Abstract
This paper addresses the task of generating fluent descriptions by training on a non-uniform combination of data sources, containing both human-annotated and web-collected captions. Large-scale datasets with noisy image-text pairs, indeed, provide a sub-optimal source of supervision because of their low-quality descriptive style, while human-annotated datasets are cleaner but smaller in scale. To get the best of both worlds, we propose to leverage and separate semantics and descriptive style through the incorporation of a style token and keywords extracted through a retrieval component. The proposed model avoids the need of object detectors, is trained with a single objective of prompt language modeling, and can replicate the style of human-collected captions while training on sources with different input styles. Experimentally, the model shows a strong capability of recognizing real-world concepts and producing high-quality captions. Extensive experiments are performed on different image captioning datasets, including CC3M, nocaps, and the competitive COCO dataset, where our model consistently outperforms baselines and state-of-the-art approaches.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated during the current study. Datasets employed for this article are all publicly available.
Notes
A reference implementation can be found in https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/gpt2/modeling_gpt2.py#L493.
The number of parameters of these models is as follows: VinVL\(^\text {base}\) (135M), VinVL\(^\text {large}\) (370M), LEMON\(^\text {large}\) (338M), LEMON\(^\text {huge}\) (675M), BLIP\(^\text {base}\) (224M), BLIP\(^\text {large}\) (446M), SimVLM\(^\text {base}\) (86M), SimVLM\(^\text {large}\) (307M), SimVLM\(^\text {huge}\) (632M).
References
Agrawal, H., Desai, K., Wang, Y., Chen, X., Jain, R., Johnson, M., Batra, D., Parikh, D., Lee, S., & Anderson, P. (2019). Nocaps: Novel object captioning at scale. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision.
Alayrac, J. B., Donahue, J., Luc, P., Miech, A., Barr, I., Hasson, Y., Lenc, K., Mensch, A., Millican, K., Reynolds, M., & Ring, R. (2022). Flamingo: A visual language model for few-shot learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35, 23716–23736.
Anderson, P., Fernando, B., Johnson, M., & Gould, S. (2016). SPICE: Semantic propositional image caption evaluation. in Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision.
Anderson, P., He, X., Buehler, C., Teney, D., Johnson, M., Gould, S., & Zhang, L. (2018). Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Banerjee, S., & Lavie, A. (2005). METEOR: An automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments. In Proceedings of the annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics workshops.
Barraco, M., Cornia, M., Cascianelli, S., Baraldi, L., & Cucchiara, R. (2022). The unreasonable effectiveness of CLIP features for image captioning: An experimental analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition workshops.
Barraco, M., Stefanini, M., Cornia, M., Cascianelli, S., Baraldi, L., & Cucchiara, R. (2022). CaMEL: Mean teacher learning for image captioning. In Proceedings of the international conference on pattern recognition.
Brown, T., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J. D., Dhariwal, P., Neelakantan, A., Shyam, P., Sastry, G., Askell, A., & Agarwal, S. (2020). Language models are few-shot learners. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33, 1877–1901.
Changpinyo, S., Sharma, P., Ding, N., & Soricut, R. (2021). Conceptual 12M: Pushing web-scale image-text pre-training to recognize long-tail visual concepts. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Chen, T., Zhang, Z., You, Q., Fang, C., Wang, Z., Jin, H., & Luo, J. (2018). “Factual” or“Emotional”: Stylized image captioning with adaptive learning and attention. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision.
Chen, Y.C., Li, L., Yu, L., El Kholy, A., Ahmed, F., Gan, Z., Cheng, Y., & Liu, J. (2020). UNITER: Learning UNiversal image-TExt representations. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision.
Cornia, M., Stefanini, M., Baraldi, L., & Cucchiara, R. (2020). Meshed-memory transformer for image captioning. in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2018). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the annual conference of the North American chapter of the association for computational linguistics.
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., & Uszkoreit, J., (2021). An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations.
Gan, C., Gan, Z., He, X., Gao, J., & Deng, L. (2017). StyleNet: Generating attractive visual captions with styles. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Gao, T., Fisch, A., & Chen, D. (2021). Making pretrained language models better few-shot learners. In Proceedings of the annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics.
