Abstract
GDSL-type esterase/lipase (GELP) is mainly characterized by a conserved GDSL domain at N terminus, and is widely found in all living species, both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. GELP gene family consists of a wide range of members playing important roles in plant physiological processes, such as development, stress responses, and functional divergences. In our study, 597 GELP genes were identified from six Rosaceae genomes (i.e., Fragaria vesca, Prunus persica, Prunus avium, Prunus mume, Pyrus bretschneideri, and Malus domestica) by a comprehensive analysis. All GELP genes were further divided into ten subfamilies based on phylogenetic tree analysis. Subfamily D and subfamily E are the two largest subfamilies. Microcollinearity analysis suggested that WGD/segmental events contribute to the expansion of the GELP gene family in M. domestica and P. bretschneideri compared to F. vesca, P. persica, P. avium, and P. mume. Some PbGELPs were expressed during the fruit development of P. bretschneideri and pollen tubes, indicating their activity in these tissues. The expression divergence of PbGELP duplication gene pairs suggests that many mutations were allowed during evolution, although the structure of GELP genes was highly conserved. The current study results provided the feasibility to understand the expansion and evolution patterns of GELP in Rosaceae genomes, and highlight the function during P. bretschneideri fruits and pollen tubes development.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akoh CC, Lee G-C, Liaw Y-C, Huang T-H, Shaw J-F (2004) GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog Lipid Res 43:534–552
Babenko VN, Rogozin IB, Mekhedov SL, Koonin EV (2004) Prevalence of intron gain over intron loss in the evolution of paralogous gene families. Nucleic Acids Res 32:3724–3733
Blanc G, Wolfe KH (2004) Widespread paleopolyploidy in model plant species inferred from age distributions of duplicate genes. Plant Cell 16:1667–1678
Budak H, Zhang B (2017) MicroRNAs in model and complex organisms. Funct Integr Genomics 17:1–4
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4(10):10
Cao YP, Han Y, Jin Q, Lin Y, Cai Y (2016a) Comparative genomic analysis of the GRF genes in Chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd), poplar (populous), grape (Vitis vinifera), Arabidopsis and rice (Oryza sativa). Front Plant Sci 7:1750. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01750
Cao Y, Han Y, Li D, Lin Y, Cai Y (2016b) MYB transcription factors in chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.): genome-wide identification, classification, and expression profiling during fruit development. Front Plant Sci 7:577
Cao Y, Han Y, Meng D, Li D, Jiao C, Jin Q, Lin Y, Cai Y (2017) B-BOX genes: genome-wide identification, evolution and their contribution to pollen growth in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). BMC Plant Biol 17:156. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1105-4
Cao Y, Han Y, Meng D, Abdullah M, Li D, Jin Q, Lin Y, Cai Y (2018) Systematic analysis and comparison of the PHD-finger gene family in Chinese pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) and its role in fruit development. Funct Integr Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0609-9
Cenci A, Guignon V, Roux N, Rouard M (2014) Genomic analysis of NAC transcription factors in banana (Musa acuminata) and definition of NAC orthologous groups for monocots and dicots. Plant Mol Biol 85:63–80
Chen C, Xia R, Chen H, He Y (2018) TBtools, a Toolkit for Biologists integrating various HTS-data handling tools with a user-friendly interface bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/289660
Chepyshko H, Lai C-P, Huang L-M, Liu J-H, Shaw J-F (2012) Multifunctionality and diversity of GDSL esterase/lipase gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L. japonica) genome: new insights from bioinformatics analysis. BMC Genomics 13:309
Daccord N, Celton JM, Linsmith G, Becker C, Choisne N, Schijlen E, van de Geest H, Bianco L, Micheletti D, Velasco R, di Pierro EA, Gouzy J, Rees DJG, Guérif P, Muranty H, Durel CE, Laurens F, Lespinasse Y, Gaillard S, Aubourg S, Quesneville H, Weigel D, van de Weg E, Troggio M, Bucher E (2017) High-quality de novo assembly of the apple genome and methylome dynamics of early fruit development. Nat Genet 49:1099–1106
