Abstract
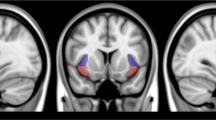
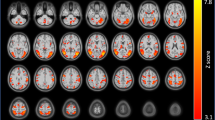
Damage to the insular cortex has been shown to disrupt smoking behavior. However, whether smoking cessation outcomes are associated with abnormal functions of insula and its subregions remains unclear. In this study, we investigated the relationship between insular functions (interregional functional connectivity and regional activity) and treatment outcomes of cigarette smoking. Thirty treatment-seeking smokers were recruited into the treatment study and underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans immediately before and after the treatment. Sixteen participants remained abstinent from smoking (quitters), while 14 relapsed to smoking (relapers). Changes in resting-state functional connectivity and fractional amplitude of low frequency fluctuation (fALFF) across groups and visits were assessed using repeated measures ANCOVA. Significant interaction effects were detected: 1) between the left anterior insula and left precuneus; and 2) between the right anterior insula and left precuneus and medial frontal gyrus. Post-hoc region-of-interest analyses in brain areas showing interaction effects indicated significantly increased functional connectivity after treatment compared with before treatment in quitters but opposite longitudinal changes in relapsers. However, no significant effects in fALFF were observed. These novel findings suggest that increased interregional functional connectivity of the anterior insula is associated with improved smoking cessation outcome: individuals with increased functional connectivity of the anterior insula during the treatment would more likely quit smoking successfully. These insular circuits may serve as therapeutic targets for more efficacious treatment of nicotine addiction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdolahi, A., Williams, G. C., Benesch, C. G., Wang, H. Z., Spitzer, E. M., Scott, B. E., et al. (2015). Damage to the insula leads to decreased nicotine withdrawal during abstinence. Addiction (Abingdon, England), 110(12), 1994–2003.
Addicott, M. A., Sweitzer, M. M., Froeliger, B., Rose, J. E., & McClernon, F. J. (2015). Increased functional connectivity in an insula-based network is associated with improved smoking cessation outcomes. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 40(11), 2648–2656.
Bi, Y., Yuan, K., Guan, Y., Cheng, J., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2017). Altered resting state functional connectivity of anterior insula in young smokers. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 11(1), 155–165.
Brody, A. L., Mandelkern, M. A., London, E. D., Childress, A. R., Lee, G. S., Bota, R. G., et al. (2002). Brain metabolic changes during cigarette craving. Archives of General Psychiatry, 59(12), 1162–1172.
Buhle, J. T., Silvers, J. A., Wager, T. D., Lopez, R., Onyemekwu, C., Kober, H., et al. (2014). Cognitive reappraisal of emotion: A meta-analysis of human neuroimaging studies. Cerebral cortex (New York, NY : 1991), 24(11), 2981–2990.
Cahill, K., Stead, L. F., & Lancaster, T. (2010). Nicotine receptor partial agonists for smoking cessation. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (12), CD006103.
Cauda, F., D'Agata, F., Sacco, K., Duca, S., Geminiani, G., & Vercelli, A. (2011). Functional connectivity of the insula in the resting brain. NeuroImage, 55(1), 8–23.
Chang, L. J., Yarkoni, T., Khaw, M. W., & Sanfey, A. G. (2013). Decoding the role of the insula in human cognition: Functional parcellation and large-scale reverse inference. Cerebral cortex (New York, NY : 1991), 23(3), 739–749.
Chen, Z., Peto, R., Zhou, M., Iona, A., Smith, M., Yang, L., et al. (2015). Contrasting male and female trends in tobacco-attributed mortality in China: Evidence from successive nationwide prospective cohort studies. Lancet (London, England), 386(10002), 1447–1456.
Craig, A. D. (2002). How do you feel? Interoception: The sense of the physiological condition of the body. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 3(8), 655–666.
Deen, B., Pitskel, N. B., & Pelphrey, K. A. (2011). Three systems of insular functional connectivity identified with cluster analysis. Cerebral cortex (New York, NY : 1991), 21(7), 1498–1506.
