Abstract
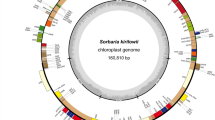
The genus Acer, commonly known as maple, is a large plant lineage that comprises many economically and ecologically important species. However, because of low interspecific morphological variations and scarcity of molecular data, it is challenging to estimate the enigmatic phylogeny of Acer, limiting further utilization and conservation of maples. In this study, we generated complete plastomes of 17 species of maples representing 10 major sections of Acer and conducted comprehensively comparative genomic and phylogenomic analyses in Acer. The 17 plastomes are perfectly conserved in linear gene order and range narrowly in length of 155–157 kb with four constituent parts (LSC, SSC, IRa and IRb), whereas three IR types (amplum-, flabellatum- and yangbiense-like) are observed and the IR borders variation resulted in remarkable gene content divergence (132–134). In addition, there are apparently heterogeneous sequence divergences across the cp genome and 20 noncoding loci with fast evolutionary rates are further identified as potential molecular markers for subsequent studies on Acer. Furthermore, whole plastome sequences obtained the highest phylogenetic resolution and provided strong support for most backbone nodes of Acer among the seven analyzed data sets (LSC, SSC, IRs, coding, noncoding, 20-markers and whole-cp-genome), highlighting the significance of increasing informative sites in resolving intractable phylogenetic relationships of Acer. The section Negundo diverged firstly in Acer and close relationships among sects. Arguta, Ginnala, Macrantha, Oblonga, Pentaphylla, Platanoidea and Trifoliata were uncovered. Interspecific relationships within species-rich sects. Macrantha, Palmata and Platanoidea are also clearly resolved by plastid phylogenomics.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Molec Biol 215:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Amiryousefi A, Hyvönen J, Poczai P (2018a) The chloroplast genome sequence of bittersweet (Solanum dulcamara): plastid genome structure evolution in Solanaceae. PLoS ONE 13:e0196069. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196069
Amiryousefi A, Hyvönen J, Poczai P (2018b) IRscope: an online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 34:3030–3031. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty220
Barrett CF, Baker WJ, Comer JR, Conran JG, Lahmeyer SC, Leebens-Mack JH, Li J, Lim GS, Mayfield-Jones DR, Perez L (2016) Plastid genomes reveal support for deep phylogenetic relationships and extensive rate variation among palms and other commelinid monocots. New Phytol 209:855–870. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13617
Birky CW (1995) Uniparental inheritance of mitochondrial and chloroplast genes: mechanisms and evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:11331–11338. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.25.11331
Chumley TW, Palmer JD, Mower JP, Fourcade HM, Calie PJ, Boore JL, Jansen RK (2006) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Pelargonium × hortorum: organization and evolution of the largest and most highly rearranged chloroplast genome of land plants. Molec Biol Evol 23:2175–2190. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msl089
Cosner ME, Raubeson LA, Jansen RK (2004) Chloroplast DNA rearrangements in Campanulaceae: phylogenetic utility of highly rearranged genomes. BMC Evol Biol 4:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-4-27
Cusimano N, Wicke S (2016) Massive intracellular gene transfer during plastid genome reduction in nongreen Orobanchaceae. New Phytol 210:680–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13784
Dan G, Bock Kane NC, Ebert DP, Rieseberg LH (2014) Genome skimming reveals the origin of the Jerusalem Artichoke tuber crop species: neither from Jerusalem nor an artichoke. New Phytol 201:1021–1030. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12560
Daniell H, Lin CS, Ming Y, Chang WJ (2016) Chloroplast genomes: diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol 17:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-1004-2
