Abstract
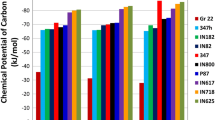
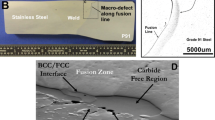
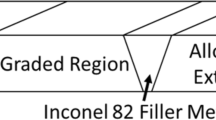
Carbon diffusion and the associated microstructural changes in dissimilar metal welds at elevated temperatures lead to a microstructure that is susceptible to premature failure. Graded transition joints (GTJs) can potentially provide a viable replacement to prolong the service life of these components. The purpose of the current investigation is to fabricate, age, and characterize GTJs using three candidate filler metals (Inconel 82, EPRI P87, and 347H) to understand the microstructural evolution at elevated temperatures. Microhardness measurements were performed on the GTJs in the as-welded and aged conditions to understand the initial strength gradients throughout the graded region and how they evolve with aging time. Additionally, energy dispersive spectrometry was performed to measure the compositional gradients, which were input into thermodynamic and kinetic calculations to understand the carbon diffusion behavior and phase stability. Enhanced carbon diffusion occurred at the layer interfaces in the graded region of the GTJ, which indicated important regions that undergo microstructural evolution. The hardness results also revealed hardness changes at the layer interfaces. The analyzed interfaces demonstrated that carbon diffusion and corresponding carbide redistribution occurred that accounted for the observed hardness gradients. Additionally, the transition from a martensitic to austenitic region was observed in each GTJ that contributed to the hardness variations in the graded region. Finally, the formation of a nickel-rich martensitic constituent was observed in the graded region of all filler metals after aging. This constituent was originally austenite at the aging temperature, and transformed to martensite with no change in composition upon cooling. The morphologies of the constituent in the three filler metals are presented and discussed.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Çam and M. Koçak: Int. Mater. Rev., 1998, vol. 43, pp. 1–44.
G. Çam and M. Koçak: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 1998, vol. 3, pp. 159–75.
G. Çam and G. Ipekoglu: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2017, vol. 91, pp. 1851–66.
R.L. Klueh and J.F. King: Weld. J., 1982, 62, pp. 302–11.
J.N. DuPont: Int. Mater. Rev., 2012, vol. 57, pp. 208–34.
R. Dooley and P. Chang: Proc. Int. Conf. on Boiler tube failures in fossil plants, 1997, pp. 2–10.
I. Ramu and S.C. Mohanty: Procedia Mater. Sci., 2014, vol. 6, pp. 460–7.
M. Bhandari and K. Purohit: IOSR J. Mech. Civ. Eng., 2014, vol. 10, pp. 46–55.
A. Gupta and M. Talha: Prog. Aerosp. Sci., 2015, vol. 79, pp. 1–14.
C.D. Lundin: Weld. J., 1982, 61, p. 58–63.
M. Gittos and T. Gooch: Weld. Res. Suppl., 1992, 71, pp. 461–72.
G.J. Brentrup and J.N. DuPont: Weld. J., 2013, vol. 92, pp. 72–9.
Brentrup, G. J., Snowden, B. S., DuPont, J. N., & Grenestedt, J. L. (2012). Design considerations of graded transition joints for welding dissimilar alloys. Welding Journal, 91, 252-59.
N. Sridharan, E. Cakmak, B. Jordan, D. Leonard, W.H. Peter, R.R. Dehoff, D. Gandy, and S.S. Babu: Weld. J., 2017, vol. 96, p. 295-306.
J.N. Dupont and A.R. Marder: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1996, vol. 27B, pp. 481–9.
J.P. Galler, J.N. Dupont, S.S. Babu, and M. Subramanian: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2018.
D. Drouin, A.R. Couture, D. Joly, X. Tastet, V. Aimez, and R. Gauvin: 2007, vol. 29, pp. 92–101.
A. Borgenstam, L. Höglund, J. Ågren, and A. Engström: J. Phase Equilibria, 2000, vol. 21, pp. 269–80.
Thermo-Calc Software MOB2 TCS Alloy Mobility Database.
