Abstract
Purpose
In recent pre-clinical studies, biomaterials and bladder tissue engineering have shown promising outcomes when addressing the need for bladder tissue replacement. To date, multiple clinical experiences have been reported. Herein, we aim to review and summarize the reported clinical experience of biomaterial usage and tissue engineering of the urinary bladder.
Methods
A systematic literature search was performed on Feb 2019 to identify clinical reports on biomaterials for urinary bladder replacement or augmentation and clinical experiences with bladder tissue engineering. We identified and reviewed human studies using biomaterials and tissue-engineered bladder as bladder substitutes or augmentation implants. The studies were then summarized for each respective procedure indication, technique, follow-up period, outcome, and important findings of the studies.
Results
An extensive literature search identified 25 studies of case reports and case series with a cumulative clinical experience of 222 patients. Various biomaterials and tissue-engineered bladder were used, including plastic/polyethylene mold, preserved dog bladder, gelatine sponge, Japanese paper with Nobecutane, lypholized human dura, bovine pericardium, amniotic membrane, small intestinal mucosa, and bladder tissue engineering with autologous cell-seeded biodegradable scaffolds. However, overall clinical experiences including the outcomes and safety reports were not satisfactory enough to replace enterocystoplasty.
Conclusion
To date, several clinical experiences of biomaterials and tissue-engineered bladder have been reported; however, various studies have reported non-satisfactory outcomes. Further technological advancements and a better understanding is needed to advance bladder tissue engineering as a future promising management option for patients requiring bladder drainage.

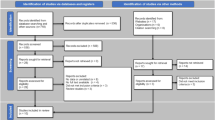
Adopted and reprinted by permission from Springer Nature: lic number 4,553,430,369,670 Ajalloueian et al. [49]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitken KJ, Bägli DJ (2009) The bladder extracellular matrix. Part I: architecture, development and disease. Nat Rev Urol 6:596–611
Singh A, Bivalacqua TJ, Sopko N (2018) Urinary tissue engineering: challenges and opportunities. Sex Med Rev 6(1):35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sxmr.2017.08.004
Fry CH, Meng E, Young JS (2010) The physiological function of lower urinary tract smooth muscle. Auton Neurosci 154(1–2):3–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2009.10.006
Stein R, Hohenfellner M, Pahernik S, Roth S, Thüroff JW, Rübben H (2012) Urinary diversion–approaches and consequences. Dtsch Arztebl Int 109(38):617–622. https://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2012.0617
Biers SM, Venn SN, Greenwell TJ (2012) The past, present and future of augmentation cystoplasty. BJU Int 109(9):1280–1293. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10650.x
Veeratterapillay R, Thorpe AC, Harding C (2013) Augmentation cystoplasty: contemporary indications, techniques and complications. Indian J Urol 29(4):322–327. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-1591.120114
Huang Y, Pan X, Zhou Q, Huang H, Li L, Cui X, Wang G, Jizhong R, Yin L, Xu D, Hong Y (2015) Quality-of-life outcomes and unmet needs between ileal conduit and orthotopic ileal neobladder after radical cystectomy in a Chinese population: a 2-to-1 matched-pair analysis. BMC Urol 27(15):117. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12894-015-0113-7
Prcic A, Aganovic D, Hadziosmanovic O (2013) Impact of complications and bladder cancer stage on quality of life in patients with different types of urinary diversions. Med Arch 67(6):418–422. https://doi.org/10.5455/medarh.2013.67.418-422