Glorot, X., & Bengio, Y. (2010). Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics.
Guo, L., Liu, J., Tang, J., Li, J., Luo, W., & Lu, H. (2019). Aligning linguistic words and visual semantic units for image captioning.
Guo, L., Liu, J., Yao, P., Li, J., & Lu, H. (2019). MSCap: Multi-style image captioning with unpaired stylized text. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Gurari, D., Zhao, Y., Zhang, M., & Bhattacharya, N. (2020). Captioning images taken by people who are blind. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision.
Hessel, J., Holtzman, A., Forbes, M., Bras, R. L., & Choi, Y. (2021). CLIPScore: A reference-free evaluation metric for image captioning. In Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing.
Hu, X., Gan, Z., Wang, J., Yang, Z., Liu, Z., Lu, Y., & Wang, L. (2022). Scaling up vision- language pre-training for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Hu, X., Yin, X., Lin, K.,Wang, L., Zhang, L., Gao, J., & Liu, Z. (2020). VIVO: Visual vocabulary pre-training for novel object captioning. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence.
Huang, L.,Wang, W., Chen, J., & Wei, X.-Y. (2019). Attention on attention for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision.
Jia, C., Yang, Y., Xia, Y., Chen, Y.-T., Parekh, Z., Pham, H., & Duerig, T. (2021). Scaling up visual and vision-language representation learning with noisy text supervision.
Johnson, J., Douze, M., & Jéegou, H. (2019). Billionscale similarity search with gpus. IEEE Transactions on Big Data, 7(3), 535–547.
Karpathy, A., & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Deep visualsemantic alignments for generating image descriptions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Kim, W., Son, B., & Kim, I. (2021). ViLT: Vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. In Proceedings of the international conference on machine learning.
Kingma, D. P., & Ba, J. (2015). Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations.
Klein, F., Mahajan, S., & Roth, S. (2021). Diverse image captioning with grounded style. In Proceeding of the DAGM German conference on pattern recognition.
Krishna, R., Zhu, Y., Groth, O., Johnson, J., Hata, K., Kravitz, J., & Fei-Fei, L. (2017). Visual genome: Connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. International Journal of Computer Vision, 123(1), 32–73.
Kuznetsova, A., Rom, H., Alldrin, N., Uijlings, J., Krasin, I., Pont-Tuset, J., & Ferrari, V. (2020). The open images dataset V4. International Journal of Computer Vision, 128(7), 1956–1981.
Li, G., Duan, N., Fang, Y., Gong, M., & Jiang, D. (2020a). Unicoder-VL: A universal encoder for vision and language by cross-modal pre-training. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence.
Li, G., Zhai, Y., Lin, Z., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Similar scenes arouse similar emotions: Parallel data augmentation for stylized image captioning. In Proceedings of the ACM international conference on multimedia.
Li, J., Li, D., Savarese, S., & Hoi, S. (2023). BLIP- 2: Bootstrapping language-image pretraining with frozen image encoders and large language models. In Proceedings of the international conference on machine learning.
Li, J., Li, D., Xiong, C., & Hoi, S. (2022a). BLIP: Bootstrapping language-image pretraining for unified vision-language understanding and generation. In Proceedings of the international conference on machine learning.
Li, X., Yin, X., Li, C., Zhang, P., Hu, X., Zhang, L., Wang, L., Hu, H., Dong, L., Wei, F., & Choi, Y. (2020b). Oscar: Object-semantics aligned pre-training for vision-language tasks. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision.
Li, Y., Pan, Y., Yao, T., & Mei, T. (2022b). Comprehending and ordering semantics for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Lin, C.-Y. (2004). Rouge: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries. In Proceedings of the Annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics workshops.
Lin, T. Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollar, P., & Zitnick, C. L. (2014). Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision.
Lu, J., Batra, D., Parikh, D., & Lee, S. (2019). ViLBERT: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and- language tasks. In Advances in neural information processing systems.