de Jong PC (2002) Worldwide maple diversity. In: Wiegrefe SJ, Angus H, Otis D, Gregorey P (eds) Proceedings of the international maple symposium. Westonbirt Arboretum and the Royal Agricultural College, Gloucestershire, England, pp 2–11
Downie SR, Jansen RK (2015) A comparative analysis of whole plastid genomes from the Apiales: expansion and contraction of the inverted repeat, mitochondrial to plastid transfer of DNA, and identification of highly divergent noncoding regions. Syst Bot 40:336–351. https://doi.org/10.1600/036364415X686620
Doyle JJ (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Dugas DV, Hernandez D, Koenen EJM, Schwarz E, Straub S, Hughes CE, Jansen RK, Nageswararao M, Staats M, Trujillo JT (2015) Mimosoid legume plastome evolution: IR expansion, tandem repeat expansions, and accelerated rate of evolution in clpP. Sci Rep 5:16958. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16958
Duvall MR, Fisher AE, Columbus JT, Ingram AL, Wysocki WP, Burke SV, Clark LG, Kelchner SA (2016) Phylogenomics and plastome evolution of the chloridoid grasses (Chloridoideae: Poaceae). Int J Pl Sci 177:235–246. https://doi.org/10.1086/684526
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucl Acids Res 32:1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Fang WP (1981) Aceraceae. In: Flora Republicae Popularis Sinicae, vol. 46. Science Press, Beijing, pp 66–273
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Feng Y, Comes HP, Zhou X, Qiu Y (2019) Phylogenomics recovers monophyly and early Tertiary diversification of Dipteronia (Sapindaceae). Molec Phylogen Evol 130:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2018.09.012
Gibbs D, Chen YS (2009) The red list of maples. Botanic Gardens Conservation International, Richmond
Gitzendanner MA, Soltis PS, Wong KS, Ruhfel BR, Soltis DE (2018) Plastid phylogenomic analysis of green plants: a billion years of evolutionary history. Amer J Bot 105:291–301. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajb2.1048
Goulding SE, Wolfe KH, Olmstead RG, Morden CW (1996) Ebb and flow of the chloroplast inverted repeat. Molec Genet Genomics 252:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02173220
Grimm GW, Denk T, Hemleben V (2007) Evolutionary history and systematics of Acer section Acer—a case study of low-level phylogenetics. Pl Syst Evol 267:215–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-007-0572-8
Han YW, Duan D, Ma XF, Jia Y, Liu ZL, Zhao GF, Li ZH (2016) Efficient identification of the forest tree species in Aceraceae using DNA barcodes. Frontiers Pl Sci 7:1707. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01707
Huang SF, Ricklefs RE, Raven PH (2002) Phylogeny and historical biogeography of Acer I—study history of the infrageneric classification. Taiwania 47:16
Jansen RK, Zhengqiu C, Raubeson LA, Henry D, Depamphilis CW, James LM, Kai F, Müller Mary GB, Haberle RC, Hansen AK (2007) Analysis of 81 genes from 64 plastid genomes resolves relationships in angiosperms and identifies genome-scale evolutionary patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19369–19374. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709121104
Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molec Biol Evol 30:772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A, Stones-Havas S, Cheung M, Sturrock S, Buxton S, Cooper A, Markowitz S, Duran C (2012) Geneious basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
Khodwekar S, Staton M, Coggeshall MV, Carlson JE, Gailing O (2015) Nuclear microsatellite markers for population genetic studies in sugar maple (Acer saccharum Marsh.). Ann Forest Res 58:193–204. https://doi.org/10.15287/afr.2015.360
Li J (2011) Phylogenetic evaluation of series delimitations in section Palmata (Acer, Aceroideae, Sapindaceae) based on sequences of nuclear and chloroplast genes. Aliso 29:43–49. https://doi.org/10.5642/aliso.20112901.05
Li J, Yue J, Shoup S (2006) Phylogenetics of Acer (Aceroideae, Sapindaceae) based on nucleotide sequences of two chloroplast non-coding regions. Harvard Pap Bot 11:101–115. https://doi.org/10.3100/1043-4534(2006)11%5b101:POAASB%5d2.0.CO;2
Li J, Stukel M, Bussies P, Skinner K, Lemmon AR, Lemmon EM, Brown K, Bekmetjev A, Swenson NG (2019) Maple phylogeny and biogeography inferred from phylogenomic data. J Syst Evol 57:594–606. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12535
