Abstract
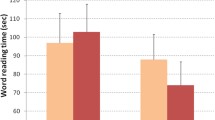
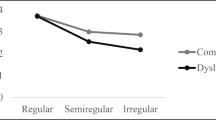
This study aimed to examine the effects of temporal processing training on the reading abilities of Chinese children with dyslexia. In total, 69 Chinese children with dyslexia in grades three through six were recruited in Taiwan. The children were divided into the following three equal groups: (1) auditory temporal processing training group, (2) visual temporal processing training group, and (3) control group with no specific training. The participants in both training groups received instruction with identical durations (30–40 min), intensities (12 times in total), and frequencies (three to four times per week). The participants in the control group were asked to independently surf some specified websites using devices similar to those used by the two experimental groups for an identical duration, intensity, and frequency. Our results indicated that the two groups who received temporal processing training exhibited significant correlations among Chinese character reading, rapid naming, and corresponding reading-related abilities, while visual temporal processing served as a significant predictor of Chinese character reading ability even if all background data, reading-related abilities, and auditory temporal processing were introduced first. Additionally, significant interactions were found between the Groups and Tested sessions in all the measures, except for phonological awareness, confirming the distinct effects of different temporal processing on most measures involved in this study. Further simple main effects revealed that only those who received the visual temporal processing training gained benefits in the corresponding reading-related ability (i.e., orthographic knowledge) and far-transfer to Chinese character reading.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alais, D., Cass, J., O’Shea, R. P., & Blake, R. (2010). Visual sensitivity underlying changes in visual consciousness. Current Biology, 20(15), 1362–1367.
Basu, M., Krishnan, A., & Weber-Fox, C. (2010). Brainstem correlates of temporal auditory processing in children with specific language impairment. Developmental Science, 13(1), 77–91.
Becker, B. J. (1988). Synthesizing standardized mean-change measures. British Journal of Mathematical and Statistical Psychology, 41(2), 257–278.
Becker, C., Elliott, M. A., & Lachmann, T. (2005). Evidence for impaired visuoperceptual organisation in developmental dyslexics and its relation to temporal processes. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 22(5), 499–522.
Boets, B., Wouters, J., van Wieringen, A., & Ghesquière, P. (2007). Auditory processing, speech perception and phonological ability in pre-school children at high-risk for dyslexia: a longitudinal study of the auditory temporal processing theory. Neuropsychologia, 45(8), 1608–1620.
Bretherton, L., & Holmes, V. M. (2003). The relationship between auditory temporal processing, phonemic awareness, and reading disability. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 84(3), 218–243.
Breznitz, Z., & Misra, M. (2003). Speed of processing of the visual–orthographic and auditory–phonological systems in adult dyslexics: the contribution of “asynchrony” to word recognition deficits. Brain and Language, 85(3), 486–502.
Catts, H. W., Gillispie, M., Leonard, L. B., Kail, R. V., & Miller, C. A. (2002). The role of speed of processing, rapid naming, and phonological awareness in reading achievement. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 35(6), 510–525.
Caylak, E. (2011). The auditory temporal processing deficit theory in children with developmental dyslexia. Journal of Pediatric Neurology, 09(02), 151–168.
Chen, H. C., Chang, L. Y., Chiou, Y. S., Sung, Y. T., & Chang, K. E. (2011). Chinese orthographic database and its application in teaching Chinese characters. Bulletin of Educational Psychology, 43(Special Issue), 269–290.
Chen, J. H., & Chen, H. Y. (2006). Raven’s progressive matrices-parallel manual. Taipei, Taiwan: Chinese Behavioral Science Corporation.
Cheung, H., Chung, K. K. H., Wong, S. W. L., McBride-Chang, C., Penney, T. B., & Ho, C. S. H. (2009). Perception of tone and aspiration contrasts in Chinese children with dyslexia. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(6), 726–733.
Chung, K. K. H., McBride-Chang, C., Cheung, H., & Wong, S. W. L. (2013). General auditory processing, speech perception and phonological awareness skills in Chinese-English biliteracy. Journal of Research in Reading, 36(2), 202–222.
