Abstract
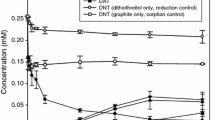
Black carbon (BC) is an important class of geosorbents that control the fate and transport of organic pollutants in soil and sediment. We previously demonstrated a new role of BC as an electron transfer mediator in the abiotic reduction of nitroaromatic and nitramine compounds by Oh and Chiu (Environ Sci Technol 43:6983–6988, 2009). We proposed that BC can catalyze the reduction of nitro compounds because it contains microscopic graphitic (graphene) domains, which facilitate both sorption and electron transfer. In this study, we assessed the ability of different types of BC—graphite, activated carbon, and diesel soot—to mediate the reduction of 2,4-dinitrotoluene (DNT) and 2,4-dibromophenol (DBP) by H2S. All three types of BC enhanced DNT and DBP reduction. H2S supported BC-mediated reduction, as was observed previously with a thiol reductant. The results suggest that BC may influence the fate of organic pollutants in reducing subsurface environments through redox transformation in addition to sorption.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accardi-Dey, A., & Gschwend, P. M. (2002). Assessing the combined roles of natural organic matter and black carbon as sorbents in sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 21–29.
Barbash, J. E., & Reinhard, M. (1989). Abiotic dehalogenation of 1, 2-dichloroethane and 1, 2-dibromoethane in aqueous solution containing hydrogen sulfide. Environmental Science and Technology, 23, 1349–1358.
Barrows, S. E., Cramer, C. J., Truhlar, D. G., Evolitz, M. S., Weber, E. J., et al. (1996). Factors controlling regioselectivity in the reduction of polynitroaromatics in aqueous solution. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 3028–3038.
Brodowski, S., Amelung, W., Haumaier, L., Abetz, C., Zech, W., et al. (2005). Morphological and chemical properties of black carbon in physical soil fractions as revealed by scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Geoderma, 128, 116–129.
Bucheli, T. D., & Gustafsson, Ö. (2000). Quantification of the soot-water distribution coefficient of PAHs provides mechanistic basis for enhanced sorption observations. Environmental Science and Technology, 34, 5144–5151.
Chiu, C. T., & Kile, D. E. (1998). Deviations from sorption linearity on soils of polar and nonpoloar organic compounds at low relative concentrations. Environmental Science and Technology, 32, 338–343.
Cho, Y. M., Ghosh, U., Kennedy, A. J., Grossman, A., Ray, G., Tomaszewski, J. E., et al. (2009). Field application of activated carbon amendment for in situ stabilization of polychlorinated biphenyls in marine sediment. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 3815–3823.
Cornelissen, G., Elmquist, M., Groth, I., Gustafsson, Ö., et al. (2004). Effect of sorbate planarity on environmental black carbon sorption. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 3574–3580.
Cornelissen, G., & Gustafsson, Ö. (2004). Sorption of phenanthrene to environmental black carbon in sediment with and without organic matter and native sorbates. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 148–155.
Cornelissen, G., & Gustafsson, Ö. (2005). Importance of unburned coal carbon, black carbon, and amorphous organic carbon to phenanthrene sorption in sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 764–769.
Cornelissen, G., Gustafsson, Ö., Bucheli, T. D., Jonker, M. T. O., Koelmans, A. A., van Noort, P. C. M., et al. (2005a). Extensive sorption of organic compounds to black carbon, coal, and kerogen in sediments and soils: Mechanisms and consequences for distribution, bioaccumulation, and biodegradation. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 6881–6895.
Cornelissen, G., Haftka, J., Parsons, J., Gustafsson, Ö., et al. (2005b). Sorption to black carbon of organic compounds with varying polarity and planarity. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 3688–3694.
Dusek, U., Reischl, G. P., Hitzenberger, R., et al. (2006). CCN activation of pure and coated carbon black particles. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 1223–1230.
Flanner, M. G., Zender, C. S., Randerson, J. T., Rasch, P. J., et al. (2007). Present-day climate forcing and response from black carbon in snow. Journal of Geophysical Research, 112, D11202.
Goldberg, E. D. (1985). Black carbon in the environment. New York: Wiley.
Gustafsson, Ö., & Gschwend, P. M. (1998). The flux of black carbon to surface sediments on the New England continental shelf. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62, 465–472.
Gustafsson, Ö., Haghseta, F., Chan, C., MacFarlane, J., Gschwend, P. M., et al. (1997). Quantification of the dilute sedimentary soot phase: Implications for PAH speciation and bioavailability. Environmental Science and Technology, 31, 203–209.
Hopkins, R. J., Tivanski, A. V., Marten, B. D., Gilles, M. K., et al. (2007). Chemical bonding and structure of black carbon reference materials and individual carbonaceous atmospheric aerosols. Journal of Aerosol Science, 38, 573–591.
Jacobson, M. Z. (2001). Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature, 409, 695–697.
Kemper, J. M., Ammar, E., Mitch, W. A., et al. (2008). Abiotic degradation of hexahydro-1, 3, 5-trinitro-1, 3, 5-triazine in the presence of hydrogen sulfide and black carbon. Environmental Science and Technology, 42, 2118–2123.