Lin L, Zhu ZY, Lin LJ, Kuai BK, Ding YL, Du TT (2019) Implications of nrDNA and cpDNA region in Acer (Aceraceae): DNA barcoding and phylogeny. Int J Agric Biol 21:1073–1082. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.0996
Liu C, Tsuda Y, Shen H, Hu L, Saito Y, Ide Y (2014) Genetic structure and hierarchical population divergence history of Acer mono var. mono in South and Northeast China. PLoS ONE 9:e87187. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087187
Logacheva MD, Schelkunov MI, Nuraliev MS, Samigullin TH, Penin AA (2014) The plastid genome of mycoheterotrophic monocot Petrosavia stellaris exhibits both gene losses and multiple rearrangements. Genome Biol Evol 6:238–246. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evu001
Ma P-F, Zhang Y-X, Zeng C-X, Guo Z-H, Li D-Z (2014) Chloroplast phylogenomic analyses resolve deep-level relationships of an intractable bamboo tribe Arundinarieae (Poaceae). Syst Biol 63:933–950. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syu054
Magee AM, Aspinall S, Rice DW, Cusack BP, Sémon M, Perry AS, Stefanović S, Milbourne D, Barth S, Palmer JD, Gray JC, Kavanagh TA, Wolfe KH (2010) Localized hypermutation and associated gene losses in legume chloroplast genomes. Genome Res 20:1700–1710. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.111955.110
Marc L, Oliver D, Sabine K, Ralph B (2013) OrganellarGenomeDRAW-a suite of tools for generating physical maps of plastid and mitochondrial genomes and visualizing expression data sets. Nucl Acids Res 41:W575–W581. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt289
Matsuoka Y, Yamazaki Y, Ogihara Y, Tsunewaki K (2002) Whole chloroplast genome comparison of rice, maize, and wheat: implications for chloroplast gene diversification and phylogeny of cereals. Molec Biol Evol 19:2084–2091. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004033
Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T (2010) Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In: 2010 gateway computing environments workshop (GCE 2010), New Orleans, LA, 2010. IEEE, pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/GCE.2010.5676129
Moore MJ, Soltis PS, Bell CD, Burleigh JG, Soltis DE (2010) Phylogenetic analysis of 83 plastid genes further resolves the early diversification of eudicots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:4623–4628. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0907801107
Ogihara Y, Terachi T, Sasakuma T (1988) Intramolecular recombination of chloroplast genome mediated by short direct-repeat sequences in wheat species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8573–8577. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.85.22.8573
Palmer JD (1985) Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annual Rev Genet 19:325–354. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001545
Qian H, Ricklefs RE (2000) Large-scale processes and the Asian bias in species diversity of temperate plants. Nature 407:180–182. https://doi.org/10.1038/35025052
Raubeson LA, Peery R, Chumley TW, Dziubek C, Fourcade HM, Boore JL, Jansen RK (2007) Comparative chloroplast genomics: analyses including new sequences from the angiosperms Nuphar advena and Ranunculus macranthus. BMC Genom 8:174. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-8-174
Renner SS, Beenken L, Grimm GW, Kocyan A, Ricklefs RE (2007) The evolution of dioecy, heterodichogamy, and labile sex expression in Acer. Evolution 61:2701–2719. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.2007.00221.x
Renner SS, Grimm GW, Schneeweiss GM, Stuessy TF, Ricklefs RE (2008) Rooting and dating maples (Acer) with an uncorrelated-rates molecular clock: implications for north American/Asian disjunctions. Syst Biol 57:795–808. https://doi.org/10.1080/10635150802422282
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, Van Der Mark P, Ayres DL, Darling A, Höhna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/sys029
Saeki I, Murakami N (2010) Chloroplast DNA phylogeography of the endangered Japanese red maple (Acer pycnanthum): the spatial configuration of wetlands shapes genetic diversity. Diversity Distrib 15:917–927. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2009.00609.x
