Abstract
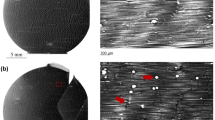
Gallium nitride (GaN) substrates grown by different methods were characterized by high-resolution x-ray diffraction and synchrotron x-ray topography. Using the monochromatic beam in the grazing incidence geometry, high-resolution x-ray topographs reveal the various dislocation types present. Dislocation contrasts were correlated with ray-tracing simulation results successfully so that the Burgers vectors of the dislocations could be determined. Ammonothermal-grown GaN substrate wafers show the best quality among all the wafers. These wafers, which are free of basal plane dislocations (BPDs) have threading mixed dislocations (TMDs) dominant among the threading dislocations (TDs). Images of patterned hydride vapor phase epitaxy (HVPE) GaN reveal a starkly heterogeneous distribution of dislocations with large areas containing low threading dislocation densities in between a grid of strain centers with higher threading dislocation densities and BPDs. The strain level of regular HVPE GaN substrates is very high, and the dislocation density is around 105–106 cm−2, which is much higher than 104 cm−2 of ammonothermal samples and dislocation-free areas in the patterned HVPE samples.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.J. Pearton, J.C. Zolper, R.J. Shul, and F. Ren, J. Appl. Phys., 1999, 86, p 1.
S. Porowski, and I. Grzegory, J. Cryst. Growth, 1997, 178, p 174.
H. Wu, J. Spinelli, P. Konkapaka, M. Spencer, Rapid growth of bulk GaN crystal using GaN powder as source material, MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive, 892, FF30-01 (2005).
D. Siche, D. Gogova, S. Lehmann, T. Fizia, R. Fornari, M. Andrasch, A. Pipa, and J. Ehlbeck, J. Cryst. Growth, 2011, 318, p 406.
M. Aoki, H. Yamane, M. Shimada, S. Sarayama, and F.J. DiSalvo, J. Cryst. Growth, 2002, 242, p 70.
H.P. Maruska, and J. Tietjen, Appl. Phys. Lett., 1969, 15, p 327.
T. Nakamura, K. Motoki, in IEEE Proceedings (2013), p. 2221
R. Dwiliński, R. Doradziński, J. Garczyński, L. Sierzputowski, A. Puchalski, Y. Kanbara, K. Yagi, H. Minakuchi, and H. Hayashi, J. Cryst. Growth, 2008, 310, p 3911.
T. Hashimoto, F. Wu, J.S. Speck, and S. Nakamura, J. Cryst. Growth, 2008, 310, p 3907.
R. Dwiliński, R. Doradziński, J. Garczyński, L. Sierzputowski, R. Kucharski, M. Zając, M. Rudziński, R. Kudrawiec, J. Serafińczuk, and W. Strupiński, J. Cryst. Growth, 2010, 312, p 2499.
J. Hsu, M. Manfra, D. Lang, S. Richter, S. Chu, A. Sergent, R. Kleiman, L. Pfeiffer, and R. Molnar, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, 78, p 1685.
E. Miller, E. Yu, P. Waltereit, and J. Speck, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 84, p 535.
K. Horibuchi, S. Yamaguchi, Y. Kimoto, K. Nishikawa, and T. Kachi, Semicond. Sci. Technol., 2016, 31, p 034002.
M. Skowronski, and S. Ha, J. Appl. Phys., 2006, 99, p 1.
Y. Chen, M. Dudley, K. Liu, R. Stahlbush, Appl. Phys. Lett., 90, (2007).
K. Maeda, in Materials and Reliability Handbook for Semiconductor Optical and Electron Devices, ed. by O. Ueda, S. J. Pearton (Springer, 2013), p. 263
Huang, M. Dudley, W. Vetter, W. Huang, S. Wang, and C. Carter Jr., Appl. Phys. Lett., 1999, 74, p 353.
Y. Chen, and M. Dudley, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 91, p 141918.
I. Kamata, M. Nagano, H. Tsuchida, Y. Chen, M. Dudley, in Mater. Sci. Forum Proceedings (2009), p. 305
Y. Chen, X. R. Huang, N. Zhang, M. Dudley, J. D. Caldwell, K. X. Liu, R. E. Stahlbush, in Mater. Sci. Forum Proceedings (2009), p. 357
M. Dudley, Y. Chen, X. R. Huang, R. H. Ma, in Mater. Sci. Forum Proceedings (2009), p. 261
T. Zhou, B. Raghothamachar, F. Wu, R. Dalmau, B. Moody, S. Craft, R. Schlesser, M. Dudley, and Z. Sitar, J. Electron. Mater., 2014, 43, p 838.
T. Zhou, B. Raghothamachar, F. Wu, and M. Dudley, MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive, 2013, 1494, p 121.
S. Sintonen, M. Rudziński, S. Suihkonen, H. Jussila, M. Knetzger, E. Meissner, A. Danilewsky, T.O. Tuomi, and H. Lipsanen, J. Appl. Phys., 2014, 116, p 083504.
X. Huang, R. Peng, M.G. Hönnicke, and T. Gog, Phys. Rev. A, 2013, 87, p 063828.
X. Huang, and M. Dudley, Acta Crystallographica Section A, 2003, 59, p 163.
W. Cho, X. Huang, and M. Dudley, Acta Crystallogr. A, 2004, 60, p 195.
B. Raghothamachar, M. Dudley, G. Dhanaraj, in Springer handbook of crystal growth, ed. by G. Dhanaraj, K. Byrappa, V. Prasad, M. Dudley (Springer, 2010), p. 1425
B. Raghothamachar, Y. Liu, H. Peng, T. Ailihumaer, M. Dudley, F. S. Shahedipour-Sandvik, K. A. Jones, A. Armstrong, A. A. Allerman, J. Han, H. Fu, K. Fu, Y. Zhao, J. Cryst. Growth, 544, (2020).
Y. Liu, B. Raghothamachar, H. Peng, T. Ailihumaer, M. Dudley, R. Collazo, J. Tweedie, Z. Sitar, F.S. Shahedipour-Sandvik, and K.A. Jones, J. Cryst. Growth, 2020, 551, p 125903.
Y. Zhang, M. Sun, J. Perozek, Z. Liu, A. Zubair, D. Piedra, N. Chowdhury, X. Gao, K. Shepard, T. Palacios, IEEE Electron Device Lett., 1 (2018).
Acknowledgments
X-ray topography work supported by ARPA-E through PNDIODES program (DE-AR0001115; Project Director: I. Kizilyalli). Synchrotron x-ray topographs were recorded using the resources of the Advanced Photon Source (Beamline 1-BM), a U.S. DOE Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357. Joint Photon Sciences Institute at Stony Brook University provided partial support for travel and subsistence at the Advanced Photon Source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Peng, H., Ailihumaer, T. et al. X-ray Topography Characterization of GaN Substrates Used for Power Electronic Devices. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 2981–2989 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-08762-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-021-08762-6