Lohmann, R., MacFarlane, J. K., Gschwend, P. M., et al. (2005). Importance of black carbon to sorption of native PAHs, PCBs, and PCDDs in Boston and New York harbor sediments. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 141–148.
Middelburg, J. J., Nieuwenhuize, J., Van Breugel, P., et al. (1999). Black carbon in marine sediments. Marine Chemistry, 65, 245–252.
Molina, M., Zaelke, D., Sarma, K. M., Anderson, S. O., Ramanathan, V., et al. (2009). Reducing abrupt climate change risk using the Montreol Protocol and other regulatory actions to complement cuts in CO2 emissions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106, 20616–20621.
Nguyen, T. H., Cho, H.-H., Poster, D. L., Ball, W. P., et al. (2007). Evidence for a pore-filling mechanism in the adsorption of aromatic hydrocarbons to a natural wood char. Environmental Science and Technology, 41, 1212–1217.
Nguyen, T. H., Sabbah, I., Ball, W. P., et al. (2004). Sorption nonlinearity for organic contaminants with diesel soot: Method development and isotherm interpretation. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 3595–3603.
Oh, S. Y., Cha, D. K., Chiu, P. C., et al. (2002). Graphite-mediated reduction of 2, 4-dinitrotoluene with elemental iron. Environmental Science and Technology, 36, 2178–2184.
Oh, S. Y., Cha, D. K., Kim, B. J., Chiu, P. C., et al. (2005). Transformation of hexahydro-1, 3, 5-trinitro-1, 3, 5-triazine (RDX), octahydro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetranitro-1, 3, 5, 7-tetrazocine (HMX) and methylene-dinitramine (MDNA) with elemental iron. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 24, 2812–2819.
Oh, S. Y., & Chiu, P. C. (2009). Graphite- and soot-mediated reduction of 2,4-dinitrotoluene and hexahydro-1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine. Environmental Science and Technology, 43, 6983–6988.
Oh, S.-Y., Cha, D. K., & Chiu, P. C. (2004) Reduction of nitroglycerin with cast iron: Pathway, kinetics, and mechanisms. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(13), 3723–3730.
Perlinger, J. A., Angst, W., Schwarzenbach, R. P., et al. (1996). Kinetics of the reduction of hexachloroethane by juglone in solutions containing hydrogen sulfide. Environmental Science and Technology, 30, 3408–3417.
Rickard, D., & Luther, G. W. (2007). Chemistry of iron sulfides. Chemical Reviews, 107, 514–562.
Sander, M., & Pignatello, J. J. (2005). Characterization of charcoal adsorption sites for aromatic compounds: Insights drawn from single-solute and bi-solute competitive experiments. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 1606–1615.
Schmidt, M. W. I., & Noack, A. G. (2000). Black carbon in soils and sediments: Analysis, distribution, implications, and current challenges. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 14, 777–793.
Schwarzenbach, R. P., Gschwend, P. M., Imboden, D. M., et al. (2002). Environmental organic chemistry (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
Thorseon, W. A., Cope, W. G., Shea, D., et al. (2004). Bioavailability of PAHs: Effects of soot carbon and PAH source. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 2029–2037.
van der Zee, F. P., Bisschops, I. A. E., Lettinga, G., Field, J. A., et al. (2003). Activated carbon as an electron acceptor and redox mediator during the anaerobic biotransformation of azo dyes. Environmental Science and Technology, 37, 402–408.
Vecitis, C. D., Zodrow, K. R., Kang, S., Elimelech, M., et al. (2010). Electronic structure-dependent bacterial cytotoxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano, 4, 5471–5479.
Xu, W., Dana, K. E., Mitch, W. A., et al. (2010). Black carbon-mediated destruction of nitroglycerin and RDX by hydrogen sulfide. Environmental Science and Technology, 44, 6409–6415.
Ye, J., & Chiu, P. C. (2006). Transport of atomic hydrogen through graphite and its reaction with azoaromatic compounds. Environmental Science and Technology, 40, 3959–3964.
Zhu, D., Kwon, S., Pignatello, J. J., et al. (2005). Adsorption of single-ring organic compounds to wood charcoals prepared under different thermochemical conditions. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 3990–3998.
Zhu, D., & Pignatello, J. J. (2005). Characterization of aromatic compound sorptive interactions with black caron (charcoal) assisted by graphite as a model. Environmental Science and Technology, 39, 2033–2041.
Zimmerman, J. R., Ghosh, U., Millward, R. N., Bridges, T. S., Luthy, R. G., et al. (2004). Addition of carbon sorbents to reduce PCB and PAH bioavailability in marine sediments: Physicochemical tests. Environmental Science and Technology, 38, 5458–5464.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2009-0064688).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, SY., Son, JG., Lim, OT. et al. The role of black carbon as a catalyst for environmental redox transformation. Environ Geochem Health 34 (Suppl 1), 105–113 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-011-9416-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-011-9416-0