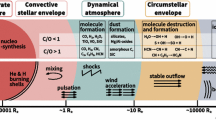
Abstract
Hot WDs in binary systems with a less evolved star are particularly invaluable astrophysical probes, the unevolved companion enabling better derivation of distance and age than is usually possible for post-AGB objects, and therefore also of their radius and luminosity. But hot white dwarfs (WD) are elusive at all wavelengths except the UV (Bianchi et al. 2011a). From our GALEX UV source catalogs (Bianchi et al. 2011a,b, 2014, 2017) matched to SDSS, we identified thousands of candidate hot WDs including WDs in binary systems consisting of a hot WD and a companion of spectral type from A to M. The identification and preliminary characterization of the stellar parameters is based on the analysis of the photometric SED from far-UV to z-band.
We have observed subsamples of the UV-selected WDs with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) to better characterize their stellar parameters. We obtained (1) UV spectroscopy with STIS and analyzed the UV spectra together with optical SDSS spectra, and (2) multi-band imaging with WFC3 (\(0.04^{\prime\prime}/\mbox{pixel}\)) to measure angular separation and individual SEDs of the pair’s components in binary systems. In our HST/WFC3 sample of 59 hot-WD binaries with late-type companions, we found that at least a dozen have possibly evolved without exchanging mass. The UV STIS spectroscopy led to the revision of previous results based on optical spectra only, because of the often undetectable or unquantifiable contribution of the hot component to the optical fluxes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babusiaux, C., van Leeuwen, F., Barstow, M.A., et al. (Gaia collaboration): Astron. Astrophys. (2018, in press)
Bianchi, L., Shiao, B., et al.: (2018a, in preparation)
Bianchi, L., Keller, G., et al.: (2018b, in preparation)
Bianchi, L., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 411, 2770 (2011a). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-010-0581-x
Bianchi, L., Herald, J., Efremova, B., et al.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 335, 161 (2011b). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-010-0581-x
Bianchi, L., Conti, A., Shiao, B.: Adv. Space Res. 53, 900–912 (2014)
Bianchi, L., Shiao, B., Thilker, D.: Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 230, 24 (2017)
Caballero-Nieves, S., et al.: Astrophys. J. 147, 40 (2014)
Cummings, et al.: Astrophys. J. (2018, in preparation)
di Criscienzo, M., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 462(1), 395 (2016)
Gustafsson, B., Edvardsson, B., Eriksson, K., Jørgensen, U.G., Nordlund, Å., Plez, B.: Astron. Astrophys. 486, 951 (2008)
Heller, R., Homeier, D., Dreizler, S., Ostensen, R.: Astron. Astrophys. 496, 191 (2009)
Herwig, F.: Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 43, 435 (2005)
Holberg, J.B., Sion, E.M., Oswalt, T., McCook, G.P., Foran, S., Subasavage, J.P.: Astron. J. 135, 1225 (2008)
Holberg, J., et al.: Astron. J. 143, 68 (2012)
Holberg, J., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 435, 2077 (2013)
Hubeny, I., Lanz, T.: Astrophys. J. 439, 875 (1995)
Karakas, A.I.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 403, 1413 (2010)
Karakas, A., Lugaro, M.: JPS Conf. Proc. 14, 010403 (2017). https://doi.org/10.7566/JPSCP.14.010403
Karakas, A.I., Lattanzio, J.C., Pols, O.R.: Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 19(4), 515 (2002)
Karakas, A., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 477, 421 (2018)
Keller, G.R., Bianchi, L., et al.: (2018, in preparation)
Kepler, S.O., Kleinman, S.J., Nitta, A., Koester, D., Castanheira, B.G., Giovannini, O., Costa, A.F.M., Althaus, L.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 375, 1315 (2007)
Maoz, D., et al.: Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 52, 187 (2014)
Marigo, P.: Astron. Astrophys. 370, 194 (2001)
Marigo, P.: In: IAUS 283: Planetary Nebulae: an Eye to the Future, p. 87 (2012)
Moe, M., di Stefano, R.: arXiv:1606.05347 (2016)
Rebassa-Mansergas, A., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 402, 620 (2010)
Rebassa-Mansergas, A., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 419, 806 (2012)
Sana, H.: In: IAUS 329: The Lives and Death-Throes of Massive Stars, p. 110 (2017)
Sion, E.: wdac.book S1, arXiv:1111.6652 (2011)
Ventura, P., et al.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 477, 438 (2018)
Weiss, A., Ferguson, J.W.: Astron. Astrophys. 508, 1343 (2009)
Yungelson, R., Livio, M.: Astrophys. J. 528, 108 (2000)
Acknowledgements
The work made use of GALEX, SDSS, and Gaia data downloaded from the MAST archive, and of data from HST programs HST-GO-13397 and HST-GO-14119 (L. Bianchi P.I.). Support for Program numbers HST-GO-13397 and HST-GO-14119 was provided by NASA through a grant from the Space Telescope Science Institute, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Incorporated, under NASA contract NAS5-26555.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This article belongs to the Topical Collection: UV Surveys, the Needs and the Means. Guest Editors: Ana I. Gómez de Castro, Noah Brosch.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bianchi, L., Keller, G.R., Bohlin, R. et al. Using GALEX-SDSS-PanSTARRS-HST-Gaia to understand post-AGB evolution. Astrophys Space Sci 363, 166 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-018-3369-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-018-3369-z