Abstract
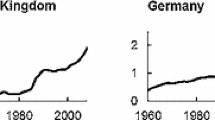
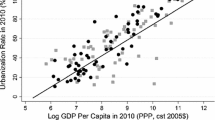
This paper considers how imperfect capital mobility affects spatial inequalities in income and industrial location. The framework of Takahashi et al. (2013) is applied to investigate the effects of integrating the capital market. Several new findings are obtained. First, the inequality in nominal income displays a bell-shaped relationship with falling trade costs if capital mobility is not too low. Second, keeping the trade costs fixed, the inequalities in nominal income and industrial location behave differently when the capital market is integrated. Finally, integration of the product market and integration of the capital market have different impacts on inequality in real income. This explains why empirical findings on spatial inequalities are mixed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin, R., Forslid, R., Martin, P., Ottaviano, G.I.P., Robert-Nicoud, F.: Economic geography and public policy. Princeton University Press, NJ (2003)
Barrios, S., Strobl, E.: The dynamics of regional inequalities. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 39(575), 591 (2009)
Behrens, K., Lamorgese, A.-R., Ottaviano, G., Tabuchi, T.: Beyond the hoe market effect: Market size and specialization in a multi-country world. J. Int. Econ. 79, 259–265 (2009)
Bouvet, F.: EMU and the dynamics of regional per capita income inequality in Europe. J. Econ. Inequal. 8, 323–344 (2010)
Davies, J.B.: Book review of capital in the twenty-first century. J. Econ. Inequal. 13, 155–160 (2015)
Ezcurra, R., Rodríguez-Pose, A.: Does economic globalization affect regional inequality? A cross-country analysis. World Dev. 52, 92–103 (2013)
Fujita, M., Krugman, P., Venables, A.J.: The Spatial Economy: Cities, Regions and International Trade. MIT Press, Cambridge (1999)
Kanbur, R., Venables, A.J., Wan, G.: Introduction to the special issue: spatial inequality and development in Asia. Rev. Dev. Econ. 9, 1–4 (2005)
Kolenikov, S., Shorrocks, A.: A decomposition analysis of regional poverty in Russia. Rev. Dev. Econ. 9, 25–46 (2005)
Lall, S.V., Chakravarty, S.: Industrial location and spatial inequality: theory and evidence from India. Rev. Dev. Econ. 9, 47–68 (2005)
Lessmann, C.: Spatial inequality and development—Is there an inverted-U relationship. Rev. Dev. Econ. 106, 35–51 (2014)
Martin, P., Rogers, C.: Industrial location and public infrastructure. Rev. Dev. Econ. 39, 335–351 (1995)
Peeters, J., de Vaal, A.: Explaining the wage gap: intra-industry trade, services linkages and falling transportation costs. J. Econ. Inequal. 1, 251–280 (2003)
Persson, T., Tabellini, G.: The politics of 1992: fiscal policy and European integration. Rev. Econ. Stud. 59, 689–701 (1992)
Piketty, T.: Capital in the Twenty-First Century. Harvard University Press, Massachusetts (2014)
Ram, R.: Real and nominal interstate income inequality in the United States: Further evidence. Int. Adv. Econ. Res. 21, 131–132 (2015)
Takahashi, T., Takatsuka, H., Zeng, D-Z.: Spatial inequality, globalization and footloose capital. Economic Theory 53, 213–238 (2013)
Tan, L., Zeng, D.-Z.: Spatial inequality between developed and developing economies. Pap. Reg. Sci. 93, 229–248 (2014)
UNCTAD: World Investment Report. (2003, 2006, 2011, and 2014). http://unctad.org/en/Pages/Publications.aspx
Yamamoto, K.: Location of industry, market size, and imperfect international capital mobility. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 38, 518–532 (2008)
Yemtsov, R.: Quo Vadis? Inequality and poverty dynamics across Russian regions. In: Kanbur, R., Venables, A (eds.) Spatial Inequality and Development, pp 348–408. Oxford University Press, New York (2005)
Zeng, D.-Z., Uchikawa, T.: Ubiquitous inequality: the home market effect in a multicountry space. J. Math. Econ. 50, 225–233 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, DZ. Capital mobility and spatial inequalities in income and industrial location. J Econ Inequal 14, 109–128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10888-015-9318-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10888-015-9318-y