Chung, K. K. H., McBride-Chang, C., Wong, S. W. L., Cheung, H., Penney, T. B., & Ho, C. S. H. (2008). The role of visual and auditory temporal processing for Chinese children with developmental dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 58(1), 15–35.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Earlbaum Associates.
Coltheart, M., & Rastle, K. (1994). Serial processing in reading aloud: evidence for dual-route models of reading. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 20(6), 1197–1211.
Corrigall, K. A., Schellenberg, E. G., & Misura, N. M. (2013). Music training, cognition, and personality. Frontiers in Psychology, 4, 222.
DeFrancis, J. (1989). Visible speech: the diverse oneness of writing systems. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press.
Donohue, S. E., Woldorff, M. G., & Mitroff, S. R. (2010). Video game players show more precise multisensory temporal processing abilities. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 72(4), 1120–1129.
Farmer, M. E., & Klein, R. M. (1995). The evidence for a temporal processing deficit linked to dyslexia: a review. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 2(4), 460–493.
Fortes, I. S., Paula, C. S., Oliveira, M. C., Bordin, I. A., de Jesus Mari, J., & Rohde, L. A. (2016). A cross-sectional study to assess the prevalence of DSM-5 specific learning disorders in representative school samples from the second to sixth grade in Brazil. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 25(2), 195–207.
Fostick, L., Eshcoly, R., Shtibelman, H., Nehemia, R., & Levi, H. (2014). Efficacy of temporal processing training to improve phonological awareness among dyslexic and normal reading students. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 40(5), 1799–1807.
Gaab, N., Gabrieli, J. D., Deutsch, G. K., Tallal, P., & Temple, E. (2007). Neural correlates of rapid auditory processing are disrupted in children with developmental dyslexia and ameliorated with training: an fMRI study. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience, 25(3–4), 295–310.
Georgiou, G. K., Protopapas, A., Papadopoulos, T. C., Skaloumbakas, C., & Parrila, R. (2010). Auditory temporal processing and dyslexia in an orthographically consistent language. Cortex, 46(10), 1330–1344.
Halliday, L. F., Taylor, J. L., Millward, K. E., & Moore, D. R. (2012). Lack of generalization of auditory learning in typically developing children. Journal of Speech Language and Hearing Research, 55(1), 168–181.
Hari, R., & Renvall, H. (2001). Impaired processing of rapid stimulus sequences in dyslexia. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 5(12), 525–532.
Hoosain, R. (1992). Psychological reality of the word in Chinese. In H. Chen & O. Tzeng (Eds.), Language processing in Chinese (pp. 111–130). Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers.
Huang, H. S. (2001). Chinese Character Recognition Test. Taipei, Taiwan: Psychological Publishing, Co., Ltd.
Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Jonides, J., & Perrig, W. J. (2008). Improving fluid intelligence with training on working memory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(19), 6829–6833.
Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Shah, P., & Jonides, J. (2014). The role of individual differences in cognitive training and transfer. Memory & Cognition, 42(3), 464–480.
Klein, R. M. (2002). Observations on the temporal correlates of reading failure. Reading and Writing, 15(1), 207–231.
Landerl, K., & Willburger, E. (2010). Temporal processing, attention, and learning disorders. Learning and Individual Differences, 20(5), 393–401.
Li, X., Rayner, K., & Cave, K. R. (2009). On the segmentation of Chinese words during reading. Cognitive Psychology, 58(4), 525–552.
Liu, C., & Georgiou, G. K. (2017). Cognitive and environmental correlates of rapid automatized naming in Chinese kindergarten children. Journal of Educational Psychology, 109(4), 465–476.
Liu, D., Chen, X., & Chung, K. K. H. (2015). Performance in a visual search task uniquely predicts reading abilities in third-grade Hong Kong Chinese children. Scientific Studies of Reading, 19(4), 307–324.
