Abstract
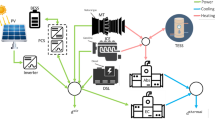
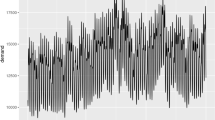
Hydro storage system optimization is becoming one of the most challenging tasks in energy finance. While currently the state-of-the-art of the commercial software in the industry implements mainly linear models, we would like to introduce risk aversion and a generic utility function. At the same time, we aim to develop and implement a computational efficient algorithm, which is not affected by the curse of dimensionality and does not utilize subjective heuristics to prevent it. For the short term power market we propose a simultaneous solution for both dispatch and bidding problems. Following the Blomvall and Lindberg (Eur J Oper Res 143(2):452–461, 2002) interior point model, we set up a stochastic multiperiod optimization procedure by means of a “bushy”recombining tree that provides fast computational results. Inequality constraints are packed into the objective function by the logarithmic barrier approach and the utility function is approximated by its second order Taylor polynomial. The optimal solution for the original problem is obtained as a diagonal sequence where the first diagonal dimension is the parameter controlling the logarithmic penalty and the second one is the parameter for the Newton step in the construction of the approximated solution. Optimal intraday electricity trading and water values for hydroassets as shadow prices are computed. The algorithm is implemented in Mathematica.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abgottspon, H.: Hydro power planning: multi-horizon modeling and its applications. Diss. ETH No. 22729 (2015)
Amini, M.H., Boroojeni, K.G., Iyengar, S.S., Pardalos, P.M., Rahmani, M.: An economic dispatch algorithm for congestion management of smart power networks: an oblivious routing approach. Energy Syst. 8, 643667 (2017)
Artzner, P., Delbaen, F., Eber, J.-M., Heath, D.: Coherent measures of risk. Math. Finance 9(3), 203–228 (1999)
Askew, A.J.: Optimum reservoir operating policies and the imposition of a reliability constraint. Water Resour. Res. 10(1), 51–56 (1974)
Barroso, L., Rebennack, S., Steeger, G.: Optimal bidding strategies for hydro-electric producers: a literature survey. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 29(4), 1758–1766 (2014)
Bellman, R.: Dynamic Programming. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1957)
Bertsekas, D., Shreve, S.E.: Stochastic Optimal Control: The Discrete-Time Case. Athena Scientific, Belmont (1996)
Bertsekas, D.: Dynamic Programming and Optimal Control, Optimization and Computation Series, vol. 1. Athena Scientific, Belmont (2005)
Blomvall, J., Lindberg, P.O.: Validation of a Riccati-Based Primal Interior Point Solver for Multistage Stochastic Programming. University of Linköping, Department of Mathematics (2000)
Blomvall, J., Lindberg, P.O.: A Riccati-based primal interior point solver for multistage stochastic programming. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 143(2), 452–461 (2002)
Blomvall, J., Lindberg, P.O.: A Riccati-based primal interior point solver for multistage stochastic programming-extensions. Optim. Methods Softw. 17, 383–407 (2002)
Blomvall, J., Lindberg, P.O.: A multistage stochastic programming algorithm suitable for parallel computing. J. Parallel Comput. Spec. Issue Parallel Comput. Numer. Optim 29(4), 431–445 (2003)
Blomvall, J., Lindberg, P.O.: Back-testing the performance of an actively managed option portfolio at the Swedish stock market, 1990–1999. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 27(6), 1099–1112 (2003)
Costa, J. D., Shapiro, A., Soares, M., Tekaya, W.: Multistage energy planning—risk neutral and risk averse approaches. In: XII SEPOPE: symposium of specialists in electric operational and expansion planning (2012)
Densing, M.: Hydro-electric power plant dispatch-planning: multi-stage stochastic programming with time-consistent constraints on risk. Diss. ETH No. 17244 (2007)
Dueholm, L., Ravn, H.F.: Modelling of short term electricity prices, hydro inflow and water values. In: Proceedings of the 6th IAEE European conference, Zurich (2004)
Egerer, J., Scharff, R., Söder, L.: A description of the operative decision-making process of a power generating company on the Nordic electricity market. Energy Syst. 5(2), 349–369 (2014)
Gjelsvik, A., Grundt, A., Mo, B.: Integrated risk management of hydro power scheduling and contract management. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 16(2), 216–221 (2001)
Farinelli, S., Vanini, P.: Joint interest rate risk management of balance sheet and hedge portfolio. Icfai Univ. J. Financ. Risk Manag. V(3), 28–56 (2008)
Farinelli, S., Tibiletti, L.: Portfolio management and stochastic optimization in discrete time: an application to intraday electricity trading and water values for hydroassets. In: Operations research proceedings 2015 selected papers of the international conference of the German, Austrian and Swiss operations research societies (GOR, ÖGOR, SVOR/ASRO), University of Vienna, Austria, September 1–4, 2015, Dörner, K.F., Ljubic, I., Pflug, G., Tragler, G. (Eds.), Springer Verlag. ISBN:978-3-319-42901-4. Forthcoming (2017)
