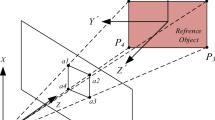
Abstract
This paper addresses the problem of estimating camera calibration parameters by using a novel method based on interval algebra. Unlike existing solutions, which usually apply real algebra, our method is capable of obtaining highly accurate parameters even in scenarios where the input data for camera calibration are severely corrupted by noise or no artificial calibration target can be introduced on the scene. We introduce some key concepts regarding the usage of interval algebra on projective space, which might be used by other computer vision methods. To demonstrate the robustness and effectiveness of our method, we present results for camera calibration with varying levels of noise on the input data of a world coordinate frame (standard deviation of up to 0.5 m) and their corresponding projections onto an image plane (standard deviation of up to 10 pixels), which are significantly larger than noise levels considered by state-of-the-art methods.














Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Available at: https://www.blender.org/.
References
Ahmed, M.T., Hemayed, E.E., Farag, A.A.: Neurocalibration: a neural network that can tell camera calibration parameters. In: The Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 1999, Vol. 1, pp. 463–468. IEEE (1999)
Ahneman, D.T., Estrada, J.G., Lin, S., Dreher, S.D., Doyle, A.G.: Predicting reaction performance in c-n cross-coupling using machine learning. Science 360(6385), 186–190 (2018)
Alemán-Flores, M., Alvarez, L., Gomez, L., Henriquez, P., Mazorra, L.: Camera calibration in sport event scenarios. Pattern Recognit. 47(1), 89–95 (2014)
Bennett, S., Lasenby, J., Kokaram, A., Inguva, S., Birkbeck, N.: Reconstruction of the pose of uncalibrated cameras via user-generated videos. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Distributed Smart Cameras, ICDSC ’14, pp. 3:1–3:8. ACM, New York, NY, USA (2014)
Brückner, M., Bajramovic, F., Denzler, J.: Intrinsic and extrinsic active self-calibration of multi-camera systems. Mach. Vis. Appl. 25(2), 389–403 (2013)
Da, F., Li, Q., Zhang, H., Fang, X.: Self-calibration using two same circles. Opt. Laser Technol. 44(6), 1924–1933 (2012)
Datta, A., Kim, J.S., Kanade, T.: Accurate camera calibration using iterative refinement of control points. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), pp. 1201–1208. IEEE (2009)
Delage, E., Lee, H., Ng, A.Y.: A dynamic Bayesian network model for autonomous 3d reconstruction from a single indoor image. In: 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), Vol. 2, pp. 2418–2428 (2006)
Fabbri, R., Kimia, B.B.: Multiview differential geometry of curves. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 120(3), 324–346 (2016)
Faugeras, O., Luong, Q.T., Papadopoulou, T.: The Geometry of Multiple Images: The Laws that Govern the Formation of Images of a Scene and Some of Their Applications. MIT Press, Cambridge (2001)
Faugeras, O.D., Luong, Q.T., Maybank, S.J.: Camera self-calibration: theory and experiments. In: Sandini, G. (ed.) Computer Vision—ECCV 92. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 588, pp. 321–334. Springer, Berlin (1992)
Furukawa, Y., Ponce, J.: Accurate camera calibration from multi-view stereo and bundle adjustment. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 84(3), 257–268 (2009)
Fusiello, A., Benedetti, A., Farenzena, M., Busti, A.: Globally convergent autocalibration using interval analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(12), 1633–1638 (2004)
Gee, T., Delmas, P., Stones-Havas, N., Sinclair, C., Mark, W.V.D., Li, W., Friedrich, H., Gimel’farb, G.: Tsai camera calibration enhanced. In: 2015 14th IAPR International Conference on Machine Vision Applications (MVA), pp. 435–438 (2015)
Geng, L.C., Li, S.Z., Su, S.Z., Cao, D.L., Lei, Y.Q., Ji, R.R.: A new camera self-calibration method based on csa. Visual Commun. Image Process. (VCIP) 2013, 1–6 (2013)
Gómez, M.J., García, F., Martín, D., de la Escalera, A., Armingol, J.M.: Intelligent surveillance of indoor environments based on computer vision and 3D point cloud fusion. Expert Syst. Appl. 42(21), 8156–8171 (2015)
Grammatikopoulos, L., Karras, G., Petsa, E.: Camera calibration approaches using single images of man-made objects. In: Proceedings of the XIX CIPA International Symposium, p. 328 (2003)
Grammatikopoulos, L., Karras, G., Petsa, E.: An automatic approach for camera calibration from vanishing points. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 62(1), 64–76 (2007)
Hammarstedt, P., Sturm, P., Heyden, A.: Degenerate cases and closed-form solutions for camera calibration with one-dimensional objects. In: Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05) Vol. 1, Vol. 1, pp. 317–324 Vol. 1 (2005)
Hansen, E., Walster, G.W.: Global Optimization Using Interval Analysis (2004)
