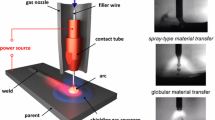
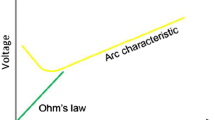
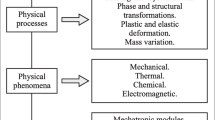
Abstract
The state-of-the-art on arc welding research is considered, with unresolved questions and future directions highlighted. Both diagnostics and modelling are discussed. The focus is on the arc plasma, and its interactions with the electrode and workpiece, in tungsten–inert-gas and metal–inert-gas welding. Areas in which the need for further work is identified include development of techniques to measure current density distributions, calculation of the distribution of different gasses in the arc plasma (for example vapours of different metallic elements when welding alloys), computational methods for modelling metal transfer, and treatments of the sheath regions. It is shown that a thorough understanding of the arc is important in welding research and development. For example, reliable calculation of the heat flux to the workpiece requires the interactions between the arc and electrodes to be considered. Computational models of welding that take into account these interactions can already predict the shape and depth of the weld pool. Extensions of these methods would enable the determination of important properties of the welded metal, such as microstructure, residual stress and distortion, raising the possibility of the development of a “virtual manufacturing” capability.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eagar TW (1990) An iconoclast’s view of the physics of welding—rethinking old ideas. In: David SA, Vitek JM (eds) 2nd international conference on trends in welding research, Gatlinburg, Tennessee, 1989. ASM International, Materials Park, OH, USA, pp 341–346
Lancaster JF (ed) (1986) The physics of welding, 2nd edn. Pergamon, Oxford
Norrish J (ed) (1992) Advanced welding processes. Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol
Murphy AB (2010) The effects of metal vapour in arc welding. J Phys D Appl Phys 43(43):434001
Valensi F, Pellerin S, Boutaghane A, Dzierzega K, Zielinska S, Pellerin N, Briand F (2010) Plasma diagnostics in gas metal arc welding by optical emission spectroscopy. J Phys D Appl Phys 43(43):434002
Murphy AB (2002) Electron heating in the measurement of electron temperature by Thomson scattering: are thermal plasmas thermal? Phys Rev Lett 89(2):025002
Snyder SC, Bentley RE (1996) A measurement of axial velocity and temperature in a free-burning arc using Thomson scattering. J Phys D Appl Phys 29(12):3045–3049
Murphy AB, Farmer AJD, Haidar J (1992) Laser-scattering measurements of temperature profiles of a free-burning arc. Appl Phys Lett 60(11):1304–1306
Zielinska S, Musiol K, Dzierzega K, Pellerin S, Valensi F, de Izarra C, Briand F (2007) Investigations of GMAW plasma by optical emission spectroscopy. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 16(4):832–838
Rouffet ME, Wendt M, Goett G, Kozakov R, Schoepp H, Weltmann KD, Uhrlandt D (2010) Spectroscopic investigation of the high-current phase of a pulsed GMAW process. J Phys D Appl Phys 43(43):434003
Murphy AB (2013) Influence of metal vapour on arc temperatures in gas–metal arc welding: convection versus radiation. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(22):224004
Kühn-Kauffeldt M, Marqués J-L, Schein J (2015) Thomson scattering diagnostics of steady state and pulsed welding processes without and with metal vapor. J Phys D Appl Phys 48(1):012001
Kozakov R, Gött G, Schöpp H, Uhrlandt D, Schnick M, Hässler M, Füssel U, Rose S (2013) Spatial structure of the arc in a pulsed GMAW process. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(22):224001
Nestor OH (1962) Heat intensity and current density distributions at the anode of high current, inert gas arcs. J Appl Phys 33(5):1638–1648
Vilarinho LO, Fanara C (2004) A modified split-anode detector for the study of the anode region of atmospheric pressure arc plasmas. Meas Sci Technol 15(1):67–74
Gonzalez JJ, Freton P, Masquère M (2007) Experimental quantification in thermal plasma medium of the heat flux transferred to an anode material. J Phys D Appl Phys 40(18):5602–5611
Siewert E, Schein J, Forster G (2014) Determination of enthalpy, temperature, surface tension and geometry of the material transfer in PGMAW for the system argon–iron. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(22):224008
Haidar J, Farmer AJD (1993) A method for the measurement of the cathode surface temperature for a high current free burning arc. Rev Sci Instrum 64(2):542–547
Wu CS, Zhong LM, Gao JQ (2009) Visualization of hump formation in high-speed gas metal arc welding. Meas Sci Technol 20(11):115702
Zhang G, Wu CS, Liu X (2015) Single vision system for simultaneous observation of keyhole and weld pool in plasma arc welding. J Mater Process Technol 215(1):71–78