Thermo-Calc Software TCFE7-TCS Steels/Fe-Alloys Database version 7.
Thermo-Calc Software Ni-Data-v7 Ni-Alloys Database.
R.L. Klueh: Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9, pp. 1591–8.
K. Laha, K.S. Chandravathi, K.B.S. Rao, S.L. Mannan, and D.H. Sastry: Metall. Mater. Trans. a, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 115–24.
J.D. Parker and G.C. Stratford: J. Mater. Sci., 2000, vol. 35, pp. 4099–107.
Y. Zhou, Y. Li, Y. Liu, Q. Guo, C. Liu, L. Yu, C. Li, and H. Li: J. Mater. Res., 2015, vol. 30, pp. 3642–52.
S.W. Banovic, J.N. Dupont, and A.R. Marder: Weld. J., 2001, 80, pp. 63–70.
J.N. Dupont and C.S. Kusko: Weld. J., 2007, vol. 86, p. 51s–54s.
K.W. Andrews: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, 203, pp. 721–27.
R.J. Christoffel and M.R. Curran: Weld. J., 1956, vol. 35, 457-468.
D.A. Porter, K.E. Easterling, and M.Y. Sherif: Phase Trasformations in Metals and Alloys, Third., Taylor and Francis Group, 2009.
L. S. Darken: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1948, vol. 41B, 430–38.
J.F. Eckel: Weld. J., 1964, vol. 43, 170-78.
G. Krauss: Steels: Processing, Structure, and Performance, ASM International, 2015.
Sindo K (2003) Welding Metallurgy, Wiley, New York, pp. 822-832.
G. Krauss: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, vol. 273–275, pp. 40–57.
E.C. Bain: Functions of the Alloying Elements in Steel, American Society for Metals, 1939.
R.W. Hertzberg, R.P. Vinci, and J.L. Hertzberg: Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, Fifth Edit., Wiley and Sons, 2013.
W.D. Callister and D.G. Rethwisch: Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, vol. 94, Wiley, New York, 2007.
I. Hajiannia, M. Shamanian, and M. Kasiri: Mater. Des., 2013, vol. 50, pp. 566–73.
B. Shalchi Amirkhiz, S. Xu, J. Liang, and C. Bibby: in: 36th Annu. CNS Conf.
Y. Minami, H. Kimura, and M. Tanimura: J. Mater. Energy Syst., 1985, vol. 7, pp. 45–54.
R. Mittal and B.S. Sidhu: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, vol. 220, pp. 76–86.
T. Sourmail: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2001, vol. 17, pp. 1–14.
H. Tanaka, M. Murata, F. Abe, and K. Yagi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1997, vol. 234–236, pp. 1049–52.
R.L. Klueh and J.F. King: 1981, p. ORNL-5783.
E.J. Barrick, D. Jain, J.N. DuPont, and D.N. Seidman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48, pp. 5890–910.
D. Isheim, A.H. Hunter, X.J. Zhang, and D.N. Seidman: Metall. Mater. Trans. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 3046–59
D. Jain, D. Isheim, X.J. Zhang, G. Ghosh, and D.N. Seidman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2017, vol. 48A, pp. 3642–54.
S.J. Wu, G.J. Sun, Q.S. Ma, Q.Y. Shen, and L. Xu: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2013, vol. 213, pp. 120–8.
F. Matsuda, K. Ikeuchi, Y. Fukada, Y. Horii, H. Okada, T. Shiwaku, C. Shiga, and S. Suzuki: Transcations JWRI, 1995, vol. 24, pp. 1–24.
Y. Li and T.N. Baker: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, vol. 26, pp. 1029–40.
C.L. Davis and J.E. King: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1993, vol. 9, pp. 8–15.
X. Li, X. Ma, S. V. Subramanian, C. Shang, and R.D.K. Misra: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 616, pp. 141–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted June 5, 2018.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galler, J.P., DuPont, J.N., Babu, S.S. et al. Microstructural Evolution of Graded Transition Joints. Metall Mater Trans A 50, 2201–2217 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05138-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-019-05138-8