Abstract
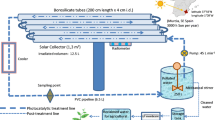
Bisphenol A is an endocrine disruptor. Complete mineralization of bisphenol A is therefore a primary environmental issue. Here, the combination of ozonation and photocatalysis by TiO2 is proposed for the degradation and final mineralization of bisphenol A. TiO2 films deposited onto two sides of an Al lamina show good stability and high surface roughness. We used a specific experimental setup employing two facing ultraviolet lamps and TiO2 layers, together with an ozone flux. High-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry determinations on bisphenol A solutions sampled at different reaction times and Fourier Transform Infrared analyses of the oxide at the end of the reaction were performed to study the reaction intermediates and the overall degradation mechanism. Our results show that pollutant mineralization achieved with the combined method is far higher, of 55% in the case of 0.3 mM bisphenol A, than those obtained by individual treatments such as photolysis (<3%), ozonation (6%), photocatalysis (6%), and by other combined processes: photolytic ozonation (13%) and catalytic ozonation (15%). This finding is explained by the occurrence of highly synergistic effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addamo M, Augugliaro V, Lopez EG, Loddo V, Marci G, Palmisano L (2005) Oxidation of oxalate ion in aqueous suspensions of TiO2 by photocatalysis and ozonation. Catal Today 107–108:612–618
Agustina TE, Ang HM, Vareek VK (2005) A review of synergistic effect of photocatalysis and ozonation on wastewater treatment. J Photochem Photobio C 6(4):264–273
Ardizzone S, Cappelletti G, Meroni D, Tailored SpadavecchiaF (2011) Tailored TiO2 layers for the photocatalytic ozonation of cumylphenol, a refractory pollutant exerting hormonal activity. Chem Commun 47:2640–2642
Augugliaro V, Litter M, Palmisano L, Soria J (2006) The combination of heterogeneous photocatalysis with chemical and physical operations: a tool for improving the photoprocess performance. J Photochem Photobio C 7(4):127–144
Bremner DH, Di Carlo S, Chakinala AG, Cravotto G (2008) Mineralisation of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by acoustic or hydrodynamic cavitation in conjunction with the advanced Fenton process. Ultrason Sonochem 15:416–419
Bremner DH, Molina R, Martínez F, Melero JA, Segura Y (2009) Degradation of phenolic aqueous solutions by high frequency sono-Fenton systems. Appl Cat B Environ 90:380–388
Cappelletti G, Bianchi CL, Ardizzone S (2008) Nano-titania assisted photoreduction of Cr(VI). The role of the different TiO2 polymorphs. Appl Cat B Environ 78(3–4):193–201
Deborde M, Rabouan S, Mazellier P, Duguet JP, Legube B (2008) Oxidation of bisphenol A by ozone in aqueous solution. Water Res 42:4299–4308
Fierro S, Comninellis C (2010) Kinetic study of formic acid oxidation on Ti/IrO2 electrodes prepared using the spin coating deposition technique. Electrochim Acta 55:7067–7073
Garoma T, Matsumoto S (2009) Ozonation of aqueous solution containing bisphenol A: effect of operational parameters. J Hazard Mater 167(1–3):1185–1191
Gultekin I, Ince NH (2007) Synthetic endocrine disruptors in the environment and water remediation by advanced oxidation processes. J Environ Manage 85(4):816–832
Guo ZB, Feng R (2009) Ultrasonic irradiation-induced degradation of low-concentration bisphenol A in aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 163(2–3):855–860
Li L, Zhang P, Zhu W, Hand W, Zhang Z (2005) Comparison of O3-BAC, UV/O3-BAC and TiO2/UV/O3-BAC processes for removing organic pollutants in secondary effluents. J Photochem Photobiol A 171:145–151
Oyama T, Yanagisawa I, Takeuchi M, Koike T, Serpone N, Hidaka H (2009) Remediation of simulated aquatic sites contaminated with recalcitrant substrates by TiO2/ozonation under natural sunlight. Appl Cat B Environ 91(1–2):242–246
Rivas FJ, Encinas Á, Acedo B, Beltrán FJ (2009) Mineralization of bisphenol A by advanced oxidation processes. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 54(4):589–594
Torres RA, Nieto JI, Combet E, Petrier C, Pulgarin C (2008) Influence of TiO2 concentration on the synergistic effect between photocatalysis and high-frequency ultrasound for organic pollutant mineralization in water. Appl Catal B 80:168–175
Torres-Palma RA, Nieto JI, Combet E, Pétrier C, Pulgarin C (2010) An innovative ultrasound, Fe2+ and TiO2 photoassisted process for bisphenol A mineralization. Water Res 44(7):2245–2252
Wang S, Shiraishi F, Nakano K (2002) A synergistic effect of photocatalysis and ozonation on decomposition of formic acid in an aqueous solution. Chem Eng J 87:261–271
Watanabe N, Horikoshi S, Kawabe H, Sugie Y, Zhao J, Hidaka H (2003) Photodegradation mechanism for BPA at the TiO2/H2O surfaces. Chemosphere 52:851–859
Acknowledgments
This research has been supported by the University of Milan Research Funds (FIRST, PUR). The authors wish to thank Prof R. Annunziata for fruitful discussions, Dr. M. De Matteo (CISI) and Dr. F. Milanesi (MIUR FIRB contract number: RBIN064YAT) for HPLC–MS analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colombo, A., Cappelletti, G., Ardizzone, S. et al. Bisphenol A endocrine disruptor complete degradation using TiO2 photocatalysis with ozone. Environ Chem Lett 10, 55–60 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-011-0328-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-011-0328-0