Abstract
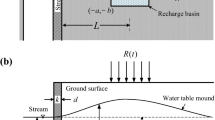
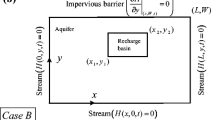
This paper reviews analytical solutions for steady state seepage of groundwater in an ideal sloping unconfined aquifer, recharged by an effective infiltration, when the unsaturated seepage is neglected. Available solutions are examined and compared. Their robustness is assessed with a finite element code, which solves the complete equations for saturated and unsaturated flow, thus making none of the simplifying assumptions of the theoretical solutions. An example is provided for a sloping aquifer on the north shore of the Saint-Lawrence River.
Résumé
L’article fait la revue des solutions analytiques pour l’écoulement souterrain permanent dans un aquifère incliné à nappe libre, rechargé par infiltration efficace, quand l’écoulement non saturé est négligé. Les solutions disponibles sont examinées et comparées. Leur robustesse est évaluée à l’aide d’un code d’éléments fins, qui résout les équations complètes des écoulements saturé et non saturé, et qui donc ne fait aucune des hypothèses simplificatrices des solutions théoriques. Un exemple est fourni pour un aquifère incliné sur la rive nord du Saint-Laurent.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubertin M, Bussière B, Aachib M, Chapuis RP (1996) Une modélisation numérique des écoulements non saturés dans les couvertures multicouches en sols. Hydrogéologie 96(1):3–13
Aubertin M, Cifuentes E, Apithy S, Bussière B, Chapuis RP, Molson JW (2010) Analysis of water diversion along inclined covers with capillary barrier effects. Can Geotech J 46(x), (in print)
Bear J (1972) Dynamics of fluids in porous media. Elsevier, New York
Beven K (1981) Kinematic subsurface stormflow. Water Res Res 17:1419–1424
Boussinesq J (1877) Essai sur la théorie des eaux courantes. Mémoire, Académie des sciences, Inst. Fra. 23(1):252–260
Brutsaert W (1994) The unit response of groundwater outflow from a hillslope. Water Res Res 30:2759–2763
Brutsaert W (1995) The unit response of groundwater outflow from a hillslope: Reply. Water Res Res 31:2379–2380
Bussière B, Aubertin M, Chapuis RP (2003) The behavior of inclined covers used as oxygen barriers. Can Geotech J 40(3):512–525
Chapman T (1995) Comment on “The unit response of groundwater outflow from a hillslope” by W Brutsaert. Water Res Res 31:2377–2378
Chapuis RP (1995) Controlling the quality of groundwater parameters: some examples. Can Geotech J 32:172–177
Chapuis RP (1998a) Overdamped slug tests in monitoring wells: review of interpretation methods with mathematical, physical and numerical analysis of storativity influence. Can Geotech J 35:697–719
Chapuis RP (1998b) Poor borehole sampling and consequences for permeability evaluation. Proc 8th Congress IAEG, Vancouver, Balkema 4:417–423
Chapuis RP (1999) Borehole variable-head permeability tests in compacted clay liners and covers. Can Geotech J 36(1):39–51
Chapuis RP (2002a) Solution analytique de l’écoulement en régime permanent dans un aquifère incliné à nappe libre, et comparaison de cette solution avec des solutions numériques plus complètes, Rapport Tech EPM-RT-02-03, août 2002, École Polytechnique, Montréal, URL:http://www.polymtl.ca/biblio/epmrt/rapports/rt2003-03.pdf
Chapuis RP (2002b) The 2000 R.M. Hardy Lecture: full-scale hydraulic performance of soil-bentonite and compacted clay liners. Can Geotech J 39(2):417–439
Chapuis RP (2005) Numerical modelling of rising-head permeability tests in monitoring wells after lowering the water level down to the screen. Can Geotech J 42:705–715
Chapuis RP (2006) Interpreting variable-head tests performed in open holes or monitoring wells with several screens. Geotech Test J 29(6):467–473
Chapuis RP (2009a) Variable head permeability tests in monitoring wells: comparing the shape factor defined by Bouwer and Rice (1976) to the shape factor given by Hvorslev (1951). Geotech News 27(1):41–43
Chapuis RP (2009b) Numerical modeling of reservoirs or pipes in groundwater seepage. Comput Geotech 36:895–901
Chapuis RP, Aubertin M (2001) Evaluation of saturated and unsaturated seepage through dikes in steady state conditions. Can Geotech J 38:1321–1328
Chapuis RP, Chenaf D (2002) Slug tests in a confined aquifer: experimental results in a large soil tank and numerical modeling. Can Geotech J 39:14–21
Chapuis RP, Chenaf D (2003a) Effects of monitoring and pumping well pipe capacities on pumping tests in confined aquifers. Can Geotech J 40(6):1093–1103
Chapuis RP, Chenaf D (2003b) Variable-head field permeability tests in driven casings: physical and numerical modeling. Geotech Testing J 26:245–256
Chapuis RP, Chesnaux R (2006) Travel time to a well pumping an unconfined aquifer without recharge. Ground Water 44:600–603
Chapuis RP, Dénes A (2009) Écoulement saturé et non saturé de l’eau souterraine vers des drains en aquifère à nappe libre. Can Geotech J 45:1210–1223
Chapuis RP, Chenaf D, Bussière B, Aubertin M, Crespo R (2001) A user’s approach to assess numerical codes for saturated and unsaturated seepage conditions. Can Geotech J 38:1113–1126