Dinur-Klein, L., Dannon, P., Hadar, A., Rosenberg, O., Roth, Y., Kotler, M., et al. (2014). Smoking cessation induced by deep repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the prefrontal and insular cortices: A prospective, randomized controlled trial. Biological Psychiatry, 76(9), 742–749.
Dosenbach, N. U., Fair, D. A., Miezin, F. M., Cohen, A. L., Wenger, K. K., Dosenbach, R. A., et al. (2007). Distinct brain networks for adaptive and stable task control in humans. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(26), 11073–11078.
Engelmann, J. M., Versace, F., Robinson, J. D., Minnix, J. A., Lam, C. Y., Cui, Y., et al. (2012). Neural substrates of smoking cue reactivity: A meta-analysis of fMRI studies. NeuroImage, 60(1), 252–262.
Fagerstrom, K. O., & Schneider, N. G. (1989). Measuring nicotine dependence: A review of the Fagerstrom tolerance questionnaire. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 12(2), 159–182.
Hayashi, T., Ko, J. H., Strafella, A. P., & Dagher, A. (2013). Dorsolateral prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortex interactions during self-control of cigarette craving. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(11), 4422–4427.
Honey, C. J., Kotter, R., Breakspear, M., & Sporns, O. (2007). Network structure of cerebral cortex shapes functional connectivity on multiple time scales. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(24), 10240–10245.
Janes, A. C., Pizzagalli, D. A., Richardt, S., de, B. F. B., Chuzi, S., Pachas, G., et al. (2010). Brain reactivity to smoking cues prior to smoking cessation predicts ability to maintain tobacco abstinence. Biological Psychiatry, 67(8), 722–729.
Kalivas, P. W., & Volkow, N. D. (2005). The neural basis of addiction: A pathology of motivation and choice. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 162(8), 1403–1413.
Kelly, C., Toro, R., Di Martino, A., Cox, C. L., Bellec, P., Castellanos, F. X., et al. (2012). A convergent functional architecture of the insula emerges across imaging modalities. NeuroImage, 61(4), 1129–1142.
Kober, H., Mende-Siedlecki, P., Kross, E. F., Weber, J., Mischel, W., Hart, C. L., et al. (2010). Prefrontal-striatal pathway underlies cognitive regulation of craving. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(33), 14811–14816.
Larson-Prior, L. J., Zempel, J. M., Nolan, T. S., Prior, F. W., Snyder, A. Z., & Raichle, M. E. (2009). Cortical network functional connectivity in the descent to sleep. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 106(11), 4489–4494.
Li, X., Hartwell, K. J., Borckardt, J., Prisciandaro, J. J., Saladin, M. E., Morgan, P. S., et al. (2013). Volitional reduction of anterior cingulate cortex activity produces decreased cue craving in smoking cessation: A preliminary real-time fMRI study. Addiction Biology, 18(4), 739–748.
Menon, V., & Uddin, L. Q. (2010). Saliency, switching, attention and control: A network model of insula function. Brain Structure & Function, 214(5–6), 655–667.
Mesulam, M. M., & Mufson, E. J. (1982a). Insula of the old world monkey. I. Architectonics in the insulo-orbito-temporal component of the paralimbic brain. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 212(1), 1–22.
Mesulam, M. M., & Mufson, E. J. (1982b). Insula of the old world monkey. III: Efferent cortical output and comments on function. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 212(1), 38–52.
Naqvi, N. H., & Bechara, A. (2010). The insula and drug addiction: An interoceptive view of pleasure, urges, and decision-making. Brain Structure & Function, 214(5–6), 435–450.
Naqvi, N. H., Rudrauf, D., Damasio, H., & Bechara, A. (2007). Damage to the insula disrupts addiction to cigarette smoking. Science (New York, N.Y.), 315(5811), 531–534.
Naqvi NH, Gaznick N, Tranel D, Bechara A (2014). The insula: a critical neural substrate for craving and drug seeking under conflict and risk. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences1316: 53–70.
