Abstract
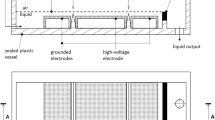
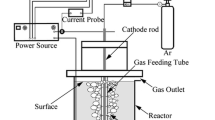
Novel apparatus for the generation of underwater plasma based on DC diaphragm discharge excited in a vapor bubble has been developed for decontamination and disinfection of conductive water. The apparatus allows deposition of relatively high applied power into the discharge (order of kW) and the treatment of a relatively large volume of liquid (order of L/min). The apparatus is operated at the quasi-pulse regime with self-terminating discharge pulses (with a repetition rate of 15–20 Hz) generated upon the formation of the vapor bubble inside the diaphragm (capillary) and its subsequent breakdown. The effects of input power, solution conductivity and the method of liquid flow through the reactor on the plasmachemical yield of H2O2 production and degradation of phenol have been determined. The biocidal effects of the apparatus were evaluated on inactivation of bacteria E. coli and E. faecalis suspended in aqueous NaCl solutions and on growth inhibition of the cyanobacterium Planktothrix sp. in natural lake water. The apparatus proved to be capable of efficiently reducing biological contamination in water, especially when operated in the plug-flow regime (up to a 5-log reduction in bacteria after 3 passes through the reactor). In the case of cyanobacteria, the growth inhibition further proceeded after exposure to the discharge and one pass of the biomass through the reactor was sufficient to reduce the algae in the water.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Locke BR, Sunka P, Sato M, Hoffmann M, Chang JS (2006) Electrohydraulic discharge and non thermal plasma for water treatment. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:882–905
Lukes P, Locke BR, Brisset JL (2012) Aqueous-phase chemistry of electrical discharge plasma in water and in gas-liquid environments. In: Parvulescu VI, Magureanu M, Lukes P (eds) Plasma chemistry and catalysis in gases and liquids. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 241–307
Lukes P, Brisset JL, Locke BR (2012) Biological effects of electrical discharge plasma in water and in gas-liquid environments. In: Parvulescu VI, Magureanu M, Lukes P (eds) Plasma chemistry and catalysis in gases and liquids. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 309–352
Locke BR, Lukes P, Brisset JL (2012) Elementary chemical and physical phenomena in electrical discharge plasma in gas-liquid environments and in liquids. In: Parvulescu VI, Magureanu M, Lukes P (eds) Plasma chemistry and catalysis in gases and liquids. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, pp 183–239
Babicky V, Clupek M, Lukes P, Sunka P (2009) Apparatus for decontamination and disinfection of aqueous solutions. PCT Application WO 2009/033436 A1, Mar 19, 2009
Monte M, De Baerdemaeker F, Leys C, Maximov AI (2002) Experimental study of a diaphragm discharge in water. Czech J Phys 52 (Suppl. D):724–730
Stara Z, Krcma F (2004) The study of H2O2 generation by DC diaphragm discharge in liquids. Czech J Phys 54:C1050–C1055
Prochazkova J, Stara Z, Krcma F (2006) Optical emission spectroscopy of diaphragm discharge in water solutions. Czech J Phys 56:B1314–B1319
Makarova EM, Khlyustova AV, Maksimov AI (2009) Diaphragm discharge influence on physical and chemical properties of electrolyte solutions. Surf Eng Appl Electrochem 45(2):133–135
Sunka P, Babicky V, Clupek M, Lukes P, Balcarova J (2003) Modified pinhole discharge for water treatment. In: Giesselmann M, Neuber A (eds) PPC-2003: 14th IEEE International Pulsed Power Conference, Vol. 1 and 2, Digest of Technical Papers, New York, 2003. IEEE, pp 229–231
Krcma F, Stara Z, Prochazkova J (2010) Diaphragm discharge in liquids: fundamentals and applications. J Phys: Conf Ser 207:012010
Joshi R, Schulze RD, Meyer-Plath A, Friedrich JF (2008) Selective surface modification of poly(propylene) with OH and COOH groups using liquid-plasma systems. Plasma Process Polym 5(7):695–707
Nikiforov AY, Leys C (2007) Influence of capillary geometry and applied voltage on hydrogen peroxide and OH radical formation in ac underwater electrical discharges. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 16(2):273–280
Bruggeman P, Degroote J, Vierendeels J, Leys C (2008) DC-excited discharges in vapour bubbles in capillaries. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 17(2):025008
De Baerdemaeker F, Simek M, Leys C (2007) Efficiency of hydrogen peroxide production by ac capillary discharge in water solution. J Phys D Appl Phys 40(9):2801–2809