Chapuis RP, Chenaf D, Acevedo N, Marcotte D, Chouteau M (2005) Unusual drawdown curves for a pumping test in an unconfined aquifer at Lachenaie, Quebec: Field data and numerical modeling. Can Geotech J 42:1133–1144
Chapuis RP, Bélanger C, Chenaf D (2006) Pumping test in a confined aquifer under tidal influence. Ground Water 44:300–305
Chapuis RP, Dallaire V, Marcotte M, Chouteau M (2007a) Falling-head permeability tests using monitoring wells in unconfined aquifers. Geotech Testing J 30:104–112
Chapuis RP, Masse I, Madinier B, Aubertin M (2007b) A long column test for determining unsaturated properties of coarse material. Geotech Test J 30:83–89
Chenaf D, Chapuis RP (1998) Étude numérique du pompage en régime permanent dans un aquifère à nappe libre. In: Proc 51st Can Geotech Conf, Edmonton 523–528
Chenaf D, Chapuis RP (2007) Seepage face height, water table position, and well efficiency for steady state. Ground Water 45:167–177
Chesnaux R, Chapuis RP (2007) Detecting and quantifying leakage through defective borehole seals: A new methodology and laboratory verification. Geotech Test 30:17–24
Chesnaux R, Molson J, Chapuis RP (2005) An analytical solution for groundwater transit time through an unconfined recharged aquifer. Ground Water 43:511–517
Chesnaux R, Chapuis RP, Molson JW (2006) A new method to characterize hydraulic short-circuits in defective borehole seals. Ground Water 44:676–681
Dunne T, Black R (1970) Partial area contributions to storm runoff in a small New England watershed. Water Res Res 6:1296–1311
Dupuit J (1857) Mémoire sur le mouvement des eaux dans les terrains perméables. Mémoire déposé en 1857, Comptes Rendus des séances de l’Acad des Sciences, Paris, tome LII, séance du 3 juin 1861
Dupuit J (1863) Études théoriques et pratiques sur le mouvement des eaux dans les canaux découverts et à travers les terrains perméables, 2e éd. Dunod Paris chap 7:229–293
Etcheverry D, Perrochet P (2000) Direct simulation of groundwater transit-time distributions using the reservoir theory. Hydrogeol J 8:200–208
Freeze RA (1972a) Role of subsurface flow in generating surface runoff: 1. Base flow contributions to channel flow. Water Res Res 8:609–623
Freeze RA (1972b) Role of subsurface flow in generating surface runoff: 2. Upstream source areas. Water Res Res 8:1272–1283
Geo-Slope (2003) Seep/W for finite element seepage analysis. User’s Guide. Geo-Slope International, Calgary, Alberta
Kamke E (1944) Differential Gleichungen. Lösungsmethoden und Lösungen, 3rd edn. Chelsea, New York, p 329
Kao C, Bouarfa S, Zimmer D (2001) Steady state analysis of unsaturated flow above a shallow water-table aquifer drained by ditches. J Hydrol 250:122–133
Kirkby M (1988) Hillslope runoff processes and models. J Hydrol 100:315–339
Koussis AD (1992) A linear conceptual subsurface storm model. Water Res Res 28:1047–1052
Koussis AD, Lien L (1982) Linear theory of subsurface storm flow. Water Res Res 18:1738–1740
Loáiciga HA (2005) Steady state phreatic surfaces in sloping aquifers. Water Res Res 41:W08402. doi:10.1029/2004WR003861
Pavlovsky NN (1956) Motion of Groundwater, Collected Works. Academy of Sciences, Moscow-Leningrad
Polubarinova-Kochina PY (1962) Theory of groundwater movement. Translated from Russian by JMR de Wiest. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey
Richards LA (1931) Capillary conduction of liquids through porous medium. Physics 1:318–333
Rupp DE, Selker JS (2006) On the use of the Boussinesq equation for interpreting recession hydrographs from sloping aquifers. Water Res Res 42:W12421. doi:10.1029/2006WR005080
Schoeller H (1962) Les eaux souterraines : hydrologie dynamique et chimique, exploitation et évaluation des ressources. Masson, Paris
Strack ODL (1989) Groundwater mechanics. Prentice-Hall, Englewoods Cliffs
Verhoest NFC, Troch PA (2000) Some analytical solutions of the linearized Boussinesq equation with recharge for a sloping aquifer. Water Res Res 36:793–800
Acknowledgments
These studies were subsidized by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada. The author thanks John Molson and Richard Darling for reading and commenting on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Figures 12 and 13 are provided as complements to Figs. 9 and 11.
Complement to Fig. 9: numerical results for the Darcy velocity (second example), below the water table, along equipotential lines starting from the substratum at x = 100, 200, 400, 600, 800 and 1,000 m. It confirms that the Darcy velocity may be assumed constant along each equipotential
Complement to Fig. 11: to illustrate the dampening capacity of the unconfined aquifer, we have considered a 50 mm rain during 1 h. There is no runoff. Before and after the rain, the mean annual effective infiltration was considered. The figure below shows that the response of the water table at x = 500 m (middle of the slope) is strongly delayed and dampened
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chapuis, R.P. Steady state groundwater seepage in sloping unconfined aquifers. Bull Eng Geol Environ 70, 89–99 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0282-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0282-2