Abstract
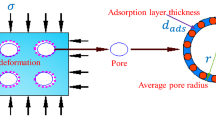
In order to investigate the effect of pore geometry structure on the gas permeability, 3 permeability models with different pore shapes were constructed, considering the sorption-induced deformation, adsorption molecular layer and variable Klinkenberg’s effect. The effect of pore geometry structure on the effective pore radius, Klinkenberg’s factor and permeability was analyzed under 3 different conditions, including constant effective stress conditions, constant pore pressure conditions and constant mean stress conditions. Results showed that, under constant effective stress conditions, the spherical pores show a greater effect on the effective radius, followed by the cylindrical pores and the slit pores. Under the constant pore pressure conditions and the constant mean stress conditions, the effective pore radius is more sensitive to the slit pores, followed by the cylindrical pores and the spherical pores. Under 3 different conditions, Klinkenberg’s factor is more sensitive to the slit pores, followed by the cylindrical pores and the spherical pores. Moreover, the permeability evolution with different pore geometry structures shows similar characteristics with effective pore radius, indicating that the effective radius dominates the permeability difference in different pore geometry structures. Furthermore, a numerical model was proposed to investigate the permeability evolution in the reservoir conditions. In the initial extraction stage, the permeability is increased with the rising slit pores. However, in the later stage, the spherical pores show more notable improvement effect on the permeability. Then, the effective pore radius and Klinkenberg’s factor were analyzed to reveal the influence mechanism of different pore geometry structures, indicating that the effective pore radius dominates the permeability difference, while Klinkenberg’s effect plays more significant role for the permeability trends and shows notable improvement effect on the permeability.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashrafi Moghadam, A., Chalaturnyk, R.: Expansion of the Klinkenberg’s slippage equation to low permeability porous media. Int. J. Coal Geol. 123, 2–9 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2013.10.008
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P.H., Teller, E.: Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 60(2), 309–319 (1938)
Cai, Y., Liu, D., Pan, Z.: Partial coal pyrolysis and its implication to enhance coalbed methane recovery: a simulation study. Energy Fuels 31(5), 4895–4903 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b00219
Cao, P., Liu, J., Leong, Y.-K.: General gas permeability model for porous media: bridging the gaps between conventional and unconventional natural gas reservoirs. Energy Fuels 30(7), 5492–5505 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00683
Cheng, W.-M., Hu, X.-M., Zhao, Y.-Y., Wu, M.-Y., Hu, Z.-X., Yu, X.-T.: Preparation and swelling properties of poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) composite hydrogels. e-Polymers 17(1), 95–106 (2017a)
Cheng, W., Hu, X., Xie, J., Zhao, Y.: An intelligent gel designed to control the spontaneous combustion of coal: fire prevention and extinguishing properties. Fuel 210, 826–835 (2017b)
Connell, L.D.: A new interpretation of the response of coal permeability to changes in pore pressure, stress and matrix shrinkage. Int. J. Coal Geol. 162, 169–182 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2016.06.012
Fink, R., Gaus, G., Krooss, B.M., Gensterblum, Y., Amann-Hildenbrand, A.: Apparent permeability of gas shales—separation of fluid-dynamic and poro-elastic effects. In: Biot Conference on Poromechanics, pp. 1930–1937 (2017)
Hou, P., Gao, F., Gao, Y., Yang, Y., Cheng, H.: Effect of pulse gas pressure fatigue on mechanical properties and permeability of raw coal. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2, 257–264 (2017)
Hu, G., Wang, H., Fan, X., Yuan, Z., Hong, S.: Mathematical model of coalbed gas flow with Klinkenberg effects in multi-physical fields and its analytic solution. Transp. Porous Media 76(3), 407–420 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-008-9254-4
Jasinski, L., Sangaré, D., Adler, P., Mourzenko, V., Thovert, J.-F., Gland, N., Békri, S.: Transport properties of a Bentheim sandstone under deformation. Phys. Rev. E 91(1), 013304 (2015)
Li, C.J., Feng, J.L.: Adsorption-induced permeability change of porous material: a micromechanical model and its applications. Arch. Appl. Mech. 86(3), 465–481 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-1041-4
Li, Y., Tang, D., Xu, H., Meng, Y., Li, J.: Experimental research on coal permeability: the roles of effective stress and gas slippage. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 21, 481–488 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2014.09.004
Liu, J., Chen, Z., Elsworth, D., Miao, X., Mao, X.: Evaluation of stress-controlled coal swelling processes. Int. J. Coal Geol. 83(4), 446–455 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2010.06.005
Liu, Q., Cheng, Y., Zhou, H., Guo, P., An, F., Chen, H.: A mathematical model of coupled gas flow and coal deformation with gas diffusion and Klinkenberg effects. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 48(3), 1163–1180 (2015)
Pan, Z., Connell, L.D.: Impact of coal seam as interlayer on CO2 storage in saline aquifers: a reservoir simulation study. Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control 5(1), 99–114 (2011a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.06.012
Pan, Z., Connell, L.D.: Modelling of anisotropic coal swelling and its impact on permeability behaviour for primary and enhanced coalbed methane recovery. Int. J. Coal Geol. 85(3–4), 257–267 (2011b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2010.12.003
