Abstract
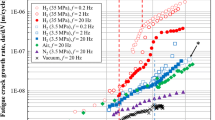
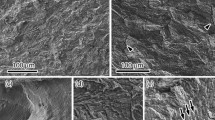
The behavior of intergranular fatigue crack growth in an interstitial-free (IF) steel in a hydrogen environment was investigated at different frequencies. Focusing on the plastic strain localization, we observed details of the striation-like feature on the intergranular fracture surface, slip behavior around microvoids, and crystallographic orientation gradient underneath the fracture surface. It was determined that the intergranular fatigue crack growth mechanism in the IF steel is microvoid formation at the crack tip and subsequent coalescence with the crack. Moreover, it was found that the grain boundaries, acting as propagation paths, suffer from pre-damage arising from plastic strain localization near the grain boundaries even before the main crack propagates to a certain location. Therefore, fatigue cracks in a hydrogen environment easily propagate to the grain boundaries. The frequency dependence of fatigue crack growth in the hydrogen environment is significantly smaller than that in a low carbon steel, probably because of the frequency dependence of the pre-damage evolution behavior.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Quantification of GRODs has also been attempted, e.g. (Sakakibara et al. 2010).
References
Birnbaum HK, Sofronis P (1994) Hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity—a mechanism for hydrogen-related fracture. Mater Sci Eng A 176:191–202. doi:10.1016/0921-5093(94)90975-X
Calcagnotto M, Ponge D, Demir E, Raabe D (2010) Orientation gradients and geometrically necessary dislocations in ultrafine grained dual-phase steels studied by 2D and 3D EBSD. Mater Sci Eng A 527:2738–2746. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2010.01.004
Ferreira PJ, Robertson IM, Birnbaum HK (1998) Hydrogen effects on the interaction between dislocations. Acta Mater 46:1749–1757. doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(97)00349-2
Hatano M, Fujinami M, Arai K, Fujii H, Nagumo M (2014) Hydrogen embrittlement of austenitic stainless steels revealed by deformation microstructures and strain-induced creation of vacancies. Acta Mater 67:342–353. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2013.12.039
James MN (2010) Intergranular crack paths during fatigue in interstitial-free steels. Eng Fract Mech 77:1998–2007. doi:10.1016/j.engfracmech.2009.12.006
Koyama M, Springer H, Merzlikin SV, Tsuzaki K, Akiyama E, Raabe D (2014) Hydrogen embrittlement associated with strain localization in a precipitation-hardened Fe–Mn–Al–C light weight austenitic steel. Int J Hydrog Energy 39:4634–4646. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.12.171
Koyama M, Xi Z-J, Yoshida Y, Yoshimura N, Ushioda K, Noguchi H (2015) Intergranular fatigue crack initiation and its associated small fatigue crack propagation in water-quenched Fe–C fully ferritic steel. ISIJ Int 55:2463–2468. doi:10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-305
Lee D, Nishikawa H, Oda Y, Noguchi H (2012) Small fatigue crack growth characteristics and fracture surface morphology of low carbon steel in hydrogen gas. Int J Fract 179:147–156. doi:10.1007/s10704-012-9783-2
Majumdar S, Bhattacharjee D, Ray KK (2011) Mechanism of fatigue failure in interstitial-free and interstitial-free high-strength steel sheets. Scr Mater 64:288–291. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2010.10.001
Matsuoka S, Tanaka H, Homma N, Murakami Y (2010) Influence of hydrogen and frequency on fatigue crack growth behavior of Cr–Mo steel. Int J Fract 168:101–112. doi:10.1007/s10704-010-9560-z
Nishikawa H-A, Oda Y, Noguchi H (2011) Investigation of mechanism for intergranular fatigue crack propagation of low carbon steel JIS S10C in hydrogen gas environment. J Solid Mech Mater Eng 5:263–278. doi:10.1299/jmmp.5.263
