Abstract
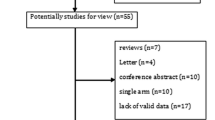
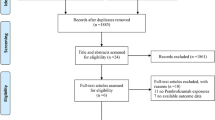
Introduction Lung cancer accounts for 20 % of cancer deaths in Spain. The most frequent subtype (87 %) is non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Pemetrexed is a recently marketed drug added to NSCLC therapeutic arsenal. It seems to have become one of the most used options for the treatment of this condition over the last 3 years. Aim of the review To evaluate the efficacy and safety of pemetrexed in NSCLC, in the different therapy lines. Method A systematic search of published literature was conducted using the main databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Library and the Center for Reviews and Dissemination) and subsequently a search of referenced literature was performed. We included clinical trials, meta-analyses and systematic reviews. The evaluation of the quality of the articles was performed by pairs using specific assessment scales, Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) adapted for CASP Spain. Then we extracted data on efficacy and safety according to the treatment line assessed. Results We identified 277 references. Finally, nine clinical trials and a meta-analysis complied with inclusion criteria. In first-line induction, treatment with pemetrexed associated with a platinum was similar in terms of efficacy to other alternative chemotherapy regimens, except in patients with non-squamous histology, in whom survival was higher in the experimental group. In maintenance treatment, greater efficacy was seen with pemetrexed in patients with non-squamous histology. In second-line treatment, there were no significant differences in terms of efficacy and safety for pemetrexed treatment versus other chemotherapy options. The most frequent adverse reactions were: hematological, gastrointestinal and neurological. All were significantly less frequent with pemetrexed versus other alternative therapies, except for liver toxicity. Conclusions Due to the high degree of uncertainty as to its efficacy in certain subgroups of patients, including conflicting data; to its recent incorporation, and therefore lack of safety data in the medium and long term, and the high budgetary impact of its incorporation into health systems, it seems reasonable to optimize its use, identifying those patients who may benefit most.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90.
Spanish Group of Lung Cancer. http://www.gecp.org/. Accessed 29 Oct 2013.
Hawes SE, Stern JE, Feng Q, Wiens LW, Rasey JS, Lu H, et al. DNA hypermethylation of tumors from non-small-cell (NSCLC) is associated with gender and histologic type. Lung Cancer. 2010;69:172–9.
Gorlova OY, Weng SF, Hernandez L, Spitz MR, Forman MR. Dietary patterns affect lung cancer risk in never smokers. Nutr Cancer. 2011;63:842–9.
De Matteis S, Consonni D, Lubin JH, Tucker M, Peters S, Vermeulen R, et al. Impact of occupational carcinogens on lung cancer risk in a general population. Int J Epidemiol. 2012;41:711–21.
Peng WJ, He Q, Yang JX, Wang BX, Lu MM, Wang S, et al. Meta-analysis of association between cytokine gene polymorphisms and lung cancer risk. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39:5187–94.
Villanueva-Herraiz S, Ortega-García MP, Camps-Herrero C, Blasco-Segura P. Study of use of pemetrexed in non-small cell lung cancer. Farm Hosp. 2010;34:194–203.
American Cancer Society Guidance on Lung Cancer Screening 2001.
Boulikas T, Vougiouka M. Recent clinical trials using cisplatin, carboplatin and their combination chemotherapy drugs (review). Oncol Rep. 2004;11:559–95.
DiPiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG, Posey LM. Pharmacotherapy A pathophysiologic approach, vol 132. 8th ed. 2011. p. 2157–2173.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology—small cell lung cancer. 2010. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/default.asp. Accessed 29 Oct 2013.
Summary of product Characteristics. European medicines agency. http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/. Accessed 29 Oct 2013.
Scagliotti GV, Parikh P, von Pawel J, Biesma B, Vansteenkiste J, Manegold C, et al. Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus gemcitabine with cisplatin plus pemetrexed in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3543–51.