Cho A, Lee SM, Noh JW, Choi DK, Lee Y, Cho ST, Kim KK, Lee YG, Lee YK (2017) Acid-base disorders after orthotopic bladder replacement: comparison of an ileal neobladder and an ileal conduit. Ren Fail 39(1):379–384. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886022X.2017.1287733
Serrano-Aroca Á, Vera-Donoso CD, Moreno-Manzano V (2018) Bioengineering approaches for bladder regeneration. Int J Mol Sci 19(6):1796. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061796
Adamowicz J, Pokrywczynska M, Van Breda SV, Kloskowski T, Drewa T (2017) Concise review: tissue engineering of urinary bladder; we still have a long way to go? Stem Cells Transl Med 6(11):2033–2043. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.17-0101
Mahfouz W, Elsalmy S, Corcos J, Fayed AS (2013) Fundamentals of bladder tissue engineering. Afr J Urol 19(2):51–57
El-Assmy A, Hafez AT, El-Sherbiny MT, El-Hamid MA, Mohsen T, Nour EM, Bazeed M (2004) Use of single layer small intestinal submucosa for long segment ureteral replacement: a pilot study. J Urol 171(5):1939–1942
Wezel F, Southgate J, Thomas DFM (2011) Regenerative medicine and urology. BJU Int 108:1046–1065. https://doi.org/10.1111/1464-410X.2011.10206.x
Chung SY, Krivorov NP, Rausei V, Thomas L, Frantzen M, Landsittel D, Kang YM, Chon CH, Ng CS, Fuchs GJ (2005) Bladder reconstitution with bone marrow derived stem cells seeded on small intestinal submucosa improves morphological and molecular composition. J Urol 174(1):353–359
Zou Q, Fu Q (2018) Tissue engineering for urinary tract reconstruction and repair: progress and prospect in China. Asian J Urol 5(2):57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajur.2017.06.010
Jayo MJ, Jain D, Wagner BJ, Bertram TA (2008) Early cellular and stromal responses in regeneration versus repair of a mammalian bladder using autologous cell and biodegradable scaffold technologies. J Urol 180:392–397
Xu Y, Sun DC, Wei ZT, Hong BF, Yang Y (2014) Experimental study on transplantation of autologous minced muscle with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for urethral reconstruction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 18:3412–3419
Alberti C (2016) Whyever bladder tissue engineering clinical applications still remain unusual even though many intriguing technological advances have been reached? G Chir 37(1):6–12
Sloff M, Simaioforidis V, de Vries R, Oosterwijk E, Feitz W (2014) Tissue engineering of the bladder–reality or myth? A systematic review. J Urol 192(4):1035–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2014.03.116
Bohne AW, Urwiller KL (1957) Experience with urinary bladder regeneration. J Urol 77(5):725–732
Portilla Sanchez R, Blanco FL, Santamarina A, Casals RJ, Mata J, Kaufman A (1958) Vesical regeneration in the human after total cystectomy and implantation of a plastic mould. Br J Urol 30:180–188
Tsulukidze A, Murvanidze D, Dvali R, Ivaschenko G (1964) Formation of a bladder by a plastic shell after total cystectomy. Br J Urol 36:102–105
Tsuji I, Kuroda K, Fujieda J, Shiraishi Y, Kassai T, Shida H (1963) A clinical and experimental study on cystoplasty not using the intestine. J Urol 89:214–225
Tsuji I, Kuroda K, Fujieda J, Shiraishi Y, Kunishima K (1967) Clinical experiences of bladder reconstruction using preserved bladder and gelatin sponge bladder in the case of bladder cancer. J Urol 98:91–92
Orikasa S, Tsuji I (1970) Enlargement of contracted bladder by use of gelatin sponge bladder. J Urol 104:107–110
Taguchi H, Ishizuka E, Saito K (1977) Cystoplasty by regeneration of the bladder. J Urol 118:752–756
Fujita K (1978) The use of resin-sprayed thin paper for urinary bladder regeneration. Invest Urol 15:355–357
Schmiedt E, Carl P, Staehler G, Wanner K (1974) Subtotal substitution of urinary bladder by a complete human dura of the skull cap (author’s transl). Urologe A 13(5):228–231
Kelami A (1975) Duroplasty of the urinary bladder—results after two to six years. Eur Urol 1:178–181
Günther M, Pietruschka U, Siegel W, Erdmann T (1979) Use of the durain the surgical treatment of bladder cancer. Z Urol Nephrol 72:473–482
