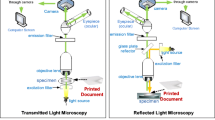
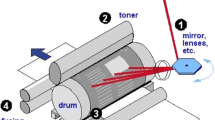
Abstract
Recently, digital forensics, which involves the collection and analysis of the origin digital device, has become an important issue. Digital content can play a crucial role in identifying the source device, such as serve as evidence in court. To achieve this goal, we use different texture feature extraction methods such as graylevel co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) and discrete wavelet transform (DWT), to analyze the Chinese printed source in order to find the impact of different output devices. Furthermore, we also explore the optimum feature subset by using feature selection techniques and use support vector machine (SVM) to identify the source model of the documents. The average experimental results attain a 98.64 % identification rate which is significantly superior to the existing known method of GLCM by 1.27 %. The superior testing performance demonstrates that the proposed identification method is very useful for source laser printer identification.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bulan O, Junwen M, Sharma G (Apr. 2009) “Geometric distortion signatures for printer identification,” in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp.1401–1404
Canny J (1986) A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell PAMI-8:679–698
Chan CS, Chang CC, Vo HP (2012) A User-Friendly Image Sharing Scheme Using JPEG-LS Median Edge Predictor. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing 3(4):340–351
Chiclana F, Herrera F, Herrera-Viedma E (1998) Integrating three representation models in fuzzy multipurpose decision making based on fuzzy preference Relations. Fuzzy Set Syst 97:33–48
Chinese Calligraphy, http://www.zein.se/patrick/chinen9p.html
Choi JH, Im DH, Lee HY, Oh JT, Ryu JH, Lee HK (Nov. 2009) “Color laser printer identification by analyzing statistical features on discrete wavelet transform,” in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1505–1508
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Mach Learn 20:273–297
Cox IJ, Kilian J, Leighton FT, Shamoon T (1997) Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 6:1673–1687
Cox IJ, Miller ML, Bloom JF, Fridrich J, Kaler T (2008) Digital Watermarking and Steganography. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, Elsevier
Daubechiesl I, Sweldens W (1998) Factoring wavelet transforms into lifting steps. J Fourier Anal Appl 4(3):247–269
Elder JH, Zucker SW (1998) Local scale control for edge detection and blur estimation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Machine Intell 20:699–716
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K, Dinstein I (1973) “Textural features for image classification,”. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics SMC–3(6):610–621. doi:10.1109/TSMC.1973.4309314
http://www.library.cornell.edu/preservation/tutorial/contents.html
Huang HC, Fang WC (2010) Metadata-Based Image Watermarking for Copyright Protection. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory 18(4):436–445
Khanna N, Mikkilineni AK, Martone AF, Ali GN, Chiu GTC, Allebach JP, Delp EJ (2006) A survey of forensic characterization methods for physical devices. Proceedings of Digital Forensic Research Workshop 3:S17–S28
Kundur D, Lin CY, Macq B, Yu H (June 2004) “Special issue on enabling security technologies for digital rights management,” in Proceedings of the IEEE, pp. 879–882
Mikkilineni AK, Ali GN, Chiang PJ, Chiu GTC, Allebach JP, Delp EJ (2004) Signature-embedding in printed documents for security and forensic applications. Proceedings of the SPIE International Conference on Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents 5306:455–466
Mikkilineni AK, Chiang PJ, Ali GN, Chiu GTC, Allebach JP, Delp EJ (2005) Printer identification based on graylevel co-occurrence features for security and forensic applications. Proceedings of the SPIE International Conference on Security 5681:430–440
Pudil P, Novovicova J, Kittler J (1994) “Floating search methods in feature selection,” Pattern Recognition Letters, pp.1119–1125
Ritchey PC, Rego VJ (2012) A Context Sensitive Tiling System for Information Hiding. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing 3(3):212–226