Hartley, R., Zisserman, A.: Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, Vol. 2. Cambridge University Press (2000). https://doi.org/10.2277/0511188951
Heikkila, J., Silven, O.: A four-step camera calibration procedure with implicit image correction. In: Proceedings of IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1106–1112 (1997)
Horáček, J., Hladík, M.: Computing enclosures of overdetermined interval linear systems. arXiv preprint. arXiv:1304.4738 (2013)
Houssineau, J., Clark, D.E., Ivekovic, S., Lee, C.S., Franco, J.: A unified approach for multi-object triangulation, tracking and camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(11), 2934–2948 (2016)
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Van Der Maaten, L., Weinberger, K.Q.: Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4700–4708 (2017)
Ismail, K., Sayed, T., Saunier, N.: A methodology for precise camera calibration for data collection applications in urban traffic scenes. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 40(1), 57–67 (2013)
Juan, L., Gwun, O.: Surf applied in panorama image stitching. In: 2010 2nd International Conference on Image Processing Theory Tools and Applications (IPTA), pp. 495–499. IEEE (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/IPTA.2010.5586723
Kim, P.: Rigid Body Dynamics for Beginners: Euler Angles and Quaternions. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform (2013)
Kumar, S., Raman, B., Wu, J.: Neuro-calibration of a camera using particle swarm optimization. In: 2009 2nd International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Technology (ICETET), pp. 273–278. IEEE (2009)
Lee, H., Shechtman, E., Wang, J., Lee, S.: Automatic upright adjustment of photographs with robust camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 36(5), 833–844 (2014)
Lee, S.C., Nevatia, R.: Robust camera calibration tool for video surveillance camera in urban environment. In: CVPR 2011 WORKSHOPS, pp. 62–67. IEEE (2011)
Li, B., Peng, K., Ying, X., Zha, H.: Simultaneous Vanishing Point Detection and Camera Calibration from Single Images, pp. 151–160. Springer, Berlin (2010)
Li, D., Tian, J.: An accurate calibration method for a camera with telecentric lenses. Opt. Lasers Eng. 51(5), 538–541 (2013)
Li, W., Zhu, G., Lin, B.: Automatically-controlled system for detecting quartz crystal based on plc. In: Jin, D., Lin, S. (eds.) Advances in Computer Science and Information Engineering, Advances in Intelligent and Soft Computing, vol. 169, pp. 619–624. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Liu, G., Mao, Z.: Structural damage diagnosis with uncertainties quantified using interval analysis. Struct. Control Health Monit. 24(10), e1989 (2017)
Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Huang, T.: Determining 3d structure and motion of man-made objects from image corners. In: Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE Southwest Symposium on Image Analysis and Interpretation, 2002, pp. 26–30 (2002)
Loaiza, M.E., Raposo, A.B., Gattass, M.: Multi-camera calibration based on an invariant pattern. Comput. Graph. 35(2), 198–207 (2011)
Lourakis, M.I., Deriche, R.: Camera self-calibration using the singular value decomposition of the fundamental matrix: from point correspondences to 3d measurements. Tech. rep., INRIA (1999)
Luhmann, T., Fraser, C., Maas, H.G.: Sensor modelling and camera calibration for close-range photogrammetry. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 115, 37–46, theme issue ’State-of-the-art in photogrammetry, remote sensing and spatial information science’ (2016)
Matthew, W.: Galib: a c++ library of genetic algorithm components. http://lancet.mit.edu/ga/ (2016)
Maybank, S.S., Faugeras, O.O.: A theory of self-calibration of a moving camera. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 151(1992), 123–151 (1992)
Medioni, G., Kang, S.B.: Emerging Topics in Computer Vision. Prentice Hall PTR, Upper Saddle River (2004)
Merras, M., Saaidi, A., Nazih, A.G., Satori, K., et al.: A new method of camera self-calibration with varying intrinsic parameters using an improved genetic algorithm. In: 2013 8th International Conference on Intelligent Systems: Theories and Applications (SITA), pp. 1–8. IEEE (2013)
Mirzaei, F.M., Roumeliotis, S.I.: A kalman filter-based algorithm for imu-camera calibration: observability analysis and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans. Rob. 24(5), 1143–1156 (2008)
Moore, R.E.: Interval Analysis, vol. 4. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1966)
Moore, R.E., Kearfott, R.B., Cloud, M.J.: Introduction to Interval Analysis (2009)
Moses, O.J.: Imageai, an open source python library built to empower developers to build applications and systems with self-contained computer vision capabilities. https://github.com/OlafenwaMoses/ImageAI (2018–)