Fleten, S.-E., Wallace, S.W.: Stochastic programming models in energy. In: Ruszczynski, A., Shapiro, A. (eds.) Stochastic Programming, Handbooks in Operations Research and Management Science, vol. 10, pp. 637–677. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2003)
Fleten, S.-E., Kristoffersen, T.K.: Stochastic programming for optimizing bidding strategies of a Nordic hydropower producer. EJOR 181(2), 916–928 (2007)
Fleten, S.-E., Kristoffersen, T.K.: Short-term hydropower production planning by stochastic programming. Comput. Oper. Res. 35(8), 2656–2671 (2008)
Fleten, S.-E., Kristoffersen, T.K.: Stochastic programming models for short-term power generation scheduling and bidding. In: Bjørndal, E., Bjørndal, M., Pardalos, P., Rönnqvist, M. (eds.) Energy, Natural Resources and Environmental Economics, Energy Systems. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Frances, D., Kwon, R.H.: Optimization-based bidding in day-ahead electricity auction markets: a review of models for power producers. In: Sorokin, A., Rebennack, S., Pardalos, P., Iliadis, N., Pereira, M. (eds.) Handbook of Networks in Power Systems I. Energy Systems. Springer, Berlin (2012)
García-González, J., Mateo, A., Parrilla, E.: Risk-averse profit-Based optimal scheduling of a hydro-chain in the day-ahead Electr. Market. EJOR 181(3), 1354–1369 (2007)
Horsley, A., Wrobel, A.: Profit-maximizing operation and valuation of hydroelectric plant: a new solution to the Koopmans problem. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 31(3), 938–970 (2007)
Labadie, J.W.: Optimal operation of multireservoir systems: state-of-the-art review. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 130(2), 93–111 (2004)
Larsson, Y., Stage, S.: Incremental cost of water power. Trans AIEE 80(3), 361–365 (1961)
Li, G., Shi, J., Qu, X.: Modeling methods for GENCO bidding strategy optimization in the liberalized electricity spot market—a state of the art review. Energy 36(8), 4686–4700 (2011)
Löhndorf, N., Minner, S., Wozabal, D.: Optimizing trading decisions for hydro storage systems using approximate dual dynamic programming. Oper. Res. 61(4), 810–823 (2013)
Löhndorf, N., Minner, S.: Optimal day-ahead trading and storage of renewable energies—an approximate dynamic programming approach. Energy Syst. 1, 61–77 (2010)
Loucks, D.P., Stedinger, J.R., Sule, B.F.: Stochastic dynamic programming models for reservoir operation optimization. Water Resour. Res. 20(11), 1499–1505 (1984)
Luenberger, D.G.: Optimization by Vector Space Methods. Wiley Professional Paperback Series. Wiley, New York (1997)
Minoux, M.: Mathematical Programming: Theory and Algorithms. Wiley, New York (1986)
Paraschiv, F., Kovacevic, R.M., Schürle, M.: Optimization of hydro storage systems and indifference pricing of power contracts. In: Presentation at energy finance conference 2015. Cass Business School, London (2015)
Pflug, G., Pichler, A.: Multistage Stochastic Optimization Springer Series in Operations Research and Financial Engineering. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Powell, W.B.: Approximate Dynamic Programming. Wiley, New york (2011)
Rockafellar, R.T.: Convex Analysis. Princeton Landmarks in Mathematics and Physics. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1996)
Ruszczyński, A.: Risk-averse dynamic programming for Markov decision processes. Math. Programm. 125(2), 235–261 (2010)
Riedel, F.: Dynamic coherent risk measures. Stoch. Process. Appl. 112(2), 185–200 (2004)
Römisch, W.: Scenario reduction techniques in stochastic programming. In: Watanabe, O., Zeugmann, T. (eds.) Stochastic Algorithms: Foundations and Applications, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 5792, pp. 1–14. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Rossman, L.A.: Reliability-constrained dynamic programing and randomized release rules in reservoir management. Water Resour. Res. 13(2), 247–255 (1977)
Sniedovich, M.: Reliability-constrained reservoir control problems: 1. Methodological issues. Water Resour. Res. 15(6), 1574–1582 (1979)
Yakowitz, S.: Dynamic programming applications in water resources. Water Resour. Res. 18(4), 673–696 (1982)
Yamin, H.: Review on methods of generation scheduling in electric power systems. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 69(2–3), 227–248 (2004)
Young, G.: Finding reservoir operating rules. J. Hydraul. Div. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 93(6), 297–321 (1967)
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Sai Anand, Rémi Janner, Nick Schäfer and Hubert Abgottspon for their hints and their very valuable feedbacks. The usual caveat applies.
Disclaimer The opinions expressed in this document are our own and do not necessarily reflect those of Core Dynamics GmbH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farinelli, S., Tibiletti, L. Hydroassets portfolio management for intraday electricity trading from a discrete time stochastic optimization perspective. Energy Syst 10, 21–57 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-017-0258-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12667-017-0258-4