Abstract
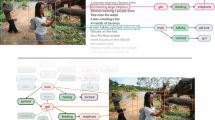
The Flickr30k dataset has become a standard benchmark for sentence-based image description. This paper presents Flickr30k Entities, which augments the 158k captions from Flickr30k with 244k coreference chains, linking mentions of the same entities across different captions for the same image, and associating them with 276k manually annotated bounding boxes. Such annotations are essential for continued progress in automatic image description and grounded language understanding. They enable us to define a new benchmark for localization of textual entity mentions in an image. We present a strong baseline for this task that combines an image-text embedding, detectors for common objects, a color classifier, and a bias towards selecting larger objects. While our baseline rivals in accuracy more complex state-of-the-art models, we show that its gains cannot be easily parlayed into improvements on such tasks as image-sentence retrieval, thus underlining the limitations of current methods and the need for further research.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In Flickr30k, NP chunks that only consist of a color term are often used to refer to clothing, e.g., man in blue.
Although in Klein et al. (2014) their combined HGLMM + GMM Fisher Vectors performed the best on bidirectional retrieval, in our experiments the addition of the GMM features made no substantial impact on performance.
We use ground truth NP chunks and ignore the non-visual mentions (i.e., mentions not associated with a box). The alternative evaluation method is to extract the phrases automatically, which introduces chunking errors and lowers our recall by around 3 %. To the best of our knowledge, the competing methods in Table 5(a) also evaluate using ground-truth NP chunks.
If a phrase includes more than one color, all the color mentions are ignored.
References
Antol, S., Agrawal, A., Lu, J., Mitchell, M., Batra, D., Zitnick, C.L., & Parikh, D. (2015). Vqa: Visual question answering. In ICCV.
Chen, X. & Zitnick, C. L. (2015). Minds eye: A recurrent visual representation for image caption generation. In CVPR.
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.-J., Li, K., & Fei-Fei, L. (2009). Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In CVPR.
Devlin, J., Cheng, H., Fang, H., Gupta, S., Deng, L., He, X., Zweig, G., & Mitchell, M. (2015). Language models for image captioning: The quirks and what works. In ACL.
Dodge, J., Goyal, A., Han, X., Mensch, A., Mitchell, M., Stratos, K., Yamaguchi, K., Choi, Y., III, H. D., Berg, A. C., & Berg, T. L. (2012). Detecting visual text. In NAACL.
Donahue, J., Hendricks, L. A., Guadarrama, S., Rohrbach, M., Venugopalan, S., Saenko, K., & Darrell, T. (2015). Long-term recurrent convolutional networks for visual recognition and description. In CVPR.
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I., Winn, J., & Zisserman, A. (2008). The PASCAL Visual Object Classes Challenge 2008 (VOC2008) Results. http://www.pascal-network.org/challenges/VOC/voc2008/workshop/index.html.
Everingham, M., Van Gool, L., Williams, C. K. I., Winn, J., & Zisserman, A. (2012). The PASCAL Visual Object Classes Challenge 2012 (VOC2012) Results. http://www.pascal-network.org/challenges/VOC/voc2012/workshop/index.html.
Fang, H., Gupta, S., Iandola, F., Srivastava, R., Deng, L., Dollar, P., Gao, J., He, X., Mitchell, M., Platt, J., Zitnick, L., & Zweig, G. (2015). From captions to visual concepts and back. In CVPR.
Farhadi, A., Hejrati, S., Sadeghi, A., Young, P., Rashtchian, C., Hockenmaier, J., & Forsyth, D. A. (2010). Every picture tells a story: Generating sentences from images. In ECCV.
Fidler, S., Sharma, A., & Urtasun, R. (2013). A sentence is worth a thousand pixels. In CVPR.
Fukui, A., Park, D. H., Yang, D., Rohrbach, A., Darrell, T., & Rohrbach, M. (2016). Multimodal compact bilinear pooling for visual question answering and visual grounding. arXiv:1606.01847.
Gao, H., Mao, J., Zhou, J., Huang, Z., Wang, L., & Xu, W. (2015). Are you talking to a machine? dataset and methods for multilingual image question answering. In NIPS.
Girshick, R. (2015). Fast r-cnn. In ICCV.
Gong, Y., Ke, Q., Isard, M., & Lazebnik, S. (2014a). A multi-view embedding space for modeling internet images, tags, and their semantics. IJCV, 106(2), 210–233.
