Abstract
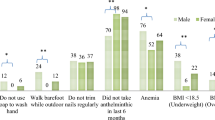
The purpose of the present study was to determine the prevalence of intestinal helminths and protozoa in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients and to evaluate the possible association between the prevalence and CRC pathogenesis. A total of 200 CRC patients and 200 residents of Tashkent, who had no complaints related to the gastrointestinal tract, were examined by triple coproscopy using a concentration method and estimations of protozoan infection intensity. Of the CRC patients tested, 144 were classified as T1-4N0M0 (without metastases) and 56 were classified as T1–4N1–2M0–1 (with metastases). Parasitological examination was performed during CRC diagnosis before and after surgery and chemotherapy. A significantly higher prevalence of Blastocystis sp., Chilomastix mesnili, Jodamoeba butschlii, and Endolimax nana was found in CRC patients than in the control population (p < 0.0001), amounting to 80, 20, 22.5, and 11.5%, respectively. The high prevalence of Blastocystis sp., as well as the patterns of infection intensity, was stable at all stages of examination. The ratio of the number of CRC patients with and without Blastocystis sp. in the T1–4N0M0 and T1–4N1–2M0–1 groups amounted to 3.3 and 7.0, respectively. The ratios for C. mesnili, E. coli, J. butschlii, and E. nana in both groups were 0.2 and 0.2, 0.07 and 0.07, 0.3 and 0.16, and 0.18 and 0.01, respectively. The prevalence of helminths and Giardia lamblia in CRC patients and the control population was not significantly different. Taken together, these data indicate a possible role for Blastocystis sp. in CRC pathogenesis. Diagnosis, treatment, and further observation of patients with Blastocystis sp. are necessary at all stages of CRC, including during diagnosis and before and after surgery and chemotherapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranzamendi C, Fransen F, Langelaar M, Franssen F, van der Ley P, van Putten JP et al (2012) Trichinella spiralis-secreted products modulate DC functionality and expand regulatory T cells in vitro. Parasite Immunol 34:210–223
Brindley PJ, da Costa JM, Sripa B (2015) Why does infection with some helminthes cause cancer? Trends Cancer 1(3):174–182
Buquéa A, Bloy N, Aranda F, Castoldi F, Eggermont A, Cremer I et al (2015) Trial watch: immunomodulatory monoclonal antibodies for oncological indications. Oncoimmunology 4(4):e1008814
Chan KH, Chandramathi S, Suresh K, Chua KH, Kuppusamy UR (2012) Effects of symptomatic and asymptomatic isolates of Blastocystis hominis on colorectal cancer cell line, HCT116. Parasitol Res 110(6):2475–2480
Chandramathi S, Suresh K (2010) Solubilized antigen of Blastocystis hominis facilitates the growth of human colorectal cancer cells, HCT116. Parasitol Res 106(4):941–945
Chandramathi S, Suresh K, Anita ZB, Kuppusamy UR (2012) Infections of Blastocystis hominis and microsporidia in cancer patients: are they opportunistic? Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 106(4):267–269
Coleman O, Nunes T (2016) Role of the microbiota in colorectal Cancer: updates on microbial associations and therapeutic implications. Biores Open Access 5(1):279–288
Devera R, Azacon B, Jiménez M (1998) Blastocystis hominis in patients at the Ruiz y Paez University hospital from Bolivar City, Venezuela. Bol Chil Parasitol 53(3–4):65–70
Edge SB, Compton CC (2010) The American joint committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol 17(6):1471–1474
Favoriti P, Carbone G, Greco M, Pirozzi F, Pirozzi RE, Corcione F (2016) Worldwide burden of colorectal cancer: a review. Updat Surg 68(1):7–11
Fukugaiti MH, Ignacio A, Fernandes MR, Ribeiro U Jr, Nakano V, Avila-Campos MJ (2015) High occurrence of fusobacterium nucleatum and Clostridium difficile in the intestinal microbiota of colorectal carcinoma patients. Braz J Microbiol 46(4):1135–1140
Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA (2000) World Health Organization classification of Tumours. Pathology and genetics of Tumours of the digestive system. In: Hamilton SR, Rubio CA et al (eds) Chapter 6. Tumours of the Colon and Rectum. IARC Press, Lyon, pp 101–117
Hogan BV, Peter MB, Shenoy HG, Horgan K, Hughes TA (2011) Surgery induced immunosuppression. Surgeon 9(1):38–43
Horiki N, Kaneda Y, Maruyama M, Fujita Y, Tachibana H (1999) Intestinal blockage by carcinoma and Blastocystis hominis infection. Am J Trop Med Hyg 60(3):400–402
Hou N, Zhang X, Zhao L, Zhao X, Li Z, Song T (2013) A novel chronic stress-induced shift in the Th1 to Th2-response promotes colon cancer growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 439(4):471–476
Kumarasamy V, Roslani AC, Rani KU, Kumar Govind S (2014) Advantage of using colonic washouts for Blastocystis detection in colorectal cancer patients. Parasit Vectors 7:162
Kumarasamy V, Kuppusamy UR, Jayalakshmi P, Samudi C, Ragavan ND, Kumar S (2017) Exacerbation of colon carcinogenesis by Blastocystis sp. PLoS One 12(8):e0183097
Landman C, Quevrain E (2016) Gut microbiota: description, role and pathophysiological implication. Rev Med Interne 37(6):418–423
Landskron G, De la Fuente M, Thuwajit P, Thuwajit C, Hermoso MA (2014) Chronic inflammation and cytokines in tumor microenvironment. J Immunol Res 2014:149185
Ling A, Lundberg IV, Eklof V, Wikberg ML, Oberg A, Edin S et al (2015) The infiltration, and prognostic importance, of Th1 lymphocytes vary in molecular subgroups of colorectal cancer. J Pathol Clin Res 2(1):21–31
