Abstract
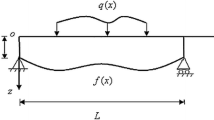
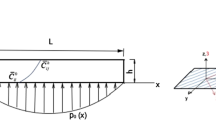
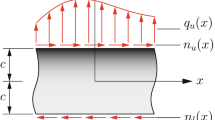
Solution is obtained for functionally graded (FG) narrow beams under plane stress condition of elasticity by using the mixed semi analytical model developed by Kant et al. (Int J Comput Methods Eng Sci Mech 8(3): 165–177, 2007a). The mathematical model consists in defining a two-point boundary value problem (BVP) governed by a set of coupled first-order ordinary differential equations (ODEs) in the beam thickness direction. Analytical solutions based on two dimensional (2D) elasticity, one dimensional (1D) first order shear deformation theory (FOST) and a new 1D higher order shear-normal deformation theory (HOSNT) are also established to show the accuracy, simplicity and effectiveness of the developed mixed semi analytical model. It is observed from the numerical investigation that the present mixed semi analytical model predicts structural response as good as the one given by the elasticity analytical solution which in turn proves the robustness of the present development.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bian, Z.G., Chen, W.Q., Lim, C.W., Zhang, N.: Analytical solution for single and multi span functionally graded plates in cylindrical bending. Int. J. Solids Struct. 42, 6433–6456 (2005)
Bodaghi, M., Saidi, A.R.: Levy-type solution for bending analysis of thick functionally graded rectangular plates based on the higher-order shear deformation plate theory. Appl. Math. Model. 34, 3659–3670 (2010)
Chakraborty, A., Gopalakrishnan, S.: A new beam finite element for the analysis of functionally graded materials. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 45, 519–539 (2003a)
Chakraborty, A., Gopalakrishnan, S.: A spectrally formulated finite element for wave propagation analysis in functionally graded beams. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40, 2421–2448 (2003b)
Ching, H.K., Chen, J.K.: Thermomechanical analysis of functionally graded composites under laser heating by the MLPG methods. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 13(3), 199–218 (2006)
Han, F., Pan, E., Roy, A.K., Yue, Z.Q.: Response of piezoelectric, transversely isotropic, functionally graded and multilayered half spaces to uniform circular surface loadings. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 14(1), 15–30 (2006)
Kang, Y.A., Li, X.F.: Bending of functionally graded cantilever beam with power-law non-linearity subjected to an end force. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 44, 696–703 (2009)
Kant, T.: Numerical analysis of thick plates. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 31(3), 1–18 (1982)
Kant, T., Manjunatha, B.S.: An unsymmetric FRC laminate C0 finite element model with 12 degrees of freedom per node. Eng. Comput. 5(3), 300–308 (1998)
Kant, T., Ramesh, C.K.: Numerical integration of linear boundary value problems in solid mechanics by segmentation method. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 17, 1233–1256 (1981)
Kant, T., Owen, D.R.J., Zienkiwicz, O.C.: A refined higher-order C0 plate bending element. Comput. Struct. 15(2), 177–183 (1982)
Kant, T., Pendhari, S.S., Desai, Y.M.: On accurate stress analysis of composite and sandwich narrow beams. Int. J. Comput. Methods Eng. Sci. Mech. 8(3), 165–177 (2007a)
Kant, T., Pendhari, S.S., Desai, Y.M.: A general partial discretization methodology for interlaminar stress computation in composite laminates. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 17(2), 135–161 (2007b)
Khabbaz, R.S., Manshadi, B.D., Abedian, A.: Nonliear analysis of FGM Plates under pressure loads using the higher-order shear deformation theories. Composite Struct. 89, 333–344 (2009)
Koizumi, M.: The concept of FGM. Ceramic transactions. Funct. Gradient Mater. 34, 3–10 (1993)
Lee, H.J.: Layerwise analysis of thermal shape control in graded piezoelectric beams. ASME Aerosp. Division (Publication) AD 68, 79–87 (2003)
Matsunaga, H.: Stress analysis of functionally graded plates subjected to thermal and mechanical loading. Composite Struct. 87, 344–357 (2009)
Nguyen, T.K., Sab, K., Bonnet, G.: First-order shear deformation plate models for functionally graded materials. Compos. Mater. 83, 25–36 (2008)
Reddy, J.N.: Analysis of functionally graded plates. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 47, 663–684 (2000)
Sankar, B.V.: An elasticity solution for functionally graded beam. Compos. Sci. Technol. 61, 689–696 (2001)
Sankar, B.V., Tzeng, J.T.: Thermal stresses in functionally graded beams. AIAA J. 410(6), 1228–1232 (2002)
Sladek, J., Slasek, V., Zhang, Ch.: The MLPG method for crack analysis in anisotropic functionally graded materials. Struct. Integr. Durab. 1(2), 131–144 (2005)
Soldatos, K.P., Liu, S.L.: On the generalised plane strain deformations of thick anisotropic composite laminated plates. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38, 479–482 (2001)
Thomson, W.T.: Transmission of elastic waves through a stratified solid medium. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 89–93 (1950)
Vel, S.S., Batra, R.C.: Analytical solution for rectangular thick laminated plates subjected to arbitrary boundary conditions. AIAA J. 37, 1464–1473 (1999)
Woo, J., Meguid, S.A.: Nonlinear analysis of functionally graded plates and shells. Int. J. Solids Struct. 38, 7409–7421 (2001)
Woo, J., Meguid, S.A., Stranart, J.C., Liew, K.M.: Thermomechanical postbuckling analysis of moderately thick functionally graded plates and shallow shells. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 47, 1147–1171 (2005)
Yamanouchi, M., Koizumi, M., Shiota, T. Proceedings of the first international symposium on functionally gradient materials, Sendai, Japan (1990)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
The elements of matrix [A] are,
and the coefficients are,
where, \( \bar{E}_{h} = \left( {{\frac{{E_{o} }}{{1 - \upsilon^{2} }}}} \right)e^{\lambda } {\text{ and }}\bar{E}_{o} = {\frac{{E_{o} }}{{(1 - \upsilon^{2} )}}} \)
and A ij = A ji (i, j = 1 to 7)
The elements of matrix [D] are,
and the coefficients are,
and D ij = D ji , (i, j = 1 to 4)
The coefficients of matrix [X] are,
and X ij = X ji , (i,j = 1 to 8)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pendhari, S.S., Kant, T., Desai, Y.M. et al. On deformation of functionally graded narrow beams under transverse loads. Int J Mech Mater Des 6, 269–282 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-010-9136-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10999-010-9136-0