Saeki I, Murakami N (2011) Comparative phylogeography of red maple (Acer rubrum L.) and silver maple (Acer saccharinum L.): impacts of habitat specialization, hybridization and glacial history. J Biogeogr 38:992–1005. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2010.02462.x
Schattner P, Brooks AN, Lowe TM (2005) The tRNAscan-SE, snoscan and snoGPS web servers for the detection of tRNAs and snoRNAs. Nucl Acids Res 33:W686–W689. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki366
Schelkunov MI, Shtratnikova VY, Nuraliev MS, Selosse M-A, Penin AA, Logacheva MD (2015) Exploring the limits for reduction of plastid genomes: a case study of the mycoheterotrophic orchids Epipogium aphyllum and Epipogium roseum. Genome Biol Evol 7:1179–1191. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evv019
Shaw J, Lickey EB, Schilling EE, Small RL (2007) Comparison of whole chloroplast genome sequences to choose noncoding regions for phylogenetic studies in angiosperms: the tortoise and the hare III. Amer J Bot 94:275–288. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.94.3.275
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu033
Straub SC, Parks M, Weitemier K, Fishbein M, Cronn RC, Liston A (2012) Navigating the tip of the genomic iceberg: next generation sequencing for plant systematics. Amer J Bot 99:349–364. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1100335
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP*: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, version 4.0 b10
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molec Biol Evol 28:2731–2739. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr121
Tian X, Guo ZH, Li DZ (2002) Phylogeny of Aceraceae based on ITS and trnL-F data sets. Acta Bot Sin 44:714–724
Tillich M, Lehwark P, Pellizzer T, Ulbricht-Jones ES, Fischer A, Bock R, Greiner S (2017) GeSeq- versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucl Acids Res 45:W6–W11. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx391
van Gelderen DM, de Jong PC, Oterdoom HJ (1994) Maples of the world. Timber Press, Portland
Wang WC, Chen SY, Zhang XZ (2016) Chloroplast genome evolution in Actinidiaceae: clpP loss, heterogenous divergence and phylogenomic practice. PLoS ONE 11:e0162324. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0162324
Wang WC, Chen SY, Zhang XZ, Wang WC, Chen SY, Zhang XZ (2017) The complete chloroplast genome of the endangered Chinese paperbark maple, Acer griseum (Sapindaceae). Conserv Genet Resour 9:527–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-017-0715-3
Wang W, Chen S, Zhang X (2018a) Whole-genome comparison reveals divergent IR borders and mutation hotspots in chloroplast genomes of herbaceous bamboos (Bambusoideae: Olyreae). Molecules 23:1537. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071537
Wang W, Chen S, Zhang X (2018b) Whole-genome comparison reveals heterogeneous divergence and mutation hotspots in chloroplast genome of Eucommia ulmoides Oliver. Int J Molec Sci 19:1037. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041037
Wang YH, Wicke S, Wang H, Jin JJ, Yi TS (2018c) Plastid genome evolution in the early-diverging legume subfamily Cercidoideae (Fabaceae). Frontiers Pl Sci 9:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00138
Wang RK, Fan JS, Chang P, Zhu L, Zhao MR, Li LL (2019) Genome survey sequencing of Acer truncatum Bunge to identify genomic information, simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers and complete chloroplast genome. Forests 10:87. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10020087
Whitfield JB, Lockhart PJ (2007) Deciphering ancient rapid radiations. Trends Ecol Evol 22:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2007.01.012
Wicke S, Schneeweiss GM (2015) Next-generation organellar genomics: potentials and pitfalls of high-throughput technologies for molecular evolutionary studies and plant systematics. Next Generation Sequencing in Plant Systematics. International Association for Plant Taxonomy (IAPT), Bratislava