Gong, Y., Wang, L., Hodosh, M., Hockenmaier, J., & Lazebnik, S. (2014b). Improving image-sentence embeddings using large weakly annotated photo collections. In ECCV.
Grubinger, M., Clough, P., Müller, H., & Deselaers, T. (2006). The iapr tc-12 benchmark: A new evaluation resource for visual information systems. In International Workshop OntoImage, pp. 13–23.
Hodosh, M., Young, P., & Hockenmaier, J. (2013). Framing image description as a ranking task: Data, models and evaluation metrics. In JAIR.
Hodosh, M., Young, P., Rashtchian, C., and Hockenmaier, J. (2010). Cross-caption coreference resolution for automatic image understanding. In CoNLL, pages 162-171. ACL.
Hotelling, H. (1936). Relations between two sets of variates. In Biometrika, pp. 321–377.
Hu, R., Xu, H., Rohrbach, M., Feng, J., Saenko, K., & Darrell, T. (2016). Natural language object retrieval. In CVPR.
Johnson, J., Karpathy, A., & Fei-Fei, L. (2016). Densecap: Fully convolutional localization networks for dense captioning. In CVPR.
Johnson, J., Krishna, R., Stark, M., Li, L.-J., Shamma, D. A., Bernstein, M., & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Image retrieval using scene graphs. In CVPR.
Karpathy, A. & Fei-Fei, L. (2015). Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions. In CVPR.
Karpathy, A., Joulin, A., & Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Deep fragment embeddings for bidirectional image sentence mapping. In NIPS.
Kazemzadeh, S., Ordonez, V., Matten, M., & Berg, T. (2014). Referitgame: Referring to objects in photographs of natural scenes. In EMNLP.
Kiros, R., Salakhutdinov, R., & Zemel, R. S. (2014). Unifying visual-semantic embeddings with multimodal neural language models. arXiv:1411.2539.
Klein, B., Lev, G., Sadeh, G., & Wolf, L. (2014). Fisher vectors derived from hybrid gaussian-laplacian mixture models for image annotation. arXiv:1411.7399.
Kong, C., Lin, D., Bansal, M., Urtasun, R., & Fidler, S. (2014). What are you talking about? text-to-image coreference. In CVPR.
Krishna, R., Zhu, Y., Groth, O., Johnson, J., Hata, K., Kravitz, J., Chen, S., Kalantidis, Y., Li, L.-J., Shamma, D. A., Bernstein, M., & Fei-Fei, L. (2016). Visual genome: Connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. arXiv:1602.07332.
Kulkarni, G., Premraj, V., Dhar, S., Li, S., Choi, Y., Berg, A. C., & Berg, T. L. (2011). Baby talk: Understanding and generating image descriptions. In CVPR.
Lebret, R., Pinheiro, P. O., & Collobert, R. (2015). Phrase-based image captioning. In ICML.
Lev, G., Sadeh, G., Klein, B., & Wolf, L. (2016). RNN fisher vectors for action recognition and image annotation. In ECCV.
Lin, T.-Y., Maire, M., Belongie, S., Hays, J., Perona, P., Ramanan, D., Dollár, P., & Zitnick, C. L. (2014). Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In ECCV.
Ma, L., Lu, Z., Shang, L., & Li, H. (2015). Multimodal convolutional neural networks for matching image and sentence. In ICCV.
Malinowski, M. & Fritz, M. (2014). A multi-world approach to question answering about real-world scenes based on uncertain input. In Ghahramani, Z., Welling, M., Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., and Weinberger, K., (eds) NIPS.
Mao, J., Jonathan, H., Toshev, A., Camburu, O., Yuille, A., & Murphy, K. (2016). Generation and comprehension of unambiguous object descriptions. CVPR.
Mao, J., Xu, W., Yang, Y., Wang, J., & Yuille, A. (2015). Deep captioning with multimodal recurrent neural networks (m-RNN). In ICLR.
McCarthy, J. F. & Lehnert, W. G. (1995). Using decision trees for coreference resolution. http://arxiv.org/abs/cmp-lg/9505043.
Mikolov, T., Sutskever, I., Chen, K., Corrado, G. S., & Dean, J. (2013). Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In NIPS.