Nishikawa H-A, Oda Y, Noguchi H (2011b) Investigation of the mechanism for brittle-striation formation in low carbon steel fatigued in hydrogen gas (fractographic observation on fracture processes visualized by controlling load sequence and testing environment). J Solid Mech Mater Eng 5:370–385. doi:10.1299/jmmp.5.370
Nishikawa H-A, Oda Y, Noguchi H (2011c) Loading-frequency effects on fatigue crack growth behavior of a low carbon steel JIS S10C in hydrogen gas environment. J Solid Mech Mater Eng 5:104–116. doi:10.1299/jmmp.5.104
Nishikawa H-A, Oda Y, Takahashi Y, Noguchi H (2011d) Microscopic observation of the brittle-striation formation mechanism in low carbon steel fatigued in hydrogen gas (TEM and EBSD observation corresponding to fractography). J Solid Mech Mater Eng 5:179–190. doi:10.1299/jmmp.5.179
Oliver EC, Daymond MR, Withers PJ (2004) Interphase and intergranular stress generation in carbon steels. Acta Mater 52:1937–1951. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2003.12.035
Onishi Y, Koyama M, Sasaki D, Noguchi H (2016) Characteristic fatigue crack growth behavior of low carbon steel under low-pressure hydrogen gas atmosphere in an ultra-low frequency. ISIJ Int 56:865–870. doi:10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2015-647
Pokluda J, Siegl J (1990) Mixed fatigue fracture morphology of ferritic ductile iron. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct 13:375–385. doi:10.1111/j.1460-2695.1990.tb00608.x
Quinta da Fonseca J, Oliver EC, Bate PS, Withers PJ (2006) Evolution of intergranular stresses during in situ straining of IF steel with different grain sizes. Mater Sci Eng A 437:26–32. doi:10.1016/j.msea.2006.04.057
Ritchie RO, Knott JF (1973) Mechanisms of fatigue crack growth in low alloy steel. Acta Metall 21:639–648. doi:10.1016/0001-6160(73)90073-4
Sakakibara Y, Kubushiro K, Nakayama G (2010) Distribution of misorientation at grain boundary by EBSD for low carbon stainless steel strained by various deformation modes. J Jpn Inst Met 74:258–263
Sofronis P, Liang Y, Aravas N (2001) Hydrogen induced shear localization of the plastic flow in metals and alloys. Eur J Mech A Solids 20:857–872. doi:10.1016/S0997-7538(01)01179-2
Sofronis P, McMeeking RM (1989) Numerical analysis of hydrogen transport near a blunting crack tip. J Mech Phys Solids 37:317–350. doi:10.1016/0022-5096(89)90002-1
Tomota Y, Lukas P, Harjo S, Park JH, Tsuchida N, Neov D (2003) In situ neutron diffraction study of IF and ultra low carbon steels upon tensile deformation. Acta Mater 51:819–830. doi:10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00473-1
von Pezold J, Lymperakis L, Neugebeauer J (2011) Hydrogen-enhanced local plasticity at dilute bulk H concentrations: The role of H–H interactions and the formation of local hydrides. Acta Mater 59:2969–2980. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2011.01.037
Yoshikawa M, Matsuo T, Tsutsumi N, Matsunaga H, Matsuoka S (2014) Effects of hydrogen gas pressure and test frequency on fatigue crack growth properties of low carbon steel in 0.1–90 MPa hydrogen gas. Trans JSME 80:SMM0254–SMM0254. doi:10.1299/transjsme.2014smm0254 (in Japanese)
Zheng LL, Gao YF, Lee SY, Barabash RI, Lee JH, Liaw PK (2011) Intergranular strain evolution near fatigue crack tips in polycrystalline metals. J Mech Phys Solids 59:2307–2322. doi:10.1016/j.jmps.2011.08.001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koyama, M., Onishi, Y. & Noguchi, H. Characteristics of hydrogen-assisted intergranular fatigue crack growth in interstitial-free steel: role of plastic strain localization. Int J Fract 206, 123–130 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-017-0205-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-017-0205-3