Pan, Z., Connell, L.D.: Modelling permeability for coal reservoirs: a review of analytical models and testing data. Int. J. Coal Geol. 92, 1–44 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2011.12.009
Peng, Y., Liu, J., Pan, Z., Connell, L.D.: A sequential model of shale gas transport under the influence of fully coupled multiple processes. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 27, 808–821 (2015)
Ranathunga, A.S., Perera, M.S.A., Ranjith, P.G., Rathnaweera, T.D., Zhang, X.G.: Effect of coal rank on CO2 adsorption induced coal matrix swelling with different CO2 properties and reservoir depths. Energy Fuels 31(5), 5297–5305 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b03321
Senthamaraikkannan, G., Gates, I., Prasad, V.: Development of a multiscale microbial kinetics coupled gas transport model for the simulation of biogenic coalbed methane production. Fuel 167, 188–198 (2016)
Seomoon, H., Lee, M., Sung, W.: Analysis of sorption-induced permeability reduction considering gas diffusion phenomenon in coal seam reservoir. Transp. Porous Media 108(3), 713–729 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-015-0498-5
Si, L., Li, Z., Xue, D., Zhou, J., Yang, Y., Zhou, Y.: Modeling and application of gas pressure measurement in water-saturated coal seam based on methane solubility. Transp. Porous Media 119(1), 163–179 (2017a). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-017-0878-0
Si, L., Li, Z., Yang, Y., Xin, L., Liu, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, X.: Experimental investigation for pore structure and CH4 release characteristics of coal during pulverization process. Energy Fuels 31(12), 14357–14366 (2017b)
Si, L., Li, Z., Yang, Y., Zhou, J., Zhou, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, L.: Modeling of gas migration in water-intrusion coal seam and its inducing factors. Fuel 210, 398–409 (2017c)
Wang, F., Cheng, Y., Lu, S., Jin, K., Zhao, W.: Influence of coalification on the pore characteristics of middle–high rank coal. Energy Fuels 28(9), 5729–5736 (2014a). https://doi.org/10.1021/ef5014055
Wang, G., Ren, T., Wang, K., Zhou, A.: Improved apparent permeability models of gas flow in coal with Klinkenberg effect. Fuel 128, 53–61 (2014b). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2014.02.066
Wang, J., Liu, H., Wang, L., Zhang, H., Luo, H., Gao, Y.: Apparent permeability for gas transport in nanopores of organic shale reservoirs including multiple effects. Int. J. Coal Geol. 152, 50–62 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2015.10.004
Wang, K., Zang, J., Wang, G., Zhou, A.: Anisotropic permeability evolution of coal with effective stress variation and gas sorption: model development and analysis. Int. J. Coal Geol. 130, 53–65 (2014c). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2014.05.006
Wang, L., Liu, S., Cheng, Y., Yin, G., Zhang, D., Guo, P.: Reservoir reconstruction technologies for coalbed methane recovery in deep and multiple seams. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 27(2), 277–284 (2017)
Wei, Z., Zhang, D.: Coupled fluid-flow and geomechanics for triple-porosity/dual-permeability modeling of coalbed methane recovery. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 47(8), 1242–1253 (2010)
Xu, H., Tang, D., Mathews, J.P., Zhao, J., Li, B., Tao, S., Li, S.: Evaluation of coal macrolithotypes distribution by geophysical logging data in the Hancheng Block, Eastern Margin, Ordos Basin, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 165, 265–277 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2016.09.002
Yan, B., Wang, Y., Killough, J.E.: Beyond dual-porosity modeling for the simulation of complex flow mechanisms in shale reservoirs. Comput. Geosci. 20(1), 69–91 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10596-015-9548-x
Yang, R., Li, Y., Guo, D., Yao, L., Yang, T., Li, T.: Failure mechanism and control technology of water-immersed roadway in high-stress and soft rock in a deep mine. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 27(2), 245–252 (2017)
Yu, B., Chen, Z., Wu, J., Wang, L.: Experimental study non-Darcy flow seepage properties of cemented broken rocks with mass loss. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2, 321–327 (2017)
Zang, J., Wang, K.: Gas sorption-induced coal swelling kinetics and its effects on coal permeability evolution: model development and analysis. Fuel 189, 164–177 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2016.10.092
Zhang, H., Liu, J., Elsworth, D.: How sorption-induced matrix deformation affects gas flow in coal seams: a new FE model. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 45(8), 1226–1236 (2008)
Zhang, T., Ellis, G.S., Ruppel, S.C., Milliken, K., Yang, R.: Effect of organic-matter type and thermal maturity on methane adsorption in shale-gas systems. Org. Geochem. 47(6), 120–131 (2012)
Zhou, Y., Li, Z., Yang, Y., Zhang, L., Si, L., Kong, B., Li, J.: Evolution of coal permeability with cleat deformation and variable Klinkenberg effect. Transp. Porous Media 115(1), 153–167 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-016-0759-y
Ziarani, A.S., Aguilera, R.: Knudsen’s permeability correction for tight porous media. Transp. Porous Media 91(1), 239–260 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-011-9842-6
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2018BSCXA02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Si, L., Li, Z. & Yang, Y. Influence of the Pore Geometry Structure on the Evolution of Gas Permeability. Transp Porous Med 123, 321–339 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1044-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1044-z