Dong X, Yi H, Han C-T, Nou I-S, Hur Y (2016) GDSL esterase/lipase genes in Brassica rapa L.: genome-wide identification and expression analysis. Mol Gen Genomics 291:531–542
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Faris JD, Zhang ZC, Fellers JP, Gill BS (2008) Micro-colinearity between rice, Brachypodium, and Triticum monococcum at the wheat domestication locus Q. Funct Integr Genomics 8:149–164
Fawcett JA, Maere S, Van de Peer Y (2009) Plants with double genomes might have had a better chance to survive the cretaceous–tertiary extinction event. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:5737–5742
Fedorov A, Merican AF, Gilbert W (2002) Large-scale comparison of intron positions among animal, plant, and fungal genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 99:16128–16133
Finn RD et al (2013) Pfam: the protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D222–D230
Force A, Lynch M, Pickett FB, Amores A, Yan YL, Postlethwait J (1999) Preservation of duplicate genes by complementary, degenerative mutations. Genetics 151:1531–1545
Gasteiger E, Hoogland C, Gattiker A, Duvaud SE, Wilkins MR, Appel RD, Bairoch A (2005) Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server Proteomics Protocols Handbook 112:571–607
Ji R, Wang H, Xin X, Peng S, Hur Y, Li Z, Feng H (2017) BrEXL6, a GDSL lipase gene of Brassica rapa, functions in pollen development. Biol Plant 61:685–692
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Bioinformatics 8:275–282
Jung S et al (2013) The genome database for rosaceae (GDR): year 10 update. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1237–D1244
Kondou Y, Nakazawa M, Kawashima M, Ichikawa T, Yoshizumi T, Suzuki K, Ishikawa A, Koshi T, Matsui R, Muto S, Matsui M (2008) RETARDED GROWTH OF EMBRYO1, a new basic helix-loop-helix protein, expresses in endosperm to control embryo growth. Plant Physiol 147:1924–1935
Kram BW, Bainbridge EA, Perera MAD, Carter C (2008) Identification, cloning and characterization of a GDSL lipase secreted into the nectar of Jacaranda mimosifolia. Plant Mol Biol 68:173–183
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA (2009) Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19:1639–1645
Lai C-P, Huang L-M, Chen L-FO, Chan M-T, Shaw J-F (2017) Genome-wide analysis of GDSL-type esterases/lipases in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 95:181–197
Lee DS, Kim BK, Kwon SJ, Jin HC, Park OK (2009) Arabidopsis GDSL lipase 2 plays a role in pathogen defense via negative regulation of auxin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:1038–1042
Letunic I, Bork P (2016) Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: an online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res 44:W242–W245
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2012) SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D302–D305
Li Z, Jiang H, Zhou L, Deng L, Lin Y, Peng X, Yan H, Cheng B (2014) Molecular evolution of the HD-ZIP I gene family in legume genomes. Gene 533:218–228
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Ling H et al (2006) Isolation and expression analysis of a GDSL-like lipase gene from Brassica napus L. J Biochem Mol Biol 39:297
Lynch M, Force A (2000) The probability of duplicate gene preservation by subfunctionalization. Genetics 154:459–473
Mistry J, Finn RD, Eddy SR, Bateman A, Punta M (2013) Challenges in homology search: HMMER3 and convergent evolution of coiled-coil regions. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e121–e121
Naranjo MA, Forment J, RoldÁN M, Serrano R, Vicente O (2006) Overexpression of Arabidopsis thaliana LTL1, a salt-induced gene encoding a GDSL-motif lipase, increases salt tolerance in yeast and transgenic plants. Plant Cell Environ 29:1890–1900
Neilson J et al (2017) Gene expression profiles predictive of cold-induced sweetening in potato. Funct Integr Genomics 17:1–18
Oh IS, Park AR, Bae MS, Kwon SJ, Kim YS, Lee JE, Kang NY, Lee S, Cheong H, Park OK (2005) Secretome analysis reveals an Arabidopsis lipase involved in defense against Alternaria brassicicola. Plant Cell 17:2832–2847