Liu, D., Chen, X., & Wang, Y. (2016). The impact of visual-spatial attention on reading and spelling in Chinese children. Reading and Writing, 29(7), 1435–1447.
Liu, Y., Georgiou, G. K., Zhang, Y., Li, H., Liu, H., Song, S., et al. (2017). Contribution of cognitive and linguistic skills to word-reading accuracy and fluency in Chinese. International Journal of Educational Research, 82, 75–90.
Lyon, G. R., Shaywitz, S. E., & Shaywitz, B. A. (2003). A definition of dyslexia. Annals of Dyslexia, 53(1), 1–14.
Mattingly, I. G. (1984). Reading, linguistic awareness, and language acquisition. In J. Downing & R. Valtin (Eds.), Language awareness and learning to read (pp. 9–25). New York, NY: Springer New York.
McBride-Chang, C., Bialystok, E., Chong, K. K. Y., & Li, Y. (2004). Levels of phonological awareness in three cultures. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 89(2), 93–111.
McBride, C. A. (2016). Is Chinese special? Four aspects of Chinese literacy acquisition that might distinguish learning Chinese from learning alphabetic orthographies. Educational Psychology Review, 28(3), 523–549.
Melby-Lervåg, M., & Hulme, C. (2013). Is working memory training effective? A meta-analytic review. Developmental Psychology, 49(2), 270–291.
Meng, X., Sai, X., Wang, C., Wang, J., Sha, S., & Zhou, X. (2005). Auditory and speech processing and reading development in Chinese school children: behavioural and ERP evidence. Dyslexia, 11(4), 292–310.
Morris, S. B. (2008). Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organizational Research Methods, 11(2), 364–386.
Murphy, C. F. B., & Schochat, E. (2010). Generalization of temporal order detection skill learning: two experimental studies of children with dyslexia. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 43(4), 359–366.
Norton, E. S., Black, J. M., Stanley, L. M., Tanaka, H., Gabrieli, J. D. E., Sawyer, C., & Hoeft, F. (2014). Functional neuroanatomical evidence for the double-deficit hypothesis of developmental dyslexia. Neuropsychologia, 61, 235–246.
Pinheiro, F. H., & Capellini, S. A. (2010). Auditory training in students with learning disabilities. Pró-Fono Revista de Atualização Científica, 22(1), 49–54.
Plaza, M., & Cohen, H. (2003). The interaction between phonological processing, syntactic awareness, and naming speed in the reading and spelling performance of first-grade children. Brain and Cognition, 53(2), 287–292.
Powers, K. L., Brooks, P. J., Aldrich, N. J., Palladino, M. A., & Alfieri, L. (2013). Effects of video-game play on information processing: a meta-analytic investigation. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 20(6), 1055–1079.
Ramus, F. (2001). Talk of two theories. Nature, 412(6845), 393–394.
Ramus, F., & Ahissar, M. (2012). Developmental dyslexia: the difficulties of interpreting poor performance, and the importance of normal performance. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 29(1–2), 104–122.
Rayner, K., Slattery, T. J., & Bélanger, N. N. (2010). Eye movements, the perceptual span, and reading speed. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 17(6), 834–839.
Schulte-Körne, G., Deimel, W., Bartling, J., & Remschmidt, H. (1999). The role of phonological awareness, speech perception, and auditory temporal processing for dyslexia. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 8(S3), S28–S34.
Siok, W. T., & Fletcher, P. (2001). The role of phonological awareness and visual-orthographic skills in Chinese reading acquisition. Developmental Psychology, 37(6), 886–899.
Stauffer, C. C., Haldemann, J., Troche, S. J., & Rammsayer, T. H. (2012). Auditory and visual temporal sensitivity: evidence for a hierarchical structure of modality-specific and modality-independent levels of temporal information processing. Psychological Research, 76(1), 20–31.
Steinbrink, C., Zimmer, K., Lachmann, T., Dirichs, M., & Kammer, T. (2014). Development of rapid temporal processing and its impact on literacy skills in primary school children. Child Development, 85(4), 1711–1726.