Lopez-Romero G, Quintero J, Astiazaran-Garcia H, Velazquez C (2015) Host defense against Giardia lamblia. Parasite Immunol 37(8):394–406
Maizels RM, Hewitson JP, Smith KA (2012) Susceptibility and immunity to helminth parasites. Curr Opin Immunol 24:459–466
Massacand JC, Stettler RC, Meier R, Humphreys NE, Grencis RK, Marsland BJ, Harris NL (2009) Helminth products bypass the need for TSLP in Th2 immune responses by directly modulating dendritic cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:13968–13973
Mohamed AM, Ahmed MA, Ahmed SA, Al-Semany SA, Alghamdi SS, Zaglool DA (2017) Predominance and association risk of Blastocystis hominis subtype I in colorectal cancer: a case control study. Infect Agents Cancer 12:21
Müller J, Sidler D, Nachbur U, Wastling J, Brunner T, Hemphill A (2008) Thiazolides inhibit growth and induce glutathione-S-transferase pi (GSTP1)-dependent cell death in human colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer 123(8):1797–1806
O'Connell JB, Maggard MA, Liu JH, Etzioni DA, Ko CY (2004) Are survival rates different for young and older patients with rectal cancer? Dis Colon Rectum 47(12):2064–2069
Panczyk M (2014) Pharmacogenetics research on chemotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer over the last 20 years. World J Gastroenterol 20(29):9775–9827
Peterson MR, Weidner N (2011) Gastrointestinal neoplasia associated with bowel Parasitosis: real or imaginary? J Trop Med 2011:234254
Rasti S, Hassanzadeh M, Hooshyar H, Momen-Heravi M, Mousavi SGA, Abdoli A (2017) Intestinal parasitic infections in different groups of immunocompromised patients in Kashan and Qom cities, central Iran. Scand J Gastroenterol 52(6–7):738–741
Senkowski W, Zhang X, Olofsson MH, Isacson R, Höglund U, Gustafsson M, Nygren P, Linder S, Larsson R, Fryknäs M (2015) Three-dimensional cell culture-based screening identifies the anthelmintic drug Nitazoxanide as a candidate for treatment of colorectal Cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 14(6):1504–1516
Sharp SP, Avram D, Stain SC, Lee EC (2017) Local and systemic Th17 immune response associated with advanced stage colon cancer. J Surg Res 208:180–186
Siegel RS, Ward EM, Jemal A (2012) Trends in colorectal Cancer incidence rates in the United States by tumor location and stage, 1992–2008. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 21(3):411–416
Steer H (2007) Blastocystis hominis and colorectal cancer. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 89(5):539
Taşova Y, Sahin B, Koltaş S, Paydaş S (2000) Clinical significance and frequency of Blastocystis hominis in Turkish patients with hematological malignancy. Acta Med Okayama 54(3):133–136
Triantafillidis JK, Nasioulas G, Kosmidis PA (2009) Colorectal cancer and inflammatory bowel disease: epidemiology, risk factors, mechanisms of carcinogenesis and prevention strategies. Anticancer Res 29:2727–2737
Truant AL, Elliott SH, Kelly MT, Smith JH (1981) Comparison of formalin-ethyl ether sedimentation, formalin-ethyl acetate sedimentation, and zinc sulfate flotation techniques for detection of intestinal parasites. J Clin Microbiol 13(5):882–884
Walsh KP, Brady MT, Finlay CM, Boon L, Mills KH (2009) Infection with a helminth parasite attenuates autoimmunity through TGF-β-mediated suppression of Th17 and Th1 responses. J Immunol 183:1577–1586
Wang X, Huycke MM (2015) Colorectal cancer: role commensal bacteria and bystander effects. Gut Microbes 6:370–376
WorldMedicalAssociation (2013) World medical association declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 310(20):2191–2194
Yersal O, Malatyali E, Ertabaklar H, Oktay E, Barutca S, Ertug S (2016) Blastocystis subtypes in cancer patients: analysis of possible risk factors and clinical characteristics. Parasitol Int 65(6 Pt B):792–796
Yu YN, Yu TC, Zhao HJ, Sun TT, Chen HM, Chen HY, An HF, Weng YR, Yu J, Li M, Qin WX, Ma X, Shen N, Hong J, Fang JY (2015) Berberine may rescue fusobacterium nucleatum-induced colorectal tumorogenesis by modulating the tum0or microenvironment. Oncotarget 6(31):32013–32026
Funding
Funding was provided by the Ministry of Public Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan (ADCC 15.21.2). The Ministry of Public Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan had no role in the design of the study or in any aspect of conducting the study (the collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data or the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethics statement
The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Uzbekistan in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki (World Medical Association 2013). The trial is registered at the US National Institutes of Health (ClinicalTrials.gov) #NCT03173001. Both informed and written consents were obtained from the patients and controls.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Julia Walochnik
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toychiev, A., Abdujapparov, S., Imamov, A. et al. Intestinal helminths and protozoan infections in patients with colorectal cancer: prevalence and possible association with cancer pathogenesis. Parasitol Res 117, 3715–3723 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-6070-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-6070-9