Selli C, Carcangiu ML, Carini M (1986) Bladder carcinoma arising from regenerated urothelium over lyophilized dura patch. Urology 27(1):53–55
Kakimoto S, Sakai H, Kubota S, Kondo A, Kishikawa M (1989) Partial cystectomy for bladder carcinoma: lyophilized human duraas a bladder wall substitute. Nihon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi 80:22–27
Romero Pérez P, Lobato Encinas J, Megía Carrigos J, Pelluch AA, Mira LA (1990) Partial parietal cystectomy and cystoplasty using alyophilized human dura mater patch as an alternative in pallia-tive surgery for bladder cancer. Arch Esp Urol. 43:867–875
Arikan N, Ozdiler E, Yaman O, Go¨gu¨ s O (1995) Augmentation duracystoplasty in neurogenic bladder dysfunction. Int J Urol 2:172–175
Moon SJ, Kim DH, Jo JK, Chung JH, Lee JY, Park SY, Kim YT, Park HK, Choi HY, Moon HS (2011) Bladder reconstruction using bovine pericardium in a case of enterovesical fistula. Korean J Urol 52:150–153
Barski D, Gerullis H, Ecke T, Varga G, Boros M, Pintelon I, Timmermans JP, Winter A, Bagner JW, Otto T (2015) Repair of a vesico-vaginal fistula with amniotic membrane—step 1 of the IDEAL recommendations of surgical innovation. Cent Eur J Urol 68(4):459–461. https://doi.org/10.5173/ceju.2015.683
Mansson W, Harzmann R (1988) Clinical experience with an alloplasticstoma prosthesis (Biocarbon) for urinary conduits and cutaneousureterostomy. Scand J Urol Nephrol 22:223–226
Atala A, Bauer SB, Soker S, Yoo JJ, Retik AB (2006) Tissue-engineered autologous bladders for patients needing cystoplasty. Lancet 367:1241–1246
Joseph DB, Borer JG, De Filippo RE et al (2014) Autologous cell seeded biodegradable scaffold for augmentation cystoplasty: phase II study in children and adolescents with spina bifida. J Urol 191:1389–1394
Bivalacqua T, Steinberg G, Smith N, Joice G, Sopko N, Lerner S, Bochner B, Lee C, Rivera E, Jain D, Bertram T, Salem W, Schoenberg M (2018) Final results of a phase 1 clinical trial evaluating the use of a tissue engineered neo-urinary conduit using adipose derived smooth muscle cells for urinary reconstruction. J Urol 199(4S):e578
Tengion. NCT00512148. An open label multicenter study of augmentation cystoplasty using an autologous neo-bladder construct in subjects with neurogenic bladder following spinal cord injury. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00512148. Accessed 20 Mar 2019
Caione P, Boldrini R, Salerno A, Nappo SG (2012) Bladder augmentation using acellular collagen biomatrix: a pilot experience in exstrophic patients. Pediatr Surg Int 28:421–428
Schaefer M, Kaiser A, Stehr M, Beyer HJ (2013) Bladder augmentation with small intestinal submucosa leads to unsatisfactory long-term results. J Pediatr Urol 9:878–883
Zhang F, Liao L (2014) Tissue engineered cystoplasty augmentation for treatment of neurogenic bladder using small intestinal submucosa: an exploratory study. J Urol 192:544–550
Del Gaudio C, Baiguera S, Ajalloueian F, Bianco A, Macchiarini P (2014) Are synthetic scaffolds suitable for the development of clinical tissue-engineered tubular organs? J Biomed Mater Res A 102(7):2427–2447. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.34883
Smolar J, Horst M, Sulser T, Eberli D (2018) Bladder regeneration through stem cell therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther 18(5):525–544. https://doi.org/10.1080/14712598.2018.1439013
Serrano-Aroca Á, Vera-Donoso CD, Moreno-Manzano V (2018) Bioengineering approaches for bladder regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061796
Ajalloueian F, Lemon G, Hilborn J, Chronakis IS, Fossum M (2018) Bladder biomechanics and the use of scaffolds for regenerative medicine in the urinary bladder. Nat Rev Urol 15(3):155–174. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2018.5
Farhat WA, Yeger H (2008) Does mechanical stimulation have any role in urinary bladder tissue engineering? World J Urol 26(4):301–305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-008-0318-4