Strehlow, U., Haffner, J., Bischof, J., Gratzka, V., Parzer, P., & Resch, F. (2006). Does successful training of temporal processing of sound and phoneme stimuli improve reading and spelling? European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 15(1), 19–29.
Tallal, P. (2000). Experimental studies of language learning impairments: from research to remediation. In D. Bishop & L. Leonard (Eds.), Speech and language impairments in children: causes, characteristics, intervention and outcome (pp. 131–155). Hove: Psychology Press.
Tong, X., McBride-Chang, C., Shu, H., & Wong, A. M. Y. (2009). Morphological awareness, orthographic knowledge, and spelling errors: keys to understanding early Chinese literacy acquisition. Scientific Studies of Reading, 13(5), 426–452.
Torgesen, J. K., Wagner, R. K., & Rashotte, C. A. (1994). Longitudinal studies of phonological processing and reading. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 27(5), 276–286.
Tzeng, Y.-L., Hsu, C.-H., Lin, W.-H., & Lee, C.-Y. (2018). Impaired orthographic processing in Chinese dyslexic children: evidence from the lexicality effect on N400. Scientific Studies of Reading, 22(1), 85–100.
Vlachos, F., Avramidis, E., Dedousis, G., Chalmpe, M., Ntalla, I., & Giannakopoulou, M. (2013). Prevalence and gender ratio of dyslexia in Greek adolescents and its association with parental history and brain injury. American Journal of Educational Research, 1(1), 22–25.
Waber, D. P., Weiler, M. D., Wolff, P. H., Bellinger, D., Marcus, D. J., Ariel, R., et al. (2001). Processing of rapid auditory stimuli in school-age children referred for evaluation of learning disorders. Child Development, 72(1), 37–49.
Wang, L.-C., Liu, D., Chen, J.-K., & Wu, Y.-C. (2018). Processing speed of dyslexia: the relationship between temporal processing and rapid naming in Chinese. Reading and Writing, 31(7), 1645–1668.
Wang, L.-C., & Yang, H.-M. (2018). Temporal processing development in Chinese primary school-aged children with dyslexia. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 51(3), 302–312.
Wang, L. C. (2017). Effects of phonological training on the reading and reading-related abilities of Hong Kong children with dyslexia. Frontiers in Psychology, 8, 1904.
Williams, C., & Bever, T. (2010). Chinese character decoding: a semantic bias? Reading and Writing, 23(5), 589–605.
Wolf, M., & Bowers, P. G. (2000). Naming-speed processes and developmental reading disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 33(4), 322–324.
Wolf, M., Bowers, P. G., & Biddle, K. (2000). Naming-speed processes, timing, and reading. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 33(4), 387–407.
Yang, L.-Y., Guo, J.-P., Richman, L. C., Schmidt, F. L., Gerken, K. C., & Ding, Y. (2013). Visual skills and Chinese reading acquisition: a meta-analysis of correlation evidence. Educational Psychology Review, 25(1), 115–143.
Zhang, J., & McBride-Chang, C. (2010). Auditory sensitivity, speech perception, and reading development and impairment. Educational Psychology Review, 22(3), 323–338.
Zhang, J., & McBride-Chang, C. (2014). Auditory sensitivity, speech perception, L1 Chinese, and L2 English reading abilities in Hong Kong Chinese children. Developmental Psychology, 50(4), 1001–1013.
Zukowski, A., & Treiman, R. (2013). Levels of phonological awareness. In S. Brady & D. Shankweiler (Eds.), Phonological processes in literacy (pp. 95–112). London: Routledge.
Funding
The work described in this article was supported by the Departmental Research Seed Fund of Department of Special Education and Counselling at the Education University of Hong Kong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, LC., Liu, D. & Xu, Z. Distinct effects of visual and auditory temporal processing training on reading and reading-related abilities in Chinese children with dyslexia. Ann. of Dyslexia 69, 166–185 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-019-00176-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-019-00176-8