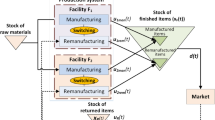
Abstract
Recently, remanufacturing systems have been studied from various viewpoints. Van der Laan and Teunter (Eur J Oper Res 175(2):1084–1102, 2006), for example, proposed simple heuristics for push and pull remanufacturing strategies. However, because they are only simple heuristics they are not very useful in a stochastic demand situation. An adaptive strategy should be incorporated into the pull strategy to improve performance; therefore, we propose an adaptive pull strategy for remanufacturing systems that can control manufacturing and remanufacturing rates in the remanufacturing system. The performance and effectiveness of our proposed system is analyzed by Markov analysis, and the results are shown in this paper.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, O.,& Larson, R. C. (2004). A queueing control model for retail service having back room operations and cross trained workers. Computers and Operations Research, 31(2), 201–220.
Bolch, G., Greiner, S., de Meer, H.,& Travedi, K. S. (1998). Queueing networks and Markov chains. New York: Wiley.
DeCroix, G. A. (2006). Optimal policy for a multiechelon inventory system with remanufacturing. Operations Research, 54(3), 532–543.
Dobos, I.,& Richter, K. (2004). An extended production/recycling model with stationary demand and return rates. International Journal of Production Economics, 90(3), 311–323.
El Saadany, A. M. A.,& Jaber, M. Y. (2011). A production/remanufacture model with returns subassemblies managed differently. International Journal of Production Economics, 133(1), 119–126.
Fleischmann, M., Ruwaard, J., Dekker, R., van del Laan, E.,& Van Wassenhove, L. (1997). Quantitative models for reverse logistics: A review. European Journal of Operational Research, 103(1), 1–17.
Framinan, J. M.,& Pierreval, H. (2012). Special issue on pull strategies in manufacturing systems and supply chains: Recent advances. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(1), 1–3.
Gharbi, A., Pellerin, R.,& Sadr, J. (2008). Production rate control for stochastic remanufacturing systems. International Journal of Production Economics, 112(1), 37–47.
Giudice, F.,& Fargione, G. (2007). Disassembly planning of mechanical systems for service and recovery: A genetic algorithms based approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 18(3), 313–329.
Gungor, A.,& Gupta, S. M. (1999). Issues in environmentally conscious manufacturing and product recovery: A survey. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 36(4), 811–853.
Hsueh, C.-F. (2011). An inventory control model with consideration of remanufacturing and product life cycle. International Journal of Production Economics, 133(2), 645–652.
Inderfurth, K. (2004). Optimal control in hybrid manufacturing/remanufacturing systems with product substitution. International Journal of Production Economics, 90(3), 325–343.
Inderfurth, K., de Kok, A. G.,& Flapper, S. D. P. (2001). Product recovery in stochastic remanufacturing systems with multiple reuse option. European Journal of Operational Research, 133(1), 130–152.
Inderfurth, K.,& van der Laan, E. (2001). Leadtime effects and policy improvement for stochastic inventory control with remanufacturing. International Journal of Production Economics, 71(3), 381–390.
Jaber, M. Y.,& El Saadany, A. M. A. (2009). The production, remanufacture and waste disposal model with lost sales. International Journal of Production Economics, 120(1), 115–124.
Jaber, M. Y.,& El Saadany, A. M. A. (2011). An economic production and remanufacturing model with learning effects. International Journal of Production Economics, 131(1), 115–127.
Joo, S.-H.,& Wilhelm, W. E. (1993). A review of quantitative approaches in just-in-time manufacturing. Production Planning and Control, 4(3), 207–222.
Jung, K. S.,& Hwang, H. (2010). Competition and cooperation in a remanufacturing system with take-back requirement. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 22(3), 427–433.
Kenné, J.-P., Dejax, P.,& Gharbi, A. (2012). Production planning of a hybrid manufacturing-remanufacturing system under uncertainty within a closed-loop supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 135(1), 81–93.
Kiesmüller, G. P.,& van der Laan, E. (2001). An inventory model with dependent product demand and returns. International Journal of Production Economics, 72(1), 73–87.
Kiesmüller, G. P. (2003). A new approach for controlling a hybrid stochastic manufacturing/remanufacturing system with inventories and different leadtimes. European Journal of Operational Research, 147(1), 62–71.
Kimura, O.,& Terada, H. (1981). Design and analysis of pull system, a method of multi-stage production control. International Journal of Production Research, 19(3), 241–253.
