Abstract
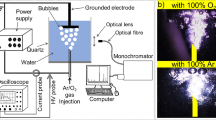
This work investigates the degradation mechanism of Acid Red 17 dye (AR-17) using HPLC-MS/MS as well as it studies the feasibility of applying ozone and ultraviolet to detoxify the wastewater containing AR-17 dye. Different parameters such as pH, initial dye concentration and treatment time were evaluated to obtain the optimal degradation conditions. The initial dye concentration and solution pH were the parameters which affected the color removal and the maximum decolorization was obtained at pH 11. A 100% color removal took place after 25 min of O3/UV treatment (for 100 ppm dye concentration). Kinetic analyses of AR-17 dye removal followed the pseudo-first-order kinetics. When ultraviolet (UV) was applied with ozone simultaneously, the first-order rate constant (kdx[O3]l) increased and the time of dye decolorization shortened to 5.5 min for 500 ppm dye concentration. GC-MS and HPLC-MS/MS studies of pre-treated dye solution which were performed during and at the end of the pre-treatment time, showed complete degradation of the AR-17 dye. The obtained results also demonstrated that the UV-ozone treatment process decreased the zooplankton toxicity of the treated AR-17 dye wastewater.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelwahab O, El Nemr A, El-Sikaily A, Khaled A (2006) Biosorption of direct yellow 12 from aqueous solution by marine green algae Ulva Lactuca. Chem Ecol 22(4):253–266
Acisli O, Khataee A, Karaca S, Sheydaei M (2016) Modification of nanosized natural montmorillonite for ultrasound enhanced adsorption of acid red 17. Ultras Sonochem 31:116–121
Alsheyab MA, Munaz AH (2006) Reducing the formation of THMS by ozone combined with hydrogen peroxide. J Desalination 194:121–126
Alvares ABC, Diaper C, Parsons SA (2001) Partial oxidation by ozone to remove recalcitrance from wastewaters. Environ Technol 22:409–427
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2005) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 21st ed., Washington DC. https://trove.nla.gov.au/version/45704677. Accessed 2 Feb 2018
Basiri Parsa J, Rezaei M, Soleymani AR (2009) Electrochemical oxidation of an azo dye in aqueous media investigation of operational parameters and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 168:997–1003
Beltran FJ (2004) Ozone reaction kinetics for water and wastewater systems. Levis Pub. Imprint of CRC Press LLC, Florida
Chen HW, Kuo YL, Chiou CS, You SW, Ma CM, Chang CT (2010) Mineralization of reactive black 5 in aqueous solution by ozone/H2O2 in the presence of magnetic catalyst. J Hazard Mater 174:795–800
Chu W, Ma CW (2000) Quantitative prediction of direct and indirect dye ozonation kinetics. Water Res 34:3153–3160
El Nemr A (2012) Non-conventional textile waste water treatment. Nova science publishers, Inc. Hauppauge, New York
El Nemr A, Abdelwahab O, Khaled A, El-Sikaily A (2009) Removal of direct blue-86 from aqueous solution by new activated carbon developed from orange peel. J Hazard Mater 161:102–110
El Nemr A, El Sadaawy M, Khaled A, El Sikaily A (2014) Adsorption of the anionic dye direct red 23 onto new activated carbons developed from Cynara Cardunculus: kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Blue Biotechnol J 3(1):121–142
El Nemr A, Khaled A, Abdelwahab O, El-Sikaily A (2008) Treatment of artificial textile dye effluent containing direct yellow 12 by orange peel carbon. Desalination 238:210–232
El-Sikaily A, El Nemr A, Khaled A, Abdelwehab O (2006) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by marine green alga Ulva lactuca. Chem Ecol 22(2):149–157
EPA (1985) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents to freshwater and marine organisms. 216 pp.
EPAP/ EEAA, (2003) The Egyptian Pollution Abatement Project and Egyptian Environmental Affiars Agency, (Self-Monitoring Manual for textile industry report)
Furlan FR, Da Silva LG, Morgado AF, De Souza AAU, Guelli UD (2010) Removal of reactive dyes from aqueous solutions using combined coagulation/flocculation and adsorption on activated carbon. Resour Conserv Recy 54:283–290
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A (2017) Advanced oxidation processes for textile wastewater treatment. Inter J Photochem Photobiol 2(3):85–93
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2017a) Testing the advanced oxidation processes on the degradation of direct blue 86 dye in wastewater. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:11–19
Hassaan MA, El Nemr A, Madkour FF (2017b) Advanced oxidation processes of mordant violet 40 dye in freshwater and seawater. Egypt J Aquat Res 43:1–9
Hisaindee S, Meetani MA, Rauf MA (2013) Application of LC-MS to the analysis of advanced oxidation process (AOP) degradation of dye products and reaction mechanisms. Trends Anal Chem 49:31–44
Javier RF, Beltran F, Gimeno O, Acedo B, Carvalho F (2003) Stabilized leachates: ozone activated carbon treatment and kinetics. J Water Res 37:4823–4834
Kazemi M, Soltan MJS, Khoshfetrat AB, Kaynejad MA (2004) Decolorization of RR- 120 dye using ozone and ozone/UV in a semi-batch reactor. Can J Chem Eng 82:1284–1288
Khadhraoui M, Trabelsi H, Ksibi M, Bouguerra S, Elleuch B (2009) Discoloration and detoxicification of a Congo red dye solution by means of ozone treatment for a possible water reuse. J Hazard Mater 161:974–981
Khaled A, El Nemr A, El Sikaily A, Abdelwahab O (2009) Adsorption isotherm and kinetics of direct Navy Blue-106 removal from artificial textile dye effluent using activated carbon from orange peel. J Hazard Mater 165:100–110
Kishimoto N, Morita Y, Tsuno H, Oomura T, Mizutani H (2005) Advanced oxidation effect of ozonation combined with electrolysis. J Water Res 39:4661–4672
Kralicek P (1995) Detection of carcinogenic amines that can be released from certain azoic dyes. Chimia 49:222–225
Kurniawan TA, Lo WH, Chan GYS (2006) Radicals-catalyzed oxidation reactions for degradation of recalcitrant compounds from landfill leachate. J Chem Eng 125:35–57
Kusic H, Koprivanac N, Bozic AL (2006) Minimization of organic pollutant content in aqueous solution by means of AOPs. UV and ozone based technologies. J Chem Eng 123:127–137
Kusvuran E, Gulnaz O, Samil A, Yildirim O (2011) Decolorization of malachite green, decolorization kinetics and stoichiometry of ozone-malachite green and removal of antibacterial activity with ozonation processes. J Hazard Mater 186(1):133–143
Lin SH, Lin CM (1993) Treatment of textile wastewater by ozonation and chemical coagulation. Water Res 27:1743–1748
Mallevialle J (1982) Ozonation manual for water and wastewater treatment, Vol. 53. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Mark J, Hammer S (2011) Water and wastewater technology, 7th edn. Prentice Hall, New Jercy, 528 pages
Moussavi GM, Khavanin A, Alizadeh R (2009) The investigation of catalytic ozonation and integrated catalytic ozonation/biological processes for the removal of phenol from saline wastewaters. J Hazard Mater 171:171–175
Moussavi G, Mahmoudi M (2009) Degradation and biodegradability improvement of the reactive red 198 azo dye using catalytic ozonation with MgO nanocrystals. Chem Eng J 152(1):1–7
Muthukumar M, Selvakumar N (2005) Discoloration of acid dye effluent with ozone: effect of pH, salt concentration and treatment time. Coloration Technol 121:7–12
Ogunjobi AA, Ademola EA, Sanuth HA (2012) Toxicity and bacterial decolourization of textile dyes. Elec J Env Agricult Food Chem 11:415–423
Oguz E, Keskinler B, Celik C, Celik Z (2006) Determination of the optimum conditions in the removal of bomaplex red CR-L dye from the textile wastewater using O3, H2O2, HCO3 − and PAC. J Hazard Mater 131:66–72
Peternel I, Koprivanac N, Kusic H (2006) UV-based processes for reactive azo dye mineralization. Water Res 40:525–532
Pielesz A, Baranowska I, Rybak A, Wlochowicz A (2002) Detection and determination of aromatic amines as products of reductive splitting from selected azo dyes. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 53:42–47
Pillai KC, Kwon TO, Shik MI (2009) Degradation of wastewater from terephthalic acid manufacturing process by ozonation catalyzed with Fe2+, H2O2 and UV light: direct versus indirect ozonation reactions. J Appl Catal B–Environ 91:319–328