Wicke S, Schneeweiss GM, Müller KF, Quandt D (2011) The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: gene content, gene order, gene function. Pl Molec Biol 76:273–297. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-011-9762-4
Wu CS, Wang YN, Hsu CY, Lin CP, Chaw SM (2011) Loss of different inverted repeat copies from the chloroplast genomes of Pinaceae and cupressophytes and influence of heterotachy on the evaluation of gymnosperm phylogeny. Genome Biol Evol 3:1284–1295. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evr095
Wyman SK, Jansen RK, Boore JL (2004) Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 20:3252–3255. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bth352
Xu TZ, Chen YS, de Jong PC, Oterdoom HJ, Chang CS (2013) Aceraceae. In: Flora of China, vol. 11. Science Press, Beijing, China, pp 515–553
Xu J, Wu H, Gao L (2017) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of the threatened trident maple Acer buergerianum (Aceraceae). Mitochondrial DNA B 2(1):273–274. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2017.1325345
Yang J, Wariss HM, Tao L, Zhang R, Yun Q, Hollingsworth P, Dao Z, Luo G, Guo H, Ma Y (2019) De novo genome assembly of the endangered Acer yangbiense, a plant species with extremely small populations endemic to Yunnan Province, China. GigaScience 8:giz085. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giz085
Zhang Y-J, Ma P-F, Li D-Z (2011) High-throughput sequencing of six bamboo chloroplast genomes: phylogenetic implications for temperate woody bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). PLoS ONE 6:e20596. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020596
Zhang X-Z, Zeng C-X, Ma P-F, Haevermans T, Zhang Y-X, Zhang L-N, Guo Z-H, Li D-Z (2016) Multi-locus plastid phylogenetic biogeography supports the Asian hypothesis of the temperate woody bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). Molec Phylogen Evol 96:118–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2015.11.025
Zhao J, Xu Y, Xi L, Yang J, Chen H, Zhang J (2018) Characterization of the chloroplast genome sequence of Acer miaotaiense: comparative and phylogenetic analyses. Molecules 23:1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071740
Zhou T, Chen C, Wei Y, Chang Y, Bai G, Li Z, Kanwal N, Zhao G (2016) Comparative transcriptome and chloroplast genome analyses of two related Dipteronia species. Frontiers Pl Sci 9:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01512
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Xun Gong, Jian Liu, Renchao Zhou, Xinxin Zhu, Yifei Li and Yongxiang Kang for their kind help in samples collection.
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31600173), Xinglin Talent Funding of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (A1-AFD018181Z3949) and the Excellent Doctor Fund of Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering (KA180581235).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
W-CW and X–ZZ conceived and designed the experiments, W-CW performed the experiments, W-CW, S-YC and X-ZZ analyzed the data, S-YC and X-ZZ contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools, and W-CW and X-ZZ wrote the paper. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Yunpeng Zhao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Online Resource 1.
The list of 30 taxa and accession numbers of the chloroplast genome sequences used in phylogenetic analysis. (PDF 215 kb)
Online Resource 2.
The seven alignments, i.e., LSC, SSC, IRs, coding, noncoding, 20-markers and whole-cp-genome data sets used in phylogenetic analysis. (NEX 18190 kb)
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Online Resource 1. The list of 30 taxa and accession numbers of the chloroplast genome sequences used in phylogenetic analysis.
Online Resource 2. The seven alignments, i.e., LSC, SSC, IRs, coding, noncoding, 20-markers and whole-cp-genome data sets used in phylogenetic analysis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Chen, S. & Zhang, X. Complete plastomes of 17 species of maples (Sapindaceae: Acer): comparative analyses and phylogenomic implications. Plant Syst Evol 306, 61 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-020-01690-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-020-01690-8