Lu, J., Xiong, C., Parikh, D., & Socher, R. (2017). Knowing when to look: Adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Mathews, A., Xie, L., & He, X. (2016). SentiCap: Generating image descriptions with sentiments. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence.
Mathews, A., Xie, L., & He, X. (2018). Semstyle: Learning to generate stylised image captions using unaligned text. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Micikevicius, P., Narang, S., Alben, J., Diamos, G., Elsen, E., Garcia, D., Ginsburg, B., Houston, M., Kuchaiev, O., Venkatesh, G., & Wu, H. (2018). Mixed precision training. in proceedings of the international conference on learning representations.
Mokady, R., Hertz, A., & Bermano, A. H. (2021). ClipCap: CLIP prefix for image captioning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.09734
Ordonez, V., Kulkarni, G., & Berg, T. (2011). Im2Text: Describing images using 1 million captioned photographs. In Advances in neural information processing systems.
Pan, Y., Yao, T., Li, Y., & Mei, T. (2020). X-linear attention networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., & Zhu, W.-J. (2002). BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics.
Radford, A., Kim, J. W., Hallacy, C., Ramesh, A., Goh, G., Agarwal, S., & Sutskever, I. (2021). Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision.
Radford, A., Wu, J., Child, R., Luan, D., Amodei, D., & Sutskever, I. (2019). Language models are unsupervised multitask learners.
Rajbhandari, S., Rasley, J., Ruwase, O., & He, Y. (2020). ZeRO: Memory optimizations toward training trillion parameter models. In Proceedings of the international conference for high performance computing, networking, storage and analysis.
Rennie, S.J., Marcheret, E., Mroueh, Y., Ross, J., & Goel, V. (2017). Self-critical sequence training for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Ridnik, T., Ben-Baruch, E., Noy, A., & Zelnik- Manor, L. (2021). ImageNet-21K pretraining for the masses. in Advances in neural information processing systems.
Sarto, S., Barraco, M., Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., & Cucchiara, R. (2023). Positive-augmented contrastive learning for image and video captioning evaluation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Sarto, S., Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., & Cucchiara, R. (2022). Retrieval-augmented transformer for image captioning.
Schuhmann, C., Beaumont, R., Vencu, R., Gordon, C., Wightman, R., Cherti, M., Coombes, T., Katta, A., Mullis, C., Wortsman, M., & Schramowski, P. (2022). LAION-5B: An open large-scale dataset for training next generation image-text models. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems., 35, 25278–25294.
Schuhmann, C., Vencu, R., Beaumont, R., Kaczmarczyk, R., Mullis, C., Katta, A., Coombes, T., Jitsev, J., & Komatsuzaki, A., (2021). LAION-400M: Open dataset of CLIP-filtered 400 million image-text pairs. In Advances in neural information processing systems.
Sennrich, R., Haddow, B., & Birch, A. (2016). Neural machine translation of rare words with subword units. In Proceedings of the annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics.
Sharma, P., Ding, N., Goodman, S., & Soricut, R. (2018). Conceptual Captions: A cleaned, hypernymed, image alt-text dataset for automatic image captioning. In Proceedings of the annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics.
Shen, S., Li, L.H., Tan, H., Bansal, M., Rohrbach, A., Chang, K.W., Yao, Z., & Keutzer, K. (2022). How much can CLIP benefit vision-and- language tasks? In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations.
Sidorov, O., Hu, R., Rohrbach, M., & Singh, A. (2020). TextCaps: A dataset for image captioning with reading comprehension. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision.
Srinivasan, K., Raman, K., Chen, J., Bendersky, M., & Najork, M. (2021). WIT: Wikipedia-based image text dataset for multimodal multilingual machine learning. In ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval.
Stefanini, M., Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Cascianelli, S., Fiameni, G., & Cucchiara, R. (2022). From show to tell: A survey on deep learningbased image captioning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 45(1), 539–559.
Su, W., Zhu, X., Cao, Y., Li, B., Lu, L., Wei, F., & Dai, J. (2020). VL-BERT: Pre-training of generic visual-linguistic representations. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations.
Tan, H., & Bansal, M. (2019). LXMERT: Learning cross-modality encoder representations from transformers. In Proceedings of the conference on empirical methods in natural language processing.
