Abstract
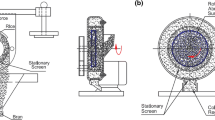
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of operating parameters including milling weight (MW; 10, 95, 220, 345, 430 g), filling ratio (FR; 1, 1.4, 2, 2.6, 3) and milling duration (MD; 6, 30, 65, 100, 124 s) on head rice yield (HRY), whiteness index (WI) and specific energy consumption (Es). The experiments were conducted based on a vertical circulation mill employing a 5 level, 3 parameters CCD design and operating parameters were optimized using response surface methodology. During the processing, MW and MD had significant negative effects on HRY. On the contrary, they both had significant positive effects on WI. All the three parameters had a significant effect on Es Taking HRY, WI, Es as the evaluative index and degree of milling, temperature rise of milled rice as the restrictive index, the best combination of operating parameters was obtained, namely MW of 345 g, FR of 2.6 and MD of 30 s. The Pearson correlation coefficients between all the milling qualities were analyzed. Results showed that the temperature rise as an easy measurement index was highly correlated with the other qualities. The regression models between temperature rise and the other milling quality indices can assist in evaluating the quality of milled rice quickly and quantifiably.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad U, Alfaro L, Yeboah-Awudzi M, Kyereh E, Dzandu B, Bonilla F et al (2017) Influence of milling intensity and storage temperature on the quality of catahoula rice (oryza sativa, L.). LWT - Food Sci Technol 75:386–392
Andrews SB, Siebenmorgen TJ, Mauromoustakos A (1992) Evaluation of the mcgill No. 2 rice miller. Cereal Chem 69(1):35–43
Bello MO, Loubes MA, Aguerre RJ, Tolaba MP (2015) Hydrothermal treatment of rough rice: effect of processing conditions on product attributes. J Food Sci Technol 52(8):5156–5163
Copper C, Siebenmorgen TJ (2007) Correcting head rice yield for surface lipid content (Degree of Milling) variation. Cereal Chem 84(1):88–91
Gujral HS, Singh J, Sodhi NS, Singh N (2002) Effect of milling variables on the degree of milling of unparboiled and parboiled rice. Int J Food Prop 5(1):193–204
Han YL, Jia FG, Zeng Y, Jiang LW, Zhang YX, Cao B (2016) Effects of rotation speed and outlet opening on particle flow in a vertical rice mill. Powder Technol 297:153–164
Jia FG, Nan JF, Bai SG (2006) Study on the relationship between the moisture content of rice and milling characteristics. J Northeast Agric Univ 37(5):665–668
Kim SY, Lee H (2012) Effects of quality characteristics on milled rice produced under different milling conditions. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 55(5):643–649
Lamberts L, Bie ED, Vandeputte GE et al (2007) Effect of milling on colour and nutritional properties of rice. Food Chem 100(4):1496–1503
Laokuldilok T, Surawang S, Klinhom J (2013) Effect of milling on the color, nutritional properties, and antioxidant contents of glutinous black rice. Cereal Chem 90(6):552–557
Mir SA, Bosco SJD, Shah MA, Mir MM, Ganai SA (2015) Rice: parboiling and milling properties. Int J Food Eng 11(6):777–787
Mohapatra D, Bal S (2004a) Wear of rice in an abrasive milling operation, part 1: prediction of degree of milling. Biosyst Eng 88(3):337–342
Mohapatra D, Bal S (2004b) Wear of rice in an abrasive milling operation, part II: prediction of bulk temperature rise. Biosyst Eng 89(1):101–108
Mohapatra D, Bal S (2007) Effect of degree of milling on specific energy consumption, optical measurements and cooking quality of rice. J Food Eng 80(1):119–125
Mohapatra D, Bal S (2010) Optimization of polishing conditions for long grain basmati rice in a laboratory abrasive mill. Food Bioprocess Technol 3(3):466–472