Niaura, R., Jones, C., & Kirkpatrick, P. (2006). Varenicline. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 5(7), 537–538.
Picard, F., Sadaghiani, S., Leroy, C., Courvoisier, D. S., Maroy, R., & Bottlaender, M. (2013). High density of nicotinic receptors in the cingulo-insular network. NeuroImage, 79, 42–51.
Power, J. D., Barnes, K. A., Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2012). Spurious but systematic correlations in functional connectivity MRI networks arise from subject motion. NeuroImage, 59(3), 2142–2154.
Power, J. D., Mitra, A., Laumann TO, Snyder, A. Z., Schlaggar, B. L., & Petersen, S. E. (2014). Methods to detect, characterize, and remove motion artifact in resting state fMRI. NeuroImage, 84, 320–341.
Raichle, M. E., MacLeod, A. M., Snyder, A. Z., Powers, W. J., Gusnard, D. A., & Shulman, G. L. (2001). A default mode of brain function. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98(2), 676–682.
Scott, D., & Hiroi, N. (2011). Deconstructing craving: Dissociable cortical control of cue reactivity in nicotine addiction. Biological Psychiatry, 69(11), 1052–1059.
Seeley, W. W., Menon, V., Schatzberg, A. F., Keller, J., Glover, G. H., Kenna, H., et al. (2007). Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 27(9), 2349–2356.
Sridharan, D., Levitin, D. J., & Menon, V. (2008). A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(34), 12569–12574.
Stoeckel, L. E., Chai, X. J., Zhang, J., Whitfield-Gabrieli, S., & Evins, A. E. (2016). Lower gray matter density and functional connectivity in the anterior insula in smokers compared with never smokers. Addiction Biology, 21(4), 972–981.
Sutherland, M. T., McHugh, M. J., Pariyadath, V., & Stein, E. A. (2012). Resting state functional connectivity in addiction: Lessons learned and a road ahead. NeuroImage, 62(4), 2281–2295.
Uddin, L. Q. (2015). Salience processing and insular cortical function and dysfunction. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 16(1), 55–61.
Wang, C., Shen, Z., Huang, P., Yu, H., Qian, W., Guan, X., et al. (2017). Altered spontaneous brain activity in chronic smokers revealed by fractional ramplitude of low-frequency fluctuation analysis: A preliminary study. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 328.
Wang, C., Huang, P., Shen, Z., Qian, W., Li, K., Luo, X., et al. (2019). Gray matter volumes of insular subregions are not correlated with smoking cessation outcomes but negatively correlated with nicotine dependence severity in chronic smokers. Neuroscience Letters, 696, 7–12.
Whitney, C., Kirk, M., O'Sullivan, J., Lambon Ralph, M. A., & Jefferies, E. (2011). The neural organization of semantic control: TMS evidence for a distributed network in left inferior frontal and posterior middle temporal gyrus. Cerebral cortex (New York, NY : 1991), 21(5), 1066–1075.
Wu, G., Yang, S., Zhu, L., & Lin, F. (2015). Altered spontaneous brain activity in heavy smokers revealed by regional homogeneity. Psychopharmacology, 232(14), 2481–2489.
Yan, C. G., Wang, X. D., Zuo, X. N., Zang, Y. F. (2016). DPABI: Data Processing & Analysis for (Resting-State) Brain Imaging. Neuroinformatics 14, 339–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12021-016-9299-4.
Zhang, D., & Raichle, M. E. (2010). Disease and the brain's dark energy. Nature Reviews Neurology, 6(1), 15–28.
Funding
This research was supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. LQ18H180001, Zhejiang Medicine and Health Science and Technology Program under Grant nos.2017KY080 and 2018KY418, National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant nos. 81,171,310 and 81,701,647. YY was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Shen, Z., Huang, P. et al. Increased interregional functional connectivity of anterior insula is associated with improved smoking cessation outcome. Brain Imaging and Behavior 14, 408–415 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00197-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00197-2