Kleber, R., Minner, S.,& Kiesmüller, G. P. (2002). A continuous time inventory model for a product recovery system with multiple options. International Journal of Production Economics, 79(2), 121–141.
Mahadeven, B., Pyke, D. F.,& Fleischmann, M. (2003). Periodic review, push inventory policies for remanufacturing. European Journal of Operational Research, 151(3), 536–551.
Naeem, M. A., Dias, D. J., Tibrewal, R., Chang, P. C.,& Tiwari, M. K. (2012). Production planning optimization for manufacturing and remanufacturing system in stochastic environment. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, (in press)
Nenes, G., Panagiotidou, S.,& Dekker, R. (2010). Inventory control policies for inspection and remanufacturing of returns: A case study. International Journal of Production Economics, 125(2), 300–312.
Oh, Y. H.,& Hwang, H. (2006). Deterministic inventory model for recycling system. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 17(4), 423–428.
Pellerin, R., Sadr, J., Gharbi, A.,& Malhamé, R. (2009). A production rate control policy for stochastic repair and remanufacturing systems. International Journal of Production Economics, 121(1), 39–48.
Powell, S. G.,& Schultz, K. L. (2004). Throughput in serial lines with state-dependent behavior. Management Science, 50(8), 1095– 1105.
Price, W., Gravel, M.,& Nsakanda, A. L. (1994). A review of optimization models of Kanban-based production systems. European Journal of Operational Research, 75(1), 1–12.
Rubio, S.,& Corominas, A. (2008). Optimal manufacturing-remanufacturing policies in a lean production environment. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 55(1), 234–242.
Sivakumar, G. D.,& Shahabudeen, P. (2008). Design of multi-stage adaptive kanban system. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 38(3–4), 321–336.
Spear, S.,& Bowen, H. K. (1999). Decoding the DNA of the Toyota production systems. Harvard Business Review, 77(5), 96–106.
Sugimori, Y., Kusunoki, K., Cho, F.,& Uchikawa, S. (1977). Toyota production system and kanban system: materialization of just-in-time and respect-for-human system. International Journal of Production Research, 15(6), 553–564.
Takahashi, K., (2006). Research and issues on kanban systems. Journal of Japan Industrial Management Association, (in Japanese), 57(2), 89–100.
Takahashi, K., Morikawa, K., Hirotani, D.,& Yoshikawa, T. (2010). Adaptive kanban control systems for two-stage production lines. International Journal of Manufacturing Technology and Management, 20(1–4), 75–93.
Takahashi, K., Morikawa, K., Myreshka, Takeda, D.,& Mizuno, A. (2007). Inventory control for a Markovian remanufacturing system with stochastic decomposition process. International Journal of Production Economics, 108(1–2), 416–425.
Takahashi, K.,& Nakamura, N. (1999). Reacting JIT ordering systems to the unstable changes in demand. International Journal of Production Research, 37(10), 2293–2313.
Takahashi, K.,& Nakamura, N. (2000). Agile control in JIT ordering systems. International Journal of Agile Management Systems, 2(3), 242–252.
Tang, O.,& Grubbström, R. W. (2005). Considering stochastic lead times in a manufacturing/remanufacturing system with deterministic demands and returns. International Journal of Production Economics, 93–94, 285–300.
Tardif, V.,& Maaseidvaag, L. (2001). An adaptive approach to controlling kanban systems. European Journal of Operational Research, 12(2), 411–424.
Thierry, M., Salomon, M., Van Nunen, J.,& Van Wassenhove, L. (1995). Strategic issues in product recovery management. California Management Review, 37(2), 114–135.
Towill, D. R. (2007). Exploiting the DNA of the Toyota production system. International Journal of Production Research, 45(16), 3619–3637.
Van der Laan, E. A.,& Teunter, R. H. (2006). Simple heuristics for push and pull remanufacturing policies. European Journal of Operational Research, 175(2), 1084–1102.
Veerakamolmal, P.,& Gupta, S. M. (2002). A case-based reasoning approach for automating disassembly process planning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 13(1), 47–60.
Acknowledgments
The work in this paper was partially supported by the Japan Society for Promotion of Science with a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research in 2006–2008 and 2010–2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takahashi, K., Doi, Y., Hirotani, D. et al. An adaptive pull strategy for remanufacturing systems. J Intell Manuf 25, 629–645 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-012-0710-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-012-0710-1