Moulard, T., Alcantarilla, P., Lamiraux, F.: Reliable Indoor Navigation on Humanoid Robots Using Vision-Based Localization. Tech. rep (2012)
Mudrova, L., Hawes, N.: Task scheduling for mobile robots using interval algebra. In: 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pp. 383–388 (2015)
Park, S.W., Seo, Y., Hong, K.S.: Real-time camera calibration for virtual studio. Real-Time Imaging 6(6), 433–448 (2000)
Qi, F., Li, Q., Luo, Y., Hu, D.: Camera calibration with one-dimensional objects moving under gravity. Pattern Recognit. 40(1), 343–345 (2007)
Rohn, J.: Enclosing solutions of overdetermined systems of linear interval equations. Reliable Comput. 2(2), 167–171 (1996)
Rohn, J., Farhadsefat, R.: Inverse interval matrix: a survey. Electron. J. Linear Algebra 22(1), 46 (2011)
Rota, G.: Interval Methods for Systems of Equations (1990)
Schindler, G., Dellaert, F.: Atlanta world: an expectation maximization framework for simultaneous low-level edge grouping and camera calibration in complex man-made environments. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2004. CVPR 2004., Vol. 1, pp. I–203–I–209 Vol. 1 (2004)
Simon, G., Fond, A., Berger, M.O.: A simple and effective method to detect orthogonal vanishing points in uncalibrated images of man-made environments. In: Eurographics 2016 (2016)
Strobl, K.H., Hirzinger, G.: More accurate pinhole camera calibration with imperfect planar target. In: 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), pp. 1068–1075 (2011)
Sukegawa, S., Umebayashi, T., Nakajima, T., Kawanobe, H., Koseki, K., Hirota, I., Haruta, T., Kasai, M., Fukumoto, K., Wakano, T., Inoue, K., Takahashi, H., Nagano, T., Nitta, Y., Hirayama, T., Fukushima, N.: A 1/4-inch 8 m pixel back-illuminated stacked cmos image sensor. In: 2013 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference Digest of Technical Papers, pp. 484–485 (2013)
Sun, J., Ma, Y., Yang, H., Zhu, X.: Camera calibration and its application of binocular stereo vision based on artificial neural network. In: International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI), pp. 761–765. IEEE (2016)
Tao, Z.S., Tu, D.W., He, S.S., Ye, J.: A camera self-calibration for machine vision based on Kruppa’s equation. Appl. Mech. Mater. (2013)
Telle, B., Aldon, M.J., Ramdani, N.: Camera calibration and 3d reconstruction using interval analysis. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, 2003, pp. 374–379. IEEE (2003)
Telle, B., Stasse, O., Ueshiba, T., Yokoi, K., Tomita, F.: 3d boundaries partial representation of objects using interval analysis. In: IROS, pp. 4013–4018 (2004)
Tsai, R.: A versatile camera calibration technique for high-accuracy 3d machine vision metrology using off-the-shelf tv cameras and lenses. IEEE J. Robot. Autom. 3(4), 323–344 (1987)
Vargas, A.C.G., Paes, A., Vasconcelos, C.N.: Um estudo sobre redes neurais convolucionais e sua aplicação em detecção de pedestres. In: Proceedings of the XXIX Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images, pp. 1–4 (2016)
Wang, L., Wu, F., Hu, Z.: Multi-camera calibration with one-dimensional object under general motions. In: 2007 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 1–7 (2007)
Wang, L., Wang, W., Shen, C., Duan, F.: A convex relaxation optimization algorithm for multi-camera calibration with 1d objects. Neurocomputing 215, 82–89, sI: Stereo Data (2016)
Whitley, D.: A genetic algorithm tutorial. Stat. Comput. 4(2), 65–85 (1994)
Wildenauer, H., Hanbury, A.: Robust camera self-calibration from monocular images of manhattan worlds. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2831–2838 (2012)
Xu, J., Deng, F.: A camera self-calibration method based on ios-pso. Chin. Autom. Cong. (CAC) 2015, 489–494 (2015)
Yang, C., Lu, Z., Yang, Z., Liang, K.: Parameter identification for structural dynamics based on interval analysis algorithm. Acta Astronaut. 145, 131–140 (2018)
Zhang, Z.: A flexible new technique for camera calibration. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(11), 1330–1334 (2000)
Zhang, Z.: Camera calibration with one-dimensional objects. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(7), 892–899 (2004)
Zhou, F., Cui, Y., Peng, B., Wang, Y.: A novel optimization method of camera parameters used for vision measurement. Opt. Laser Technol. 44(6), 1840–1849 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the support of CNPq under Procs. 307510/2017-4 and 313163/2014-6, FAPEMIG under Proc. PPM-00542-15, CEFET-MG and CAPES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brito, D.N., Pádua, F.L.C. & Lopes, A.P.C. Using Geometric Interval Algebra Modeling for Improved Three-Dimensional Camera Calibration. J Math Imaging Vis 61, 1342–1369 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-019-00907-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-019-00907-x