De Baerdemaeker F, Simek M, Schmidt J, Leys C (2007) Characteristics of ac capillary discharge produced in electrically conductive water solution. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 16(2):341–354
Bruggeman P, Leys C (2009) Non-thermal plasmas in and in contact with liquids. J Phys D Appl Phys 42(5):053001
Zhang L, Sun B, Zhu XM (2009) Organic dye removal from aqueous solution by pulsed discharge on the pinhole. J Electrost 67(1):62–66
Sun B, Aye NN, Wang XM, Zhu XM, Sato M (2011) Eradication of invasive organisms from ballast water with electrodeless pulsed-discharge hybrid reactor. IEEE Trans Ind Appl 47(3):1079–1085
De Baerdemaeker F, Simek M, Leys C, Verstraete W (2007) Pump effect of a capillary discharge in electrically conductive liquids. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 27(4):473–485
Locke BR, Shih KY (2011) Review of the methods to form hydrogen peroxide in electrical discharge plasma with liquid water. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 20(3):034006
Lukes P (2002) Water treatment by pulsed streamer corona discharge in water. PhD Dissertation, Institute of Plasma Physics AS CR, Prague, Czech Republic. http://www.ipp.cas.cz/Ips/public/lukes_dissert.pdf
Sunka P (2001) Pulse electrical discharges in water and their applications. Phys Plasmas 8:2587–2594
An W, Baumung K, Bluhm H (2007) Underwater streamer propagation analyzed from detailed measurements of pressure release. J Appl Phys 101(5):053302
Namihira T, Sakai S, Yamaguchi T, Yamamoto K, Yamada C, Kiyan T, Sakugawa T, Katsuki S, Akiyama H (2007) Electron temperature and electron density of underwater pulsed discharge plasma produced by solid-state pulsed-power generator. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 35(3):614–618
Bruggeman P, Schram D, Gonzalez MA, Rego R, Kong MG, Leys C (2009) Characterization of a direct dc-excited discharge in water by optical emission spectroscopy. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 18(2):025017
Locke BR, Mededovic Thagard S (2012) Analysis and review of chemical reactions and transport processes in pulsed electrical discharge plasma formed directly in liquid water. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 32(5):875–917
Polyakov OV, Badalyan AM, Bakhturova LF (2004) Relative contributions of plasma pyrolysis and liquid-phase reactions in the anode microspark treatment of aqueous phenol solutions. High Energ Chem 38(2):131–133
Lukes P, Clupek M, Babicky V, Sunka P (2008) Ultraviolet radiation from the pulsed corona discharge in water. Plasma Sources Sci Technol 17(2):024012
Li Z, Sakai S, Yamada C, Wang D, Chung S, Lin X, Namihira T, Katsuki S, Akiyama H (2006) The effects of pulsed streamerlike discharge on cyanobacteria cells. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 34:1719–1725
Li Z, Ohno T, Sato H, Sakugawa T, Akiyama H, Kunitomo S, Sasaki K, Ayukawa M, Fujiwara H (2008) A method of water-bloom prevention using underwater pulsed streamer discharge. J Environ Sci Health A 43:1209–1214
Wang CH, Li GF, Wu Y, Wang Y, Li J, Li D, Wang NH (2007) Role of bipolar pulsed DBD on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa in three-phase discharge plasma reactor. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 27(1):65–83
Wang CH, Wu Y, Shen XQ (2010) A multi-wire-to-cylindrical type packed-bed plasma reactor for the inactivation of M. aeruginosa. J Electrost 68(1):31–35
Drabkova M, Admiraal W, Marsalek B (2007) Combined exposure to hydrogen peroxide and light—selective effects on cyanobacteria, green algae, and diatoms. Environ Sci Technol 41(1):309–314
Drabkova M, Matthijs HCP, Admiraal W, Marsalek B (2007) Selective effects of H2O2 on cyanobacterial photosynthesis. Photosynthetica 45(3):363–369
Barrington DJ, Ghadouani A (2008) Application of hydrogen peroxide for the removal of toxic cyanobacteria and other phytoplankton from wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 42(23):8916–8921
Matthijs HCP, Visser PM, Reeze B, Meeuse J, Slot PC, Wijn G, Talens R, Huisman J (2012) Selective suppression of harmful cyanobacteria in an entire lake with hydrogen peroxide. Water Res 46(5):1460–1472
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Grant Agency of AS CR (project No. IAAX00430802) and the Czech Science Foundation (No. 104/09/H080).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lukes, P., Clupek, M., Babicky, V. et al. High Power DC Diaphragm Discharge Excited in a Vapor Bubble for the Treatment of Water. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 33, 83–95 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-012-9432-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-012-9432-6