Novelló S, Pimentel FL, Douillard JY, O’Brien M, von Pawel H, Eckardt J, et al. Safety and resource utilization by non-small cell lung cancer histology: results from the randomized phase III study of pemetrexed plus cisplatin versus gemcitabine plus cisplatin in chemonaïve patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:1602–8.
Grønberg BH, Bremnes RM, Fløtten O, Amuelasen T, Brunsvig PF, Hjelde HH, et al. Phase III study by the Norwegian lung cancer study group: pemetrexed plus carboplatin compared with gemcitabine plus carboplatin as first-line chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:3217–24.
Socinski MA, Raju RN, Stinchcombe T, Kocs DM, Couch LS, Barrera D, et al. Randomized phase II trial of pemetrexed and carboplatin with or without enzastaurin versus docetaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment of patients with stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:1963–9.
Rodriguez-Pereira J, Kim JH, Magallanes M, Lee DH, Wang J, Ganju V, et al. A randomized phase 3 trial comparing pemetrexed/carboplatin and docetaxel/carboplatin as first-line treatment for advanced, nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:1907–14.
Ciuleanu T, Brodowicz T, Zielinski C, Kim JH, Krzakowski M, Laack E, et al. Maintenance pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care for non-small-cell lung cancer: a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2009;374:1432–40.
Belani CP, Brodowicz T, Ciuleanu TE, Krzakowski M, Yang SH, Franke F, et al. Quality of life in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer given maintenance treatment with pemetrexed versus placebo (H3E-MC-JMEN): results from a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:292–9.
Paz-Ares L, de Marinis F, Dediu M, Thomas M, Pujol JL, Bidoli P, et al. Maintenance therapy with pemetrexed plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care after induction therapy with pemetrexed plus cisplatin for advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (PARAMOUNT): a double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:247–55.
Hanna N, Shepherd FA, Fossella FV, Rodrigues-Pereira J, De Marinis F, von Pawel J, et al. Randomized phase III trial of pemetrexed versus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer previously treated with chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1589–97.
Al-Saleh K, Quinton C, Ellis PM. Role of pemetrexed in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, with histology subgroup analysis. Curr Oncol. 2012;19:9–15.
Agulló-Ortuño MT, López-Ríos F, Paz-Ares L. Lung cancer genomic signatures. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:1673–91.
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Pemetrexed for the first-line treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. NICE TA 181. 2009a. http://guidance.nice.org.uk/TA181. Accessed 29 Oct 2013.
Scagliotti GV, ParK K, Patil S, Rolski J, Goksel T, Martins R, et al. Survival without toxicity for cisplatin plus pemetrexed versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine in chemonaïve patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a risk-benefit analysis of a large phase III study. Eur J Cancer. 2009;45:2298–303.
Li M, Zhang Q, Fu P, Li P, Peng A, Zhang G, et al. Pemetrexed plus platinum as the first-line treatment option for evinced non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. 2012;7:e37229.
Carlson J, Reyes C, Oestreicher N, Lubeck D, Ramsey SD, Veenstra DL. Comarative clinical and economic outcomes of treatments for refractory non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 2008;61:405–15.
Fleeman N, Bagust A, McLeod C, Greenhalgh J, Boland A, Dundar Y, et al. Pemetrexed for the first-line treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14:47–53.
Greenhalgh J, Mc Leod C, Bagust A, Boland A, Fleeman N, Dundar Y, et al. Pemetrexed for the maintenance treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Health Technol Assess. 2010;14:47–53.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge their cooperation with other parts of the Pharmacy Department of Virgen del Rocio Hospital and to Postgraduate Department of the Faculty of Pharmacy from the University of Granada.
Funding
This study was supported by the Health Department of the Spanish Government. (Investigación Clínica Independiente. Ministerio de Sanidad y Política Social).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Moreno, M.A., Galván-Banqueri, M., Flores-Moreno, S. et al. Systematic review of efficacy and safety of pemetrexed in non-small-cell-lung cancer. Int J Clin Pharm 36, 476–487 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-014-9920-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-014-9920-2