Farhat W, Chen J, Erdeljan P, Shemtov O, Courtman D, Khoury A, Yeger H (2003) Porosity of porcine bladder acellular matrix: impact of ACM thickness. J Biomed Mater Res A 67(3):970–974
Loai Y, Yeger H, Coz C, Antoon R, Islam SS, Moore K, Farhat WA (2010) Bladder tissue engineering: tissue regeneration and neovascularization of HA-VEGF-incorporated bladder acellular constructs in mouse and porcine animal models. J Biomed Mater Res A 94(4):1205–1215. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.32777
Horst M, Madduri S, Gobet R, Sulser T, Milleret V, Hall H, Atala A, Eberli D (2013) Engineering functional bladder tissues. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 7(7):515–522. https://doi.org/10.1002/term.547
Oerlemans AJ, Feitz WF, van Leeuwen E, Dekkers WJ (2013) Regenerative urology clinical trials: an ethical assessment of road blocks and solutions. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 19(1):41–47. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEB.2012.0136
Ling Q, Wang T, Yu X, Wang SG, Ye ZQ, Liu JH, Yang SW, Zhu XB, Yu J (2017) UC-VEGF-SMC three dimensional (3d) nano scaffolds exhibits good repair function in bladder damage. J Biomed Nanotechnol 13(3):313–323
Bishop ES, Mostafa S, Pakvasa M, Luu HH, Lee MJ, Wolf JM, Ameer GA, He TC, Reid RR (2017) 3-D bioprinting technologies in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: current and future trends. Genes Dis 4(4):185–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2017.10.002
Pi Q, Maharjan S, Yan X, Liu X, Singh B, van Genderen AM, Robledo-Padilla F, Parra-Saldivar R, Hu N, Jia W, Xu C, Kang J, Hassan S, Cheng H, Hou X, Khademhosseini A, Zhang YS (2018) Digitally tunable microfluidic bioprinting of multilayered cannular tissues. Adv Mater 30(43):e1706913. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201706913
Alarçin E, Guan X, Kashaf SS, Elbaradie K, Yang H, Jang HL, Khademhosseini A (2016) Recreating composition, structure, functionalities of tissues at nanoscale for regenerative medicine. Regen Med 11(8):849–858
Yudintceva NM, Nashchekina YA, Blinova MI, Orlova NV, Muraviov AN, Vinogradova TI, Sheykhov MG, Shapkova EY, Emeljannikov DV, Yablonskii PK, Samusenko IA, Mikhrina AL, Pakhomov AV, Shevtsov MA (2016) Experimental bladder regeneration using a poly-l-lactide/silk fibroin scaffold seeded with nanoparticle-labeled allogenic bone marrow stromal cells. Int J Nanomed 11:4521–4533 (eCollection 2016)
Moe AA, Suryana M, Marcy G et al (2012) Microarray with micro- and nanotopographies enables identification of the optimal topography for directing the differentiation of primary murine neural progenitor cells. Small 8:3050–3061
Acknowledgements
The author group would like to acknowledge the kind assistance of the library staffs from Edward E. Brickell Medical Sciences Library of Eastern Virginal Medical School in providing technical support and retrieving the full-text articles for the literature review of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MEC: project development, data Collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing. WAF: data collection, data analysis, and manuscript writing/editing. JMM: data analysis and manuscript writing/editing. KAM: project development, data collection, and manuscript writing/editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Authors have nothing to disclose.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable for current article.
Informed consent
Not applicable for current article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chua, M.E., Farhat, W.A., Ming, J.M. et al. Review of clinical experience on biomaterials and tissue engineering of urinary bladder. World J Urol 38, 2081–2093 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02833-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-019-02833-4