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT, Salzberg SL (2016) Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc 11:1650–1667
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2009) FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol Biol Evol 26:1641–1650
Qiao X, Yin H, Li L, Wang R, Wu J, Wu J, Zhang S (2018) Different modes of gene duplication show divergent evolutionary patterns and contribute differently to the expansion of gene families involved in important fruit traits in pear (Pyrus bretschneideri). Front Plant Sci 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00161
Riemann M, Gutjahr C, Korte A, Riemann M, Danger B, Muramatsu T, Bayer U, Waller F, Furuya M, Nick P (2007) GER1, a GDSL motif-encoding gene from rice is a novel early light-and jasmonate-induced gene. Plant Biol 9:32–40
Rodgers-Melnick E et al. (2011) Contrasting patterns of evolution following whole genome versus tandem duplication events in Populus. Genome Res 22:95–105
Shirasawa K, Isuzugawa K, Ikenaga M, Saito Y, Yamamoto T, Hirakawa H, Isobe S (2017) The genome sequence of sweet cherry (Prunus avium) for use in genomics-assisted breeding DNA Research:dsx020
Shulaev V, Sargent DJ, Crowhurst RN, Mockler TC, Folkerts O, Delcher AL, Salama DY (2010) The genome of woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca). Nat Genet 43:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.740
Tang H, Bowers JE, Wang X, Ming R, Alam M, Paterson AH (2008) Synteny and collinearity in plant genomes. Science 320:486–488
Updegraff EP, Zhao F, Preuss D (2009) The extracellular lipase EXL4 is required for efficient hydration of Arabidopsis pollen. Sex Plant Reprod 22:197–204
Upton C, Buckley JT (1995) A new family of lipolytic enzymes? Trends Biochem Sci 20:178–179
Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Affourtit J, Dhingra A, Cestaro A, Kalyanaraman A, Fontana P, Bhatnagar SK, Troggio M, Pruss D, Salvi S, Pindo M, Baldi P, Castelletti S, Cavaiuolo M, Coppola G, Costa F, Cova V, Dal Ri A, Goremykin V, Komjanc M, Longhi S, Magnago P, Malacarne G, Malnoy M, Micheletti D, Moretto M, Perazzolli M, Si-Ammour A, Vezzulli S, Zini E, Eldredge G, Fitzgerald LM, Gutin N, Lanchbury J, Macalma T, Mitchell JT, Reid J, Wardell B, Kodira C, Chen Z, Desany B, Niazi F, Palmer M, Koepke T, Jiwan D, Schaeffer S, Krishnan V, Wu C, Chu VT, King ST, Vick J, Tao Q, Mraz A, Stormo A, Stormo K, Bogden R, Ederle D, Stella A, Vecchietti A, Kater MM, Masiero S, Lasserre P, Lespinasse Y, Allan AC, Bus V, Chagné D, Crowhurst RN, Gleave AP, Lavezzo E, Fawcett JA, Proost S, Rouzé P, Sterck L, Toppo S, Lazzari B, Hellens RP, Durel CE, Gutin A, Bumgarner RE, Gardiner SE, Skolnick M, Egholm M, van de Peer Y, Salamini F, Viola R (2010) The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus [times] domestica Borkh). Nat Genet 42:833–839
Verde I et al (2013) The high-quality draft genome of peach (Prunus persica) identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution. Nat Genet 45:487–494
Volokita M, Rosilio-Brami T, Rivkin N, Zik M (2010) Combining comparative sequence and genomic data to ascertain phylogenetic relationships and explore the evolution of the large GDSL-lipase family in land plants. Mol Biol Evol 28:551–565
Wang Y, Tang H, DeBarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, Lee TH, Jin H, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH (2012) MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e49–e49
Wang Y, Wang X, Tang H, Tan X, Ficklin SP, Feltus FA, Paterson AH (2011) Modes of gene duplication contribute differently to genetic novelty and redundancy, but show parallels across divergent angiosperms. PLoS One 6:e28150
Wu J, Wang Z, Shi Z, Zhang S, Ming R, Zhu S, Khan MA, Tao S, Korban SS, Wang H, Chen NJ, Nishio T, Xu X, Cong L, Qi K, Huang X, Wang Y, Zhao X, Wu J, Deng C, Gou C, Zhou W, Yin H, Qin G, Sha Y, Tao Y, Chen H, Yang Y, Song Y, Zhan D, Wang J, Li L, Dai M, Gu C, Wang Y, Shi D, Wang X, Zhang H, Zeng L, Zheng D, Wang C, Chen M, Wang G, Xie L, Sovero V, Sha S, Huang W, Zhang S, Zhang M, Sun J, Xu L, Li Y, Liu X, Li Q, Shen J, Wang J, Paull RE, Bennetzen JL, Wang J, Zhang S (2013) The genome of the pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.). Genome Res 23:396–408