Wahab MA, Painter MJ, Davies MH (1998) The prediction of the temperature distribution and weld pool geometry in the gas metal arc welding process. J Mater Process Technol 77(1–3):233–239
Yamamoto K, Tanaka M, Tashiro S, Nakata K, Yamamoto E, Yamazaki K, Suzuki K, Murphy AB, Lowke JJ (2009) Numerical simulation of diffusion of multiple metal vapours in a TIG arc plasma for welding of stainless steel. Weld World 53(7–8):R166–R170
Zhang XN, Murphy AB, Li HP, Xia WD (2014) Combined diffusion coefficients for a mixture of three ionized gases. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 23(6):065044
Hertel M, Spille-Kohoff A, Füssel U, Schnick M (2013) Numerical simulation of droplet detachment in pulsed gas–metal arc welding including the influence of metal vapour. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(22):224003
Hertel M, Füssel U, Schnick M (2014) Numerical simulation of the plasma–MIG process—interactions of the arcs, droplet detachment and weld pool formation. Weld World 58(1):85–92
Crowe CT, Sharma MP, Stock DE (1977) The particle-source-in cell (PSI-CELL) model for gas-droplet flows. J Fluid Eng 99(2):325–332
Murphy AB (2013) Influence of droplets in gas–metal arc welding—a new modelling approach, and application to welding of aluminium. Sci Technol Weld Join 18(1):32–37
Jäckel S, Hertel M, Füssel U, Rose S (2014) Three-dimensional modelling of the GMAW process using time-dependent electrode shapes from experimental observations. In: Visual-JW2014 PCo (ed) International symposium on visualization in joining & welding science through advanced measurements and simulation, Osaka, 26–28 November 2014. Joining and Welding Research Institute, Osaka University, Osaka, pp 11–12
Kim J-W, Na S-J (1995) A study on the effect of contact tube-to-workpiece distance on weld pool shape in gas metal arc welding. Weld J 74(5):141s–152s
Lowke JJ, Tanaka M (2006) ‘LTE-diffusion approximation’ for arc calculations. J Phys D Appl Phys 39(16):3634–3643
Sansonnens L, Haidar J, Lowke JJ (2000) Prediction of properties of free burning arcs including effects of ambipolar diffusion. J Phys D Appl Phys 33(2):148–157
Coulombe S, Meunier J-L (1997) Thermo-field emission: a comparative study. J Phys D Appl Phys 30(5):776–780
Lowke JJ, Tanaka M The physics of non-thermionic cathodes of electric arcs. In: Jones JE (ed) Proceedings of 17th international conference on gas discharges and their applications, Cardiff, UK, 7–12 September 2008, pp 137–140
Yokomizu Y, Matsumura T, Sun WY, Lowke JJ (1998) Electrode sheath voltages for helium arcs between non-thermionic electrodes of iron, copper and titanium. J Phys D Appl Phys 31(7):880–883
Lowke JJ, Morrow R, Haidar J (1997) A simplified unified theory of arcs and their electrodes. J Phys D Appl Phys 30(14):2033–2042
Baeva M, Uhrlandt D, Benilov MS, Cunha MD (2013) Comparing two non-equilibrium approaches to modelling of a free-burning arc. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 22(6):065017
Baeva M, Kozakov R, Gorkachov S, Uhrlandt D (2012) Two-temperature chemically non-equilibrium modelling of transferred arcs. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 21(5):055027
Benilov MS, Benilova LG, Li H-P, Wu G-Q (2012) Sheath and arc-columns voltages in high-pressure arc discharges. J Phys D Appl Phys 45(35):355201
Murphy AB (1994) Laser-scattering temperature measurement of a free-burning arc in nitrogen. J Phys D Appl Phys 27(7):1492–1498
Baeva M, Uhrlandt D (2013) Plasma chemistry in the free-burning Ar arc. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(32):325202
Mentel J (1977) The influence of vaporization upon the roots of a high current arc. I. Different forms of vaporization in the arc roots. Appl Phys 14(3):269–276
Mentel J (1978) The influence of vaporization upon the roots of a high current arc. III. Determination of the vapour temperature by molecular spectroscopy and conclusions concerning the arc-root instability. Appl Phys 15(2):179–183
Tanaka M, Heberlein JVR, Watanabe T (2009) Initiation of anode material evaporation in a transferred arc device. In: von Keudell A, Winter J (eds) 19th international symposium on plasma chemistry, Bochum, Germany, 26–31 July 2009, paper P1.1.19
Feng Z (ed) (2005) Processes and mechanisms of welding residual stress and distortion. Woodhead, Cambridge
Muránsky O, Smith MC, Bendeich PJ, Holden TM, Luzin V, Martins RV, Edwards L (2012) Comprehensive numerical analysis of a three-pass bead-in-slot weld and its critical validation using neutron and synchrotron diffraction residual stress measurements. Int J Sol Struct 49(9):1045–1062
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murphy, A.B. A Perspective on Arc Welding Research: The Importance of the Arc, Unresolved Questions and Future Directions. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 35, 471–489 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-015-9620-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-015-9620-2