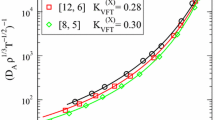
Abstract
The calculation of the intrinsic viscosity by means of classical treatments of bead models, typically composed of a number of identical beads, presents some problems when applied to models where the beads are unequal and their number is not very large. A correction to this problem was proposed 10 years ago (García de la Torre and Carrasco in Eur Biophys J 27:549–557, 1998). This so-called volume correction, which consisted of adding a term proportional to the volume of the model, was proved to be rigorous in physico-mathemathical terms, and produced improved results in some circumstances, but not always. Recently, the volume correction is being reconsidered so that with some deduced or empirical modifications, it can allow for safer predictions of the intrinsic viscosity. This paper contributes a discussion and further improvements of that correction for the intrinsic viscosity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe F, Einaga Y, Yamakawa H (1991) Intrinsic viscosity of oligo- and polyisobutylenes. Treatments of negative intrinsic viscosities. Macromolecules 24:4423–4428
Bianchi U, Peterlin A (1968) Intrinsic viscosity of polymers of low molecular weight. J Polym Sci Part A-2 6:1759–1772
Bloomfield VA, Dalton WO, Holde KEV (1967) Frictional coefficients of multisubunit structures. I Theory. Biopolymers 5:135–148
Byron O (1997) Construction of hydrodynamic bead models from high resolution X-ray crystallographic or nuclear magnetic resonance data. Biophys J 72:408–415
Fixman M (1983) Variational bounds for polymer transport coefficients. J Chem Phys 78:1594–1599
Freire J (2008) Realistic numerical simulations of dendrimer molecules. Soft Matter 4:2139–2143
Freire J, Rey A (1990) Lower bounds for the intrinsic viscosity of flexible polymers. comparison with Brownian dynamics simulation results for different types of chains. Comput Phys Commun 61:297–303
Freire J, Rubio A (2008) Conformational properties and Rouse dynamics of different dendrimer molecules. Polymer 49:2762–2769
García Bernal J, García dela Torre J (1981) Transport properties of oligomeric subunit structures. Biopolymers 20:129–139
García de la Torre J (2001) Building hydrodynamic bead-shell models for rigid particles of arbitrary shape. Biophys Chem 94:265–274
García de la Torre J, Bloomfield V (1977) Hydrodynamic properties of macromolecular complexes. I Translation. Biopolymers 16:1747–1763
García de la Torre J, Bloomfield V (1978) Hydrodynamic properties of macromolecular complexes. IV Intrinsic viscosity theory with applications to once-broken rods and multisubunit proteins. Biopolymers 17:1605–1627
García de la Torre J, Bloomfield V (1981) Hydrodynamic properties of complex, rigid, biological macromolecules. Theory and applications. Q Rev Biophys 14:81–139
García de la Torre J, Carrasco B (1998) Intrinsic viscosity and rotational diffusion of bead models for rigid macromolecules and bioparticles. Eur Biophys J 27:549–557
García de la Torre J, Carrasco B (2002) Hydrodynamic properties of rigid macromolecules composed of ellipsoidal and cylindrical subunits. Biopolymers 63:163–167
García de la Torre J, Navarro S, López Martínez M, Díaz F, López Cascales J (1994) HYDRO: a computer software for the prediction of hydrodynamic properties of macromolecules. Biophys J 67:530–531
García de la Torre J, Huertas M, Carrasco B (2000a) Calculation of hydrodynamic properties of globular proteins from their atomic-level structures. Biophys J 78:719–730
García de la Torre J, Huertas M, Carrasco B (2000b) HYDRONMR: prediction of NMR relaxation of globular proteins from atomic-level structures and hydrodynamic calculations. J Magn Reson 147:138–146
García de la Torre J, Llorca O, Carrascosa J, Valpuesta J (2001) HYDROMIC: prediction of hydrodynamic properties of rigid macromolecular structures obtained from electron microscopy images. Eur Biophys J 30:457–462
García de la Torre J, Del Río Echenique G, Ortega A (2007) Improved calculation of rotational diffusion and intrinsic viscosity of bead models for macromolecules and nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 111:955–961
Haney M (1985) A new differential viscometer—part one. Am Lab 17:41–56
Harding SE (1997) The intrinsic viscosity of biological macromolecules. Progress in measurement, interpretation and application to structure in dilute solution. Prog Biophys Molec Biol 68:207–262
Kirkwood J, Riseman J (1948) The intrinsic viscosities and diffusion constants of flexible macromolecules in solution. J Chem Phys 16:565–573
Lee J, Tripathi A (2005) Intrinsic viscosity of polymers and biopolymers measured by microchip. Anal Chem 77:7137–7147
Longman E, Harding SE, Marheineke N (2006) Identifying differences in solution conformations of two chimeric IgG3 antibodies through triple detection SEC. LCGC North America (Suppl):86–90
Pamies R, Cifre JH, López Martínez M, García de la Torre J (2008) Determination of intrinsic viscosities of macromolecules and nanoparticles. Comparison of single-point and dilution procedures. Colloid Polym Sci 286:1223–1231
Rai N, Nollman M, Spotorno B, Tassara G, Byron O, Rocco M (2005) SOMO (Solution Modeller differences between X-ray and NMR-derived bead models suggest a role for side chain flexibility in protein dynamics. Structure 13:722–734
Riseman J, Kirkwood J (1950) The intrinsic viscosity, translational and rotatory diffusion constants of rod-like macromolecules in solution. J Chem Phys 18:512–516
Rodríguez E, Freire JJ, del Río Echenique G, Garcia de la Torre J (2007) Improved simulation method for the calculation of the intrinsic viscosity of some dendrimer molecules. Polymer 48:1155–1163
Serdyuk IN, Zaccai NR, Zaccai J (2007) Methods in molecular biophysics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Solomon O, Ciuta I (1962) Détermination de la viscosité intrinséque de solutions de polyméres par une simple détermination de la viscosité. J Appl Polym Sci 6:683–686
Wei G, Eichinger B (1990) On shape asymmetry of gaussian molecules. J Chem Phys 93:1430–1435
Wilson RW, Bloomfield V (1979) Hydrodynamic properties of macromolecular complexes. V. Improved calculation of rotational diffusion coefficient and intrinsic viscosity. Biopolymers 18:1205–1211
Yamakawa H (1971) Modern theory of polymer solutions. Harper and Row, New York
Yoshizaki T, Nita I, Yamakawa H (1988) Transport coefficients of helical wormlike chains 4 intrinsic viscosity of the touched-bead model. Macromolecules 21:165–171
Zipper P, Durchschlag H (2000) Prediction of hydrodynamic and small-angle scattering parameters from crystal and electro-microscopic studies. J Appl Crystallogr 33:788–792
Zipper P, Durchschlag H (2007) Modeling complex biological macromolecules: reduction of multibead models. J Biol Phys 33:523–539
Acknowledgments
The possibility of an intermediate correction for the intrinsic viscosity was suggested to us by Prof. S. Harding (Nottingham University, UK). Our previous implementation of the correction (García de la Torre et al. 2007