. Journal of Operations Management 21 (5): 523–539.
Victorino, L., R. Verma, G. Plaschka, and C. Dev. 2005. Service innovation and customer choices in the hospitality industry. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal 15 (6): 555–576.
Voss, C.A. 1992. Measurement of INNOVATION and design performance IN SERVICES. Design Management Journal (Former Series) 3 (1): 40–46.
Walsh, G., K. Dinnie, and K.P. Wiedmann. 2006. How do corporate reputation and customer satisfaction impact customer defection? A study of private energy customers in Germany. Journal of Services Marketing 20 (6): 412–420.
Walsh, G., V.W. Mitchell, P.R. Jackson, and S.E. Beatty. 2009. Examining the antecedents and consequences of corporate reputation: a customer perspective. British Journal of Management 20 (2): 187–203.
Wang, C.L., and P.K. Ahmed. 2004. The development and validation of the organizational innovativeness construct using confirmatory factor analyses. European Journal of Innovation Management 7 (4): 303–313.
Wang, Y.S., T.I. Tang, and J.T.E. Tang. 2001. An instrument for measuring customer satisfaction toward web sites that market digital products and services. Journal Electronic Commerce Research 2 (3): 89–102.
Wischnevsky, J.D., and F. Damanpour. 2006. Organizational transformation and performance: An examination of three perspectives. Journal of Managerial Issues 18 (1): 104–128.
Yoon, E., H.J. Guffey, and V. Kijewski. 1993. The effects of information and company reputation on intentions to buy a business service. Journal of Business Research 27 (3): 215–228.
Zaltman, G., R. Duncan, and J. Holbek. 1973. Innovations and Organizations. New York: Wiley.
Zhang, Q., M.A. Vonderembse, and J.S. Lim. 2003. Manufacturing flexibility: Defining and analyzing relationships among competence, capability, and customer satisfaction. Journal of Operations Management 21 (2): 173–191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
Questionnaire
This questionnaire is to measure Innovation, Corporate Reputation, and Cross-Buying Intention with Telecommunication Service Provider. There is no right or wrong answers. You are requested to choose the best as per your knowledge or experience and mark ( ) in the space provided. Please fill all questions.



Appendix 2

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sridhar, M., Mehta, A. The Moderating and Mediating Role of Corporate Reputation in the Link Between Service Innovation and Cross-Buying Intention. Corp Reputation Rev 21, 50–70 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41299-018-0044-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1057/s41299-018-0044-9