Abstract
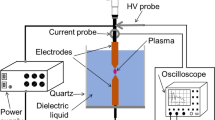
A new method to fabricate nanomaterials by using Impulse Plasma in Liquid is presented. Impulse plasma appears from inter-electrode space break-down in high potential difference between two electrodes submerged into a dielectric liquid, while the power supply is relatively small that is insufficient to excite an arc discharge. By changing the dielectric liquid, we can obtain metallic particles, oxides, carbides. This method does not require vacuum chamber and high energy, thus, can provide economical preparation of various types of nanomaterials. Nanocrystalline powder of titanium oxide was prepared using purified water as a dielectric liquid. Metallic nanoparticles of ytterbium, silver and copper were also prepared by the impulse plasma between a pair of the same material electrodes submerged in styrene. In addition, fullerene C60 was synthesized by the impulse plasma in toluene. Nanoparticles of TiC, WC, TaC were also synthesized by the impulse plasma in styrene.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. L. Feldheim and C. A. Foss Jr., Metal Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications (Marcel Dekker, New York, 2002).
T. Satsuta, et al. (1993). Jpn. Inst. Metal. 57, 296.
T. Sato, et al. (1992). J. Mater. Sci. 27, 3879.
S. Y. Xie, et al. (2004). J. Solid State Chem. 177, 3743.
H. W. Kroto, et al. (1985). Nature 318, 162.
S. Iijima (1991). Nature 354, 56.
W. Kratschmer, et al. (1990). Nature 347, 354.
F. Gao, et al. (2003). Chem. Commun. (21), 2676.
S. K. Sulaimankulova, et al. (1979). Proc. Kyrgyz Sci. Acad. 3, 60.
S. K. Sulaimankulova, et al. (1981). Proc. Kyrgyz Sci. Acad. 4, 46.
S. K. Sulaimankulova and U. A. Asanov, Energy-Saturated Media in the Plasma of Spark Discharge (Kyrgyzpatent, Bishkek, 2002).
A. D. Pomogailo, et al., Metal Nanoparticles in Polymers (Khimia, Moscow, 2000).
E. T. Murzabekova, S. K. Sulaimankulova, and J. Maatkerimova (1998). J. Chem. Inst. Kyrgyzstan 2, 191.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sulaimankulova, S., Omurzak, E., Jasnakunov, J. et al. New Preparation Method of Nanocrystalline Materials by Impulse Plasma in Liquid. J Clust Sci 20, 37–49 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-008-0225-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-008-0225-2