Xu J, Ding Z, Vizcay-Barrena G, Shi J, Liang W, Yuan Z, Werck-Reichhart D, Schreiber L, Wilson ZA, Zhang D (2014) ABORTED MICROSPORES acts as a master regulator of pollen wall formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 26:1544–1556
Yim WC, Lee B-M, Jang CS (2009) Expression diversity and evolutionary dynamics of rice duplicate genes. Mol Gen Genomics 281:483–493
Zdobnov EM, Apweiler R (2001) InterProScan--an integration platform for the signature-recognition methods in InterPro. Bioinformatics 17:847–848
Zhang Q, Chen W, Sun L, Zhao F, Huang B, Yang W, Tao Y, Wang J, Yuan Z, Fan G, Xing Z, Han C, Pan H, Zhong X, Shi W, Liang X, du D, Sun F, Xu Z, Hao R, Lv T, Lv Y, Zheng Z, Sun M, Luo L, Cai M, Gao Y, Wang J, Yin Y, Xu X, Cheng T, Wang J (2012) The genome ofPrunus mume. Nat Commun 3:1318
Acknowledgments
We extend our thanks to the reviewers and editors for their careful reading and helpful comments on this manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 31640068).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YCao designed and performed the experiments. YCao, DM, and YH analyzed the data. YH, DM, YL, QJ, DL, JY, YCao, AM, and YCai contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools. YCao and YH wrote the paper. All authors reviewed and approved this submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Figure S1
The Maximum Likelihood tree for GELP genes identified among the six Rosaceae genomes. Totally, 597 GELP genes were divided into ten subfamilies (A-J), and were indicated by different colors. (PNG 699 kb)
High Resolution Image
(TIF 3080 kb)
Figure S2
The phylogenetic tree for GELP genes identified in six Rosaceae genomes. Subfamilies are numbered at the right part of the ML tree and marked with alternating tones to facilitate subfamily identification. (PNG 4633 kb)
High Resolution Image
(TIF 6556 kb)
Figure S3
Motif logo of four conserved blocks found in Rosaceae GELP proteins: I (a), II (b), III (c), and V (d). The red triangles indicate conserved residues Ser-Gly-Asn-His in blocks. In the present study, the full-length GELP protein sequences were submitted to MEME website to scan conserved motifs in these proteins, based on previous research manuscripts (Dong et al. 2016). (PNG 1060 kb)
High Resolution Image
(TIF 660 kb)
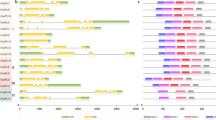
Figure S4
Exon–intron structure analysis of Rosaceae GELP genes. The scale represents the length of the DNA sequence. Legend is at the top right of the Figure. (PNG 3048 kb)
High Resolution Image
(TIF 4507 kb)
Figure S5
Heat map of P. bretschneideri GELP genes in different tissues, including MP (Mature pollen grains), HP (Hydrated pollen grains), PT (Pollen tube), SPT (Stop-growth pollen tube), fruit_stage1 (15 days after full blooming (DAB)), fruit_stage2 (30 DAB), fruit_stage3 (55 DAB), fruit_stage4 (85 DAB), fruit_stage5 (115 DAB), fruit_stage6 (mature stage), and fruit_stage7 (fruit senescence stage), and PbGELP gene expression levels in different conditions, including pear leaf with inoculated distilled water (Leaf_CK), pear leaf with inoculated black spot (Alternarlia alternate) 2 (Leaf_T2), pear leaf with inoculated black spot (Alternarlia alternate) 3 (Leaf_T3), pear fruit with no any treatment (Fruit_CK), pear fruit with Gibberellins treatment (Fruit_GA), pear with salt treatment (Leaf_Salt), pear fruit pericarp-russet (pericarp-russet), and pear fruit pericarp-green (pericarp-green). Blue and red colors correspond to down-regulation and up-regulation, respectively. (PNG 210 kb)
High Resolution Image
(TIF 358 kb)
Figure S6
The Maximum likelihood tree of GELP genes in six Rosaceae species, Arabidopsis and rice. (PDF 87 kb)
Table S1
(XLSX 11 kb)
Table S2
(XLSX 54 kb)
Table S3
(XLSX 139 kb)
Table S4
(XLSX 15 kb)
Table S5
(XLSX 33 kb)
Table S6
(XLSX 17 kb)
Table S7
(XLSX 10 kb)
ESM 1
(DOCX 593 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Y., Han, Y., Meng, D. et al. Expansion and evolutionary patterns of GDSL-type esterases/lipases in Rosaceae genomes. Funct Integr Genomics 18, 673–684 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0620-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0620-1