Abstract
Purpose
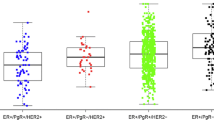
The ETS transcription factor ESE-1 has been shown to be important in HER2+ breast cancer and ESE-1 mRNA expression has been shown to associate with prognostic outcomes in the HER2+ subtype, as well as in ER+, HER2+ luminal B patients. However, the clinical significance of ESE-1 protein expression remains unknown. The purpose of the current exploratory study is to evaluate the prognostic value of ESE-1 protein expression in molecular breast cancer subtypes with special emphasis on hormone receptor positive HER2+(HR+ HER2+) and the HER2 positive (HER2+-only) breast cancer patients.
Methods
We developed a mouse monoclonal anti-ESE-1 antibody, verified its specificity, epitope, and used immunohistochemical staining to assess ESE-1 expression in an IBC approved archive of 957 breast tumor samples. Using Pearson product correlation, contingency analysis, and long rank P value testing, we analyzed the association of ESE-1 expression with clinicopathological features and survival outcomes in HR+HER2−; HR+HER2+; HR− HER2− (Triple negative) and HR−HER2+ (HER2 subtype) patients.
Results
ESE-1, nuclear or cytoplasmic, was not significantly associated with survival outcomes in HR+HER2−, triple-negative, or HER2+-only breast cancer patients. However, high nuclear ESE-1 was associated with poor survival outcomes in hormone receptor positive (ERα+, PR+) HER2+ patients and was an independent prognostic marker for that group.
Conclusions
This study provides evidence for prognostic significance of nuclear ESE-1 in ERalpha positive breast cancers patients also positive for HER2 indicating that crosstalk between ERalpha and ESE-1 in HER2+ tumors could be important for prognostic outcomes. Further studies regarding the nature of interaction between ESE-1 and ERalpha in these tumors are warranted.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ER:
-
Estrogen receptor
- PgR:
-
Progesterone receptor
- ErbB2:
-
Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- AR:
-
Androgen receptor
- Apop:
-
Apoptotic
- Mit:
-
Mitotic
- LN:
-
Lymph node
- Elf3/ESE-1:
-
E74 like ETS transcription factor 3/Epithelial specific ETS transcription factor
- TAD:
-
Transcription activation domain
- AT-hook:
-
AT-hook DNA binding motif
References
Chang CH, Scott GK, Baldwin MA, Benz CC (1999) Exon 4-encoded acidic domain in the epithelium-restricted Ets factor, ESX, confers potent transactivating capacity and binds to TATA-binding protein (TBP). Oncogene 18(25):3682–3695. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1202674
Scott GK, Chang CH, Erny KM, Xu F, Fredericks WJ, Rauscher FJ 3rd, Thor AD, Benz CC (2000) Ets regulation of the erbB2 promoter. Oncogene 19(55):6490–6502
Oh S, Shin S (1826) Janknecht R (2012) ETV1, 4 and 5: an oncogenic subfamily of ETS transcription factors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2012.02.002
Dittmer J (2015) The role of the transcription factor Ets1 in carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol 35:20–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.09.010
Luk IY, Reehorst CM, Mariadason JM (2018) ELF3, ELF5, EHF and SPDEF transcription factors in tissue homeostasis and cancer. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23092191
Kar A, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (2013) Molecular mechanisms of ETS transcription factor-mediated tumorigenesis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 48(6):522–543
Seth A, Watson DK (2005) ETS transcription factors and their emerging roles in human cancer. Eur J Cancer 41(16):2462–2478
Prescott JD, Koto KS, Singh M, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (2004) The ETS transcription factor ESE-1 transforms MCF-12A human mammary epithelial cells via a novel cytoplasmic mechanism. Mol Cell Biol 24(12):5548–5564. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.24.12.5548-5564.2004
Prescott JD, Poczobutt JM, Tentler JJ, Walker DM, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (2011) Mapping of ESE-1 subdomains required to initiate mammary epithelial cell transformation via a cytoplasmic mechanism. Mol Cancer 10:103. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-10-103
Zhang Z, Zhang J, Li J, Geng H, Zhou B, Zhang B, Chen H (2020) miR-320/ELF3 axis inhibits the progression of breast cancer via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncol Lett 19(4):3239–3248. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11440
Darius M, Walker JMP, Gonzales MS, Horita H, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (2010) ESE-1 is required to maintain the transformed phenotype of MCF-7 and ZR-75-1 human breast cancer cells. The Open Cancer J 3:77–88
Eckel KL, Tentler JJ, Cappetta GJ, Diamond SE, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (2003) The epithelial-specific ETS transcription factor ESX/ESE-1/Elf-3 modulates breast cancer-associated gene expression. DNA Cell Biol 22(2):79–94. https://doi.org/10.1089/104454903321515896
Neve RM, Ylstra B, Chang CH, Albertson DG, Benz CC (2002) ErbB2 activation of ESX gene expression. Oncogene 21(24):3934–3938
Kar A, Gutierrez-Hartmann A (2017) ESE-1/ELF3 mRNA expression associates with poor survival outcomes in HER2(+) breast cancer patients and is critical for tumorigenesis in HER2(+) breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 8(41):69622–69640. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18710
Ringner M, Fredlund E, Hakkinen J, Borg A, Staaf J (2011) GOBO: gene expression-based outcome for breast cancer online. PLoS ONE 6(3):e17911. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0017911
Nikolai BC, Lanz RB, York B, Dasgupta S, Mitsiades N, Creighton CJ, Tsimelzon A, Hilsenbeck SG, Lonard DM, Smith CL, O'Malley BW (2016) HER2 signaling drives DNA Anabolism and proliferation through SRC-3 phosphorylation and E2F1-regulated genes. Can Res 76(6):1463–1475. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-15-2383
Wang YC, Morrison G, Gillihan R, Guo J, Ward RM, Fu X, Botero MF, Healy NA, Hilsenbeck SG, Phillips GL, Chamness GC, Rimawi MF, Osborne CK, Schiff R (2011) Different mechanisms for resistance to trastuzumab versus lapatinib in HER2-positive breast cancers—role of estrogen receptor and HER2 reactivation. Breast Cancer Res 13(6):R121. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3067
Shou J, Massarweh S, Osborne CK, Wakeling AE, Ali S, Weiss H, Schiff R (2004) Mechanisms of tamoxifen resistance: increased estrogen receptor-HER2/neu cross-talk in ER/HER2-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 96(12):926–935
Manavathi B, Rayala SK, Kumar R (2007) Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of stability and transforming potential of ETS transcriptional factor ESE-1 by p21-activated kinase 1. J Biol Chem 282(27):19820–19830
Sauerbrei W, Taube SE, McShane LM, Cavenagh MM, Altman DG (2018) Reporting recommendations for tumor marker prognostic studies (REMARK): an abridged explanation and elaboration. J Natl Cancer Inst 110(8):803–811. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djy088
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Virginia Borges and Dr. Traci Lyons for reviewing the manuscript and for providing kind suggestions regarding interpretation of results. This work has been funded by Cancer league of Colorado grant
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors report no competing financial interest in relation to the work described.
Ethical approval
This study was performed according to REMARK guidelines for tumor prognostic studies [20]. The patient samples used were originally covered by an approved IRB protocol from the Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from the participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kar, A., Koto, K., Walker, D. et al. ETS transcription factor ESE-1/Elf3 is an independent prognostic factor of survival in HR+HER2+ breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 182, 601–612 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05734-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05734-y