Abstract
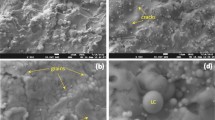
Our previous work demonstrated the good biocompatibility and bactericidal activity of a plasma-sprayed Zn and Ag co-incorporated calcium silicate ceramic coating (Ag-Ca2ZnSi2O7), namely Ag-HT. In this work, we evaluated the influence of the surface roughness of Ag-HT coatings for Escherichia coli adhesion behavior, considering that surface topography is an important factor that regulates bacterial responses to biomaterials. Surface characteristics of as-sprayed and satin-finished Ag-HT coatings were investigated by scanning electron microscopy and measured using a surface roughness tester. Bacterial adhesion experiments showed that the number of viable E. coli cells on the as-sprayed or satin-finished coating surfaces was substantially lower than on the Ti-6Al-4V control surface, which can be explained by the antimicrobial effect of Ag and/or Zn. Moreover, the density of E. coli on the as-sprayed Ag-HT coating was considerably lower than on the satin-finished derivative. We attribute this difference to the fact that the as-sprayed coating surface was relatively smooth at a scale comparable to the size of an individual bacterium, while the satin-finished surface was slightly rough at this length scale and thus favored bacterial adhesion.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Fini, G. Giavaresi, L. Rimondini, and R. Giardino, Titanium Alloy Osseointegration in Cancellous and Cortical Bone of Ovariectomized Animals: Histomorphometric and Bone Hardness Measurements, Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants, 2002, 17(1), p 28-37
A. Besinis, S.D. Hadi, H.R. Le, C. Tredwin, and R.D. Handy, Antibacterial Activity and Biofilm Inhibition by Surface Modified Titanium Alloy Medical Implants Following Application of Silver, Titanium Dioxide and Hydroxyapatite Nanocoatings, Nanotoxicology, 2017, 11(3), p 327-338
B. Tavangar, S. Arasteh, H. Edalatkhah, A. Salimi, A. Doostmohammadi, and E. Seyedjafari, Hardystonite-Coated Poly(l-lactide) Nanofibrous Scaffold and Efficient Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells, Artif. Organs, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1111/aor.12891
K. Li, Y.T. Xie, L.P. Huang, H. Ji, and X.B. Zheng, Antibacterial Mechanism of Plasma Sprayed Ca2ZnSi2O7 Coating Against Escherichia coli, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 2013, 24(1), p 171-178 (in English)
K. Li, Y.T. Xie, H.Y. Ao, L.P. Huang, H. Ji, and X.B. Zheng, The Enhanced Bactericidal Effect of Plasma Sprayed Zinc-Modified Calcium Silicate Coating by the Addition of Silver, Ceram. Int., 2013, 39(7), p 7895-7902 (in English)
D.X. Wei, J.W. Dao, and G.Q. Chen, A Micro-Ark for Cells: Highly Open Porous Polyhydroxyalkanoate Microspheres as Injectable Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration, Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(31), p e1802273
D.X. Wei, J.W. Dao, H.W. Liu, and G.Q. Chen, Suspended Polyhydroxyalkanoate Microspheres as 3D Carriers for Mammalian Cell Growth, Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol., 2018, 2018(1), p 1-11
D. Wei, R. Qiao, J. Dao, J. Su, C. Jiang, X. Wang, M. Gao, and J. Zhong, Soybean Lecithin-Mediated Nanoporous PLGA Microspheres with Highly Entrapped and Controlled Released BMP-2 as a Stem Cell Platform, Small, 2018, 14(22), p e1800063
M.M. Stevens, Exploring and Engineering the Cell-Surface Interface, Biophys. J., 2011, 100(3), p 189 (in English)
M. Jager, C. Zilkens, K. Zanger, and R. Krauspe, Significance of Nano- and Microtopography for Cell-Surface Interactions in Orthopaedic Implants, J. Biomed. Biotechnol., 2007, 2007(8), p 69036 (in English)
R.D. Boyd, J. Verran, M.V. Jones, and M. Bhakoo, Use of the Atomic Force Microscope to Determine the Effect of Substratum Surface Topography on Bacterial Adhesion, Langmuir, 2002, 18(6), p 2343-2346 (in English)
N. Harrasser, S. Jussen, I.J. Banke, R. Kmeth, R. von Eisenhart-Rothe, B. Stritzker, H. Gollwitzer, and R. Burgkart, Antibacterial Efficacy of Titanium-Containing Alloy with Silver-Nanoparticles Enriched Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings, AMB Express, 2015, 5(1), p 77