Ordonez, V., Kulkarni, G., & Berg, T. L. (2011). Im2Text: Describing images using 1 million captioned photographs. NIPS.
Perronnin, F., Sánchez, J., & Mensink, T. (2010). Improving the Fisher kernel for large-scale image classification. In ECCV.
Plummer, B. A., Wang, L., Cervantes, C. M., Caicedo, J. C., Hockenmaier, J., & Lazebnik, S. (2015). Flickr30k entities: Collecting region-to-phrase correspondences for richer image-to-sentence models. In ICCV.
Ramanathan, V., Joulin, A., Liang, P., & Fei-Fei, L. (2014). Linking people in videos with “their” names using coreference resolution. In ECCV.
Rashtchian, C., Young, P., Hodosh, M., & Hockenmaier, J. (2010). Collecting image annotations using Amazon’s mechanical turk. In NAACL HLT Workshop on Creating Speech and Language Data with Amazon’s Mechanical Turk, pp. 139-147. ACL.
Ren, M., Kiros, R., & Zemel, R. (2015). Exploring models and data for image question answering. In NIPS.
Rohrbach, A., Rohrbach, M., Hu, R., Darrell, T., & Schiele, B. (2016). Grounding of textual phrases in images by reconstruction. In ECCV.
Silberman, N., Hoiem, D., Kohli, P., & Fergus, R. (2012). Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images. In ECCV.
Simonyan, K. & Zisserman, A. (2014). Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556.
Soon, W. M., Ng, H. T., & Lim, D. C. Y. (2001). A machine learning approach to coreference resolution of noun phrases. Computational Linguistics, 27(4), 521–544.
Sorokin, A. & Forsyth, D. (2008). Utility data annotation with Amazon Mechanical Turk. In Internet Vision Workshop.
Su, H., Deng, J., & Fei-Fei, L. (2012). Crowdsourcing annotations for visual object detection. In AAAI Technical Report, 4th Human Computation Workshop.
Tommasi, T., Mallya, A., Plummer, B. A., Lazebnik, S., Berg, A., & Berg., T. (2016). Solving visual madlibs with multiple cues. In BMVC.
Uijlings, J., van de Sande, K., Gevers, T., & Smeulders, A. (2013). Selective search for object recognition. IJCV, 104(2), 154–171.
Vinyals, O., Toshev, A., Bengio, S., & Erhan, D. (2015). Show and tell: A neural image caption generator. In CVPR.
Wang, L., Li, Y., & Lazebnik, S. (2016a). Learning deep structure-preserving image-text embeddings. In CVPR.
Wang, M., Azab, M., Kojima, N., Mihalcea, R., & Deng, J. (2016b). Structured matching for phrase localization. In ECCV.
Xu, K., Ba, J., Kiros, R., Courville, A., Salakhutdinov, R., Zemel, R., & Bengio, Y. (2015). Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In ICML.
Yao, B., Yang, X., Lin, L., Lee, M. W., & Zhu, S.-C. (2010). I2T: Image parsing to text description. Proceedings of the IEEE, 98(8), 1485–1508.
Young, P., Lai, A., Hodosh, M., & Hockenmaier, J. (2014). From image descriptions to visual denotations: New similarity metrics for semantic inference over event descriptions. TACL, 2, 67–78.
Yu, L., Park, E., Berg, A. C., & Berg, T. L. (2015). Visual Madlibs: Fill in the blank Image Generation and Question Answering. In ICCV.
Zhang, J., Lin, Z., Brandt, Jonathan, S. X., & Sclaroff, S. (2016). Top-down neural attention by excitation backprop. In ECCV.
Zitnick, C. L. & Dollár, P. (2014). Edge boxes: Locating object proposals from edges. In ECCV.
Zitnick, C. L. & Parikh, D. (2013). Bringing semantics into focus using visual abstraction. In CVPR.
Acknowledgments
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grants No. 1053856, 1205627, 1405883, 1228082, 1302438, 1563727, as well as support from Xerox UAC and the Sloan Foundation. We thank the NVIDIA Corporation for the generous donation of the GPUs used for our experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Margaret Mitchell, John Platt, and Kate Saenko.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plummer, B.A., Wang, L., Cervantes, C.M. et al. Flickr30k Entities: Collecting Region-to-Phrase Correspondences for Richer Image-to-Sentence Models. Int J Comput Vis 123, 74–93 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0965-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-016-0965-7