Thomee, B., Shamma, D. A., Friedland, G., Elizalde, B., Ni, K., Poland, D., & Li, L.-J. (2016). YFCC100M: The new data in multimedia research. Communications of the ACM, 59(2), 64–73.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A.N., Kaiser, L., & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. In Advances in neural information processing systems.
Vedantam, R., Lawrence Zitnick, C., & Parikh, D. (2015). CIDEr: Consensus-based image description evaluation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., & Erhan, D. (2015). Show and tell: A neural image caption generator. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Wang, Z., Yu, J., Yu, A.W., Dai, Z., Tsvetkov, Y., & Cao, Y. (2022). SimVLM: Simple visual language model pretraining with weak supervision. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations.
Xu, H., Yan, M., Li, C., Bi, B., Huang, S., Xiao, W., & Huang, F. (2021). E2E-VLP: End-to-end vision-language pre-training enhanced by visual learning. In Proceedings of the annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics.
Xu, K., Ba, J., Kiros, R., Cho, K., Courville, A., Salakhudinov, R., Zemel, R., & Bengio, Y. (2015). Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the international conference on machine learning.
Yan, M., Xu, H., Li, C., Bi, B., Tian, J., Gui, M., & Wang, W. (2021). Grid-VLP: Revisiting grid features for vision-language pretraining. arXiv preprint arXiv:2108.09479
Yang, X., Tang, K., Zhang, H., & Cai, J. (2019). Auto-encoding scene graphs for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Xu, K., Ba, J., Kiros, R., Cho, K., Courville, A., Salakhudinov, R., Zemel, R., & Bengio, Y. (2020). Large batch optimization for deep learning: Training BERT in 76 minutes. In Proceedings of the international conference on learning representations.
Young, P., Lai, A., Hodosh, M., & Hockenmaier, J. (2014). From image descriptions to visual denotations: New similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2, 67–78.
Yu, J., Wang, Z., Vasudevan, V., Yeung, L., Seyedhosseini, M., & Wu, Y. (2022). CoCa: Contrastive captioners are image- text foundation models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.01917
Zhang, P., Li, X., Hu, X., Yang, J., Zhang, L., Wang, L., Choi, Y., & Gao, J. (2021). VinVL: Revisiting visual representations in vision-language models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition.
Zhang, S., Roller, S., Goyal, N., Artetxe, M., Chen, M., Chen, S., Dewan, C., Diab, M., Li, X., Lin, X. V., & Mihaylov, T. (2022). OPT: Open pre-trained transformer language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.01068
Zhao, W., Wu, X., & Zhang, X. (2020). Mem-Cap: Memorizing style knowledge for image captioning. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence.
Zhou, L., Palangi, H., Zhang, L., Hu, H., Corso, J. J., & Gao, J. (2020). Unified vision-language pre-training for image captioning and VQA. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence.
Acknowledgements
We thank CINECA for providing computational resources. This work has been supported by the PNRR-M4C2 project (PE00000013) “FAIR—Future Artificial Intelligence Research” funded by the European Commission and the PRIN “CREATIVE: CRoss-modal understanding and gEnerATIon of Visual and tExtual content” co-funded by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (CUP B87G22000460001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Bodo Rosenhahn.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
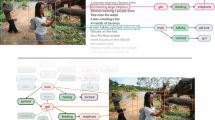
Appendix A Additional Qualitative Results
Appendix A Additional Qualitative Results
We report different qualitative results obtained on images from nocaps (Fig. 8), VizWiz (Fig. 9), TextCaps (Fig. 10), CC3M and Open Images (Fig. 11). We observe how our model can describe objects, people, and scenes with a significantly increased level of detail when compared to the current state of the art and regardless of the dataset. Also, our approach qualitatively appears to be less prone to hallucination and can constantly generate fluent textual descriptions.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cornia, M., Baraldi, L., Fiameni, G. et al. Generating More Pertinent Captions by Leveraging Semantics and Style on Multi-Source Datasets. Int J Comput Vis 132, 1701–1720 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01949-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-023-01949-w