Stearns S (1976) “On selecting features for pattern classifiers,” In: 3rd International Conf. Pattern Recognition. Coronado, California, pp.71–75
Talbot V, Perrot P, Murie C (Sep. 2006) “Inkjet printing discrimination based on invariant moments,” in Proceedings of the IS&T’s NIP22: International Conference on Digital Printing Technologies, pp. 427–431
Tsai MJ, Liu J, Wang CS, Chuang CH (May 2011) “Source Color Laser Printer Identification Using Discrete Wavelet Transform and Feature Selection Algorithms,” IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), pp. 2633–2636
Tsai MJ, Wang CS, Liu J, Yin JS (2012) Using Decision Fusion of Feature Selection in Digital Forensics for Camera Source Model Identification. Computer Standards & Interfaces 34:292–304
Vapnik V (2000) The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Inc., New York
Villasenor JD, Belzer B, Liao J (1995) Wavelet filter evaluation for image compression. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 4(8):1053–1060
World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), http://www.wipo.int/
Yager RR (1998) “On ordered weighted averaging aggregation operators in multicriteria decision making,”. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics 18:183–190
Zhu B, Wu J, Kankanhalli M (2003) “Print signatures for document authentication”. CCS’03, Washington
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Science Council in Taiwan, Republic of China, under Grant NSC99-2410-H-009-053-MY2 and NSC101-2410-H-009-006-MY2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The revised/adjusted formulas in this study and in Mikkilineni [15]
The formulas in this study | The Formulas in Mikkilineni [15] | |
|---|---|---|
Revised formula | \( GLDHenergy={\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^N GLDM{(k)}^2} \) | \( GLDHenergy={\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^N GLDM(k)} \) |
\( GLSHenergy={\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^{2N} GLSH{(k)}^2} \) | \( GLSHenergy={\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^{2N} GLSH(k)} \) | |
\( \begin{array}{l} GLSHshade=\\ {}\kern1.5em {\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^{2N}\frac{{\left(k-{\mu}_x-{\mu}_y\right)}^3 GLSH(k)}{{\left({\sigma}_x^2-{\sigma}_y^2+2\rho {\sigma}_x{\sigma}_y\right)}^{\raisebox{1ex}{$3$}\!\left/ \!\raisebox{-1ex}{$2$}\right.}}}\end{array} \) | \( \begin{array}{l} GLSHshade=\\ {}\kern1.5em {\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^{2N}\frac{{\left(k-{\mu}_x-{\mu}_y\right)}^3 GLSH(k)}{{\left({\sigma}_x^2-{\sigma}_y^2+2\rho {\sigma}_x{\sigma}_y\right)}^{\raisebox{1ex}{$3$}\!\left/ \!\raisebox{-1ex}{$2$}\right.}}}\end{array} \) | |
\( \begin{array}{l} GLSHprom=\\ {}\kern1.25em {\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^{2N}\frac{{\left(k-{\mu}_x-{\mu}_y\right)}^4 GLSH(k)}{{\left({\sigma}_x^2+{\sigma}_y^2+2\rho {\sigma}_x{\sigma}_y\right)}^{\raisebox{1ex}{$4$}\!\left/ \!\raisebox{-1ex}{$2$}\right.}}}\end{array} \) | \( \begin{array}{l} GLSHprom=\\ {}\kern1.25em {\displaystyle \sum_{k=0}^{2N}\frac{{\left(k-{\mu}_x-{\mu}_y\right)}^4 GLSH(k)}{{\left({\sigma}_x^2-{\sigma}_y^2+2\rho {\sigma}_x{\sigma}_y\right)}^{\raisebox{1ex}{$4$}\!\left/ \!\raisebox{-1ex}{$2$}\right.}}}\end{array} \) | |
Adjusted formula | \( {\mu}_x={\displaystyle \sum_{i=0}^Ni\times {p}_x(i)} \) | \( {\mu}_x={\displaystyle \sum_{i=0}^N{p}_x(i)} \) |
\( {\mu}_y={\displaystyle \sum_{j=0}^Nj\times {p}_y(j)} \) | \( {\mu}_y={\displaystyle \sum_{j=0}^N{p}_y(j)} \) | |
\( {\sigma}_x^2={\displaystyle \sum_{i=0}^N{\left(i-{\mu}_x\right)}^2{p}_x(i)} \) | \( {\sigma}_x^2={\displaystyle \sum_{i=0}^N{i}^2\times {p}_x(i)-{\mu}_x{}^2} \) | |
\( {\sigma}_y^2={\displaystyle \sum_{j=0}^N{\left(j-{\mu}_y\right)}^2{p}_y(j)} \) | \( {\sigma}_y^2={\displaystyle \sum_{j=0}^N{j}^2\times {p}_y(j)-{\mu}_y{}^2} \) |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, MJ., Yin, JS., Yuadi, I. et al. Digital forensics of printed source identification for Chinese characters. Multimed Tools Appl 73, 2129–2155 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1642-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1642-2