Abstract
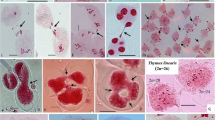
Detailed meiotic analysis in 28 North West Himalayan populations of dioecious plant Rumex acetosa L. was carried out. The species is generally discussed as an important plant having sex chromosomes. Male meiosis in all the studied populations clearly showed the formation of six bivalents and one trivalent during diakinesis and metaphase-I. The sex chromosomes in male plants exhibit a chain of trivalent (Y1–X–Y2). In addition, among the presently investigated populations ring-shaped trivalents were also observed for the first time in the species. Varied frequency of abnormal segregation of sex trivalent was also observed leading to XY:Y segregation instead of normal X:Y1Y2 segregation. A majority of the populations exhibit normal meiosis. Plants of six populations show meiotic abnormalities like cytomixis, laggards, bridges, chromatin stickiness, etc., leading to reduced pollen fertility. Translocation between an autosome and sex chromosomes was also observed in some of the populations. 0–1B chromosomes were noticed in one population. This is the first ever meiotic analysis of the species from India.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baptista-Giacomelli FR, Pagliarini MS, Almeida JL (2000) Meiotic behaviour in several Brazilian oat cultivars (Avena sativa L.). Cytologia 65:371–378
Błocka-Wandas M, Sliwinska E, Grabowska-Joachimiak A, Musial K, Joachimiak AJ (2007) Male gametophyte development and two different DNA classes of pollen grains in Rumex acetosa L., a plant with an XX/XY1 Y2 sex chromosome system and a female-biased sex ratio. Sex Plant Reprod 20:171–180
Clark MS, Parker JS, Ainsworth CC (1993) Repeated DNA and heterochromatin structure in Rumex acetosa. Heredity 70:527–536
Darlington CD (1939) The evolution of genetic systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Falistoco E, Tosti T, Falcinelli M (1995) Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of diploid Dactylis, one of the origins of 2n gametes. J Hered 86:448–453
Gaulden ME (1987) Some mutagens directly alter specific chromosomal proteins (DNA topoisomerase II and peripheral proteins) to produce stickiness, which causes chromosomal aberrations. Mutagenesis 2:357–365
Hodgkin J (1992) Genetic sex determination mechanisms and evolution. Bioessays 14:253–261
Jeelani SM, Kumari S, Gupta RC (2012) Male meiosis in Lotus corniculatus L. Pl Syst Evol 298(10):1977–1985
Kihara H, Ono T (1923) Cytological studies on Rumex L. Bot Magazine 37:84–90
Korpelainen H (2002) A genetic method to resolve gender complements investigations on sex ratios in Rumex acetosa. Mol Ecol 11:2151–2156
Koul MLH (1971) Cytogenetics of polyploids. IV. Cytology of photoperiodic races and cytotypes of Ageratum conyzoides L. Cytologia 36:421–434
Lattoo SK, Khan S, Bamotra S, Dhar AK (2006) Cytomixis impairs meiosis and influences reproductive success in Chlorophytum comosum (Thunb.) Jacq.-an additional strategy and possible implications. J Biosci 31:629–637
Lengerova M, Vyskot B (2001) Sex chromatin and nucleolar analyses in Rumex acetosa L. Protoplasma 217:147–153
Marks GE (1954) An acetocarmine glycerol jelly for use in pollen fertility counts. Stain Tech 29:277
Mosiolek M, Pasierberk P, Malarz L, Mos M, Joachimiak AJ (2005) Rumex acetosa Y chromosomes: constitutive or facultative heterochromatin? Folia Histochem Cytobiol 43:161–167
Navajas-Pérez R, de la Herran R, Jamilena M, Lozano R, Rejón CR, Rejón MR, Garrido Ramos MA (2005) The evolution of reproductive systems and sex-determining mechanisms within Rumex (Polygonaceae) inferred from nuclear and chloroplastidial sequence data. Mol Biol Evol 22:1929–1939
Nirmala A, Rao PN (1996) Genesis of chromosome numerical mosaicism in higher plants. Nucleus 39:151–175
Parker JS (1990) Sex chromosomes and sexual differentiation in flowering plants. Chromosomes Today 10:187–198
Parker JS, Clark MS (1991) Dosage sex chromosome systems in plants. Plant Sci 80:79–82
Ruiz Rejon C, Jamilena M, Garrido Ramos M, Parker JS, Ruiz Rejon M (1994) Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of multiple sex chromosome system of Rumex acetosa. Heredity 72:209–215
Rychlewski J, Zarzycki K (1973) Analysis of natural population of Rumex acetosa L. and R. thyrsiflorus Fing. in respect of the sex ratio. Genet Pol 14:189–191
Saggoo MIS, Farooq U, Loveleen (2011) Meiotic Studies in Sarcococca species (Buxaceae) from Western Himalayas. Cytologia 76:329–335
Shabrangi A, Sheidai M, Majd A, Nabiuni M, Dorranian D (2010) Cytological abnormalities caused by extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields in Canola. Sci Asia 36:292–296
Sharma A (1976) The Chromosomes. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co., New Delhi
Stehlik I, Barrett SCH (2005) Mechanisms governing sex-ratio variation in dioecious Rumex nivalis. Evolution 59:814–825
Wilby AS, Parker JS (1988) The supernumerary segment systems of Rumex acetosa. Heredity 60:109–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farooq, U., Lovleen & Saggoo, M.I.S. Male meiosis and behaviour of sex chromosomes in different populations of Rumex acetosa L. from the Western Himalayas, India. Plant Syst Evol 300, 287–294 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0881-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0881-z