S.E. Woodling and C.I. Moraru, Influence of Surface Topography on the Effectiveness of Pulsed Light Treatment for the Inactivation of Listeria innocua on Stainless-Steel Surfaces, J. Food Sci., 2005, 70(7), p M345-M351 (in English)
K.A. Whitehead, J. Colligon, and J. Verran, Retention of Microbial Cells in Substratum Surface Features of Micrometer and Sub-micrometer Dimensions, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 2005, 41(2-3), p 129-138
J. Yu, L. Xu, N. Xie, K. Li, Y. Xi, X. Liu, X. Zheng, X. Chen, X. Ye, and D. Wei, Optimal Zn-Modified Ca–Si-Based Ceramic Nanocoating with Zn Ion Release for Osteoblast Promotion and Osteoclast Inhibition in Bone Tissue Engineering, J. Nanomater., 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7374510
X.H. Zhou, D.X. Wei, H.M. Ye, X.C. Zhang, X.Y. Meng, and Q. Zhou, Development of Poly(vinyl alcohol) Porous Scaffold with High Strength and Well Ciprofloxacin Release Efficiency, Mater. Sci. Eng., C, 2016, 67, p 326-335 (in English)
K. Kalwar and D. Shan, Antimicrobial Effect of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) and Their Mechanism: A Mini Review, Micro Nano Lett., 2018, 13(3), p 277-280 (in English)
Y. Li, J. Zhao, E. Shang, X. Xia, J. Niu, and J. Crittenden, Effects of Chloride Ions on Dissolution, ROS Generation, and Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles under UV Irradiation, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52(8), p 4842-4849
O. Choi, K.K. Deng, N.J. Kim, L. Ross, Jr., R.Y. Surampalli, and Z. Hu, The Inhibitory Effects of Silver Nanoparticles, Silver Ions, and Silver Chloride Colloids on Microbial Growth, Water Res., 2008, 42(12), p 3066-3074
C. Wu, M. Chen, T. Zheng, and X. Yang, Effect of Surface Roughness on the Initial Response of MC3T3-E1 Cells Cultured on Polished Titanium Alloy, Bio-Med. Mater. Eng., 2015, 26(Suppl 1), p S155-S164
M. Nikkhah, F. Edalat, S. Manoucheri, and A. Khademhosseini, Engineering Microscale Topographies to Control the Cell-Substrate Interface, Biomaterials, 2012, 33(21), p 5230-5246
K.A. Whitehead, D. Rogers, J. Colligon, C. Wright, and J. Verran, Use of the Atomic Force Microscope to Determine the Effect of Substratum Surface Topography on the Ease of Bacterial Removal, Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 2006, 51(1), p 44-53
Y. Wu, J.P. Zitelli, K.S. TenHuisen, X. Yu, and M.R. Libera, Differential Response of Staphylococci and Osteoblasts to Varying Titanium Surface Roughness, Biomaterials, 2011, 32(4), p 951-960
L.G. Harris and R.G. Richards, Staphylococcus aureus Adhesion to Different Treated Titanium Surfaces, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med., 2004, 15(4), p 311-314
L.C. Hsu, J. Fang, D.A. Borca-Tasciuc, R.W. Worobo, and C.I. Moraru, Effect of Micro- and Nanoscale Topography on the Adhesion of Bacterial Cells to Solid Surfaces, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2013, 79(8), p 2703-2712 (in English)
X. Liu, D. Wei, J. Zhong, M. Ma, J. Zhou, X. Peng, Y. Ye, G. Sun, and D. He, Electrospun Nanofibrous P(DLLA-CL) Balloons as Calcium Phosphate Cement Filled Containers for Bone Repair: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces., 2015, 7(33), p 18540-18552
G. Sun, D. Wei, X. Liu, Y. Chen, M. Li, D. He, and J. Zhong, Novel Biodegradable Electrospun Nanofibrous P(DLLA-CL) Balloons for the Treatment of Vertebral Compression Fractures, Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med., 2013, 9(6), p 829-838
P. Pei, D. Wei, M. Zhu, X. Du, and Y. Zhu, The Effect of Calcium Sulfate Incorporation on Physiochemical and Biological Properties of 3D-printed Mesoporous Calcium Silicate Cement Scaffolds, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2017, 241, p 11-20
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51172264, 81300917), the Foundation of the Shanghai Biomaterial and Clinical Research Centre (Grant No. BMCRC2010004) and Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning Foundation of Shanghai (20174Y0211).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Xu, N., Xi, Y. et al. Adhesion Behavior of Escherichia coli on Plasma-Sprayed Zn and Ag Co-incorporated Calcium Silicate Coatings with Varying Surface Roughness. J Therm Spray Tech 27, 1428–1435 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-018-0800-5
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-018-0800-5