Monks JLF, Vanier NL, Casaril J, Berto RM, Oliveira MD, Gomes CB et al (2013) Effects of milling on proximate composition, folic acid, fatty acids and technological properties of rice. J Food Compos Anal 30(2):73–79
Pan ZL, Thompson JF, Amaratunga KSP, Anderson T, Zheng XZ (2005) Effect of cooling methods and milling procedures on the appraisal of rice milling quality. Trans ASABE 48(5):1865–1871
Pan ZL, Amaratunga KSP, Thompson JF (2007) Relationship between rice sample milling conditions and milling quality. Trans ASABE 50(4):1307–1313
Pan ZL, Khir R, Thompson JF (2013) Effect of milling temperature and postmilling cooling procedures on rice milling quality appraisals. Cereal Chem 90(2):107–113
Park JK, Kim SS, Kim KO (2007) Effect of milling ratio on sensory properties of cooked rice and on physicochemical properties of milled and cooked rice. Cereal Chem 78(2):151–156
Prasert W, Suwannaporn P (2009) Optimization of instant jasmine rice process and its physicochemical properties. J Food Eng 95(1):54–61
Rahaman MA, Miah MAK, Ahmed A (1996) Status of rice processing technology in Bangladesh. Ama Agric Mech Asia Afr Latin Am 27(1):46–50
Roberts RL (1979) Composition and taste evaluation of rice milled to different degrees. J Food Sci 44(1):127–129
Roberts RL, Wasserman T (1977) Effect of milling conditions on yields, milling time and energy requirements in a pilot scale engelberg rice mill. J Food Sci 42(3):802–803
Rodríguezarzuaga M, Cho S, Billiris MA, Siebenmorgen T, Seo H (2016) Impacts of degree of milling on the appearance and aroma characteristics of raw rice. J Sci Food Agric 96(9):3017–3022
Roy P, Ijiri T, Okadome H, Nei D, Orikasa T, Nakamura N et al (2008) Effect of processing conditions on overall energy consumption and quality of rice (oryza sativa, L.). J Food Eng 89(3):343–348
Sandhu RS, Singh N, Kaler RSS, Kaur A, Shevkani K (2018) Effect of degree of milling on physicochemical, structural, pasting and cooking properties of short and long grain indica rice cultivars. Food Chem 260:231–238
Singh N, Singh H, Kaur K, Singh MB (2000) Relationship between the degree of milling, ash distribution pattern and conductivity in brown rice. Food Chem 69:147–151
Srikham W, Noomhorm A (2015) Milling quality assessment of khao dok mali 105, milled rice by near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy technique. J Food Sci Technol 52(11):7500–7506
Sun H, Siebenmorgen TJ (1993) Milling characteristics of various rough rice kernel thickness fractions. Cereal Chem 70(6):727–733
Takai H, Barredo IR (1981) Milling characteristics of a friction laboratory rice mill. J Agric Eng Res 26(5):441–448
USDA (1990) Inspection handbook for the sampling, inspection, grading, and certification of rice. HB918-11, Agriculture Marketing Service, Washington, DC
Vishwakarma RK, Shivhare US, Nanda SK (2012) Predicting guar seed splitting by compression between two plates using hertz theory of contact stresses. J Food Sci 77(9):E231–E239
Yadav BK, Jindal VK (2008) Changes in head rice yield and whiteness during milling of rough rice (oryza sativa L.). J Food Eng 86(1):113–121
Yan TY, Hong JH, Chung JH (2005) An improved method for the production of white rice with embryo in a vertical mill. Biosyst Eng 92(3):317–323
Yoon SH, Kim SK (2004) Physicochemical properties of rice differing in milling degrees. Food Sci Biotechnol 13(1):57–62
Acknowledgements
The authors express their acknowledgment to the Chinese Natural Science Foundation (51575098) for financial support and all of the persons who assisted in this writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Jia, F., Xiao, Y. et al. Effect of operating parameters on milling quality and energy consumption of brown rice. J Food Sci Technol 56, 674–682 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3522-2
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-018-3522-2