Prat C, Vicente M, Esplugas S (1990) Ozone andozone/UV decolorization of bleaching waters of the paper industry. Ind Eng Chem Res 29:349–355
Reife A, Freeman HS (1996) Environmental chemistry of dyes and pigments. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, pp 43–60
Selçuk H, Eremektar G, Meriç S (2006) The effect of pre-ozone oxidation on acute toxicity and inert soluble COD fractions of a textile finishing industry wastewater. J Hazard Mater 37:254–260
Sevimli MF, Kinaci C (2002) Decolorization of textile wastewater by ozonation and Fenton's process. Water Sci Technol 45:279–286
Shang NC, Yu YH, Ma HW (2002) Variation of toxicity during the ozonation of monochlorophenolic solutions. J Environ Sci Health 37A:261–271
Shu HY (2006) Degradation of dyehouse effluent containing C.I. Direct blue 199 by processes of ozonation. UV/H2O2 and in sequence of ozonation with UV/H2O2. J Hazard Mater 133:92–98
Shu HY, Chang MC (2005) Decolorization effects of six azo dyes by O3, UV/O3 and UV/H2O2 processes. Dyes Pigments 65:25–31
Snell TW, Persooneb G (1989) Acute toxicity bioassays using rotifers. I. A test for brackish and marine environments with Brachionu splicatilis. Aquat Toxicol 14:65–80
Somensi CA, Simionatto EL, Bertoli SL, Wisniewski A Jr, Radetski CM (2010) Use of ozone in a pilot-scale plant for textile wastewater pre-treatment: Physico-chemical efficiency, degradation by-products identification and environmental toxicity of treated wastewater. J Hazard Mater 175:235–240
Song S, Xu X, Xu L, He Z, Ying H, Chen J, Yan B (2008a) Mineralization of CI reactive yellow 145 in aqueous solution by ultraviolet-enhanced ozonation. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:1386–1391
Song S, Xu X, Xu L, He Z, Ying H, Chen J, Yan B (2008b) Mineralization of CI reactive yellow 145 in aqueous solution by ultraviolet-enhanced ozonation. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:1386–1391
Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (1985) American Public Health Association. Washington DC:689–823. https://trove.nla.gov.au/version/4081157. Accessed 2 Feb 2018
Swaminathan K, Pachhade K, Sandhya S (2005) Decomposition of a dye intermediate, (H-acid) 1 amino-8-naphthol-3, 6 disulfonic acid in aqueous solution by ozonation. Desalin 186:155–164
Tehrani AR, Mahmoodi NM, Arami M (2008) Study of the efficiency of effective parameters on decolorization of CI. Reactive black 5 wastewater by ozonation. J Color Sci Technol 2:67–75
Thabet M, El-Zomrawy AA (2016) Degradation of acid red 17 dye with ammonium persulphate in acidic solution using photoelectrocatalytic methods. Arab J Chem 9:S204–S208
USEPA (1996) Test methods for evaluating solid waste. SW-846, USEPA Office of Solid Waste and Emergency Response, Washington, DC
Vanhulle S, Trovaslet M, Enaud E, Lucas M, Taghavi S, Van DLD, Van AB, Foret M, Onderwater RCA, Wesenberg D, Agathos SN, Schneider YJ, Corbisier AM (2008) Decolorization, cytotoxicity, and genotoxicity reduction during a combined ozonation/fungal treatment of dye-contaminated wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 42:584–589
Wang XJ, Chen SL, Gu XY, Wang KY, Qian YZ (2008) Biological aerated filter treated textile washing wastewater for reuse after ozonation pretreatment. Water Sci Technol 58(4):919–923
Wu J, Wang T (2001) Ozonation of aqueous azo dye in a semi-batch reactor. Water Res 35:1093–1099
Yasar A, Ahmad N, Amanat AKA, Yousaf A (2007) Decolorization of blue CL-BR dye by AOPs using bleach wastewater as source of H2O2. J Environ Sci 19:1183–1188
Zhang F, Yediler A, Liang X, Kettrup A (2004) Effect of dyes additives on the ozonation process and oxidation by-products: a comparative study using hydrolyzed C.I. Reactive red 120. Dyes Pigments 60:1–7
Zhang H, Duan L, Zhang D (2006) Decolorization of methyl orange by ozonation in combination with ultrasonic irradiation. J Hazard Mater 138(1):53–59
Zhao W, Shi H, Wang D (2004) Ozonation of cationic red X-GRL in aqueous solution: degradation and mechanism. Chemosphere 57:1189–1199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Nemr, A., Hassaan, M.A. & Madkour, F.F. Advanced Oxidation Process (AOP) for Detoxification of Acid Red 17 Dye Solution and Degradation Mechanism. Environ. Process. 5, 95–113 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-018-0284-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-018-0284-9