Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the toxicity of the silver nanoparticle against earthworms - Eudrilus eugeniae, a model for soil organism.
Methods
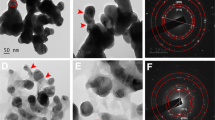
Silver nanoparticles were synthesised by chemical reduction and further characterised by UV Visible Spectroscopy and FeSEM. Earthworms were allowed to interact with different concentrations of the synthesized silver nanoparticles. After exposure period, histology and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) were done to determine the accumulation and toxic effects exhibited by the nanoparticle on earthworms.
Results
The synthesized nanoparticle was found to be between the size of 180 and 200 nm. Histology studies revealed that silver nanoparticles to cause fibrosis, lipofuscin-like deposits and also gut disruption in earthworms.
Conclusion
Silver nanoparticles were found to be toxic to Eudrilus eugeniae, which was evidenced by histology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hongyin, Z. Application of Silver Nanoparticle in Drinking Water Purification, Open Access Dissertations (2013).
Duncan, T. V. Applications of nanotechnology in food packaging and food safety: barrier materials, antimicrobials and sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 363, 1–24 (2011).
Caro, C., Castillo, P. M. Klippstein, R., Pozo, D. & Zaderenko, A. P. Silver Nanoparticle: Sensing and Imaging Application: In Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials, Intech Publishers. 201–205 (2010).
Anuradha, P., Prajapati, P. & Boghra, R. Overview on application of nanoparticles in cosmetics. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. Clin. Res. 1, 40–55 (2011).
Ahn, S. J., Lee, S. J., Kook, J. K. & Lim, B. S. Experimental antimicrobial orthodontic adhesives using nanofillers and silver nanoparticles. Dent. Mater. J. 25, 206–213 (2009).
Prabhu, S. & Poulose, E. K. Silver Nanoparticles: Mechanism of Antimicrobial Action, Synthesis, Medical Applications, and Toxicity Effects. Int. Nano Lett. 2, 32 (2012).
EI-Deeb, N. M., EI-Sherbiny, I. M., EI-Aassara, M. R. & Hafez, E. E. Novel Trends in Colon Cancer Therapy Using Silver Nanoparticle Synthesised by Honey Bee. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 6, 265 (2015).
Soumya, R. S. & Hela, P. H. Nano silver based targeted drug delivery for treatment of cancer. Pharm. Lett. 5, 189–197 (2013).
Rodriguez-Leon, E. et al. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using reducing agents obtained from natural sources (Rumex hymenosepalus extracts). Nanoscale Res. Lett. 8, 318 (2013).
Selvi, K. V. & Sivakumar, T. Isolation and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Fusarium oxysporum. Int. J. Curr. Microbial. App. Sci. 1, 56–62 (2012).
Malina, D., Sobczak-Kupiec, A., Wzorek, Z. & Kowalaski, Z. Silver nanoparticles synthesis with different concentrations of polyvinylpyrrolidone. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 7, 1527–1534 (2012).
Su, C., Jiang, L. & Zhang, W. A review on heavy metal contamination in the soil worldwide: Situation, impact and remediation techniques. Environ. Skep. Crit. 3, 24–38 (2014).
Viljoen, S. A. & Reinecke, A. J. Life-cycle of the African nightcrawler, Eudrilus eugeniae (Oligochaeta). S. Afr. J. Zoo. 24, 27–32 (1989).
Rashid, M. U., Bhuiyan, M. K. H. & Quayum, M. E. Synthesis of Silver Nano Particle (Ag-NPs) and Their Uses for Quantitative Analysis of Vitamin C Tablets. Dhaka Univ. J. Pharm. Sci. 12, doi:10.3329/dujps. v12i1.16297 (2013).
Devaraj, P., Kumari, P., Aarti, C. & Renganathan, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles Using Cannonball Leaves and Their Cytotoxic Activity against MCF-7 Cell Line. J. Nanotechnol. 2013, doi: 10.1155/2013/598328 (2013).
Mulvaney, P. Surface plasmon spectroscopy of nanosized metal particles. Langmuir 12, 788–800 (1996).
Hussain, J. I., Kumar, S., Hashmi, A. A. & Khan, Z. Silver nanoparticles: preparation, characterization and kinetics. Adv. Mat. Lett. 2, 188–194 (2011).
Guzman, M. G., Dille, J. & Godet, S. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2, 91–98 (2009).
Raza, M. K. et al. Size-and Shape-Dependent Antibacterial Studies of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized by Wet Chemical Routes. Nanomaterials 6, doi:10.3390/ nano6040074 (2016).
Jiang, X. C., Chen, W. M., Chen, C. Y., Xiong, S. X. & Yu, A. B. Role of temperature in the growth of silver nanoparticles through a synergetic reduction approach. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, doi:10.1007/s11671-010-9780-1 (2011).
Ploeg, M. J. C. V. et al. Effects of silver nanoparticles (nm-300k) on Lumbricus rubellus earthworms and particle characterization in relevant test matrices including soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 33, 743–752 (2014).
Shoults-Wilson, et al. Role of Particle Size and Soil Type in Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles to Earthworms. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 75, doi:10.2136/sssaj2010.0127nps (2011).
Barua, S. et al. Non-hazardous anticancerous and antibacterial colloidal ‘green’ silver nanoparticles. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces. 105, 37–42 (2013).
Goswami, L. et al. Hazard remediation and recycling of tea industry and paper mill bottom ash through vermi conversion. Chemosphere 92, 708–713 (2013).
Sahariah, B., Goswami, L., Kim, K. H., Bhattacharyya, P. C. & Bhattacharya, S. S. Metal remediation and biodegradation potential of earthworm species on municipal solid waste: A parallel analysis between Metaphire posthuma and Eisenia fetida. Bioresour. Technol. 180, 230–236 (2015).
Goswami, L. et al. Exploring metal detoxification and accumulation potential during vermicomposting of Tea factory coal ash: sequential extraction and fluorescence probe analysis. Sci. Rep. 6, 30402 (2016).
Schlich, K., Klawonn, T., Terytze, K. & Hund-rinke, K. Effects of silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate in the earthworm reproduction test. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 32, 181–188 (2013).
Sherman, R. Raising earthworms successfully. EBAE 103, 83 (2003).
Samrot, A. V., Bhavya, K. S., Sahithya, C. S. & Sowmya, N. Evaluation of toxicity of chemically synthesised gold nanoparticles against Eudrilus eugeniae. J. Clust. Sci. 29, 1217–1225 (2018).
Button, M., Watts, M. J., Cave, M. R., Harrington, C. F. & Jenkin, G. T. Earthworms and in vitro physiologically-based extraction tests: complementary tools for a holistic approach towards understanding risk at arsenic-contaminated sites. Environ. Geochem. Health. 31, 273–282 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samrot, A.V., Burman, U., S, P. et al. A Study on Toxicity of Chemically Synthesised Silver Nanoparticle on Eudrilus eugeniae. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 10, 162–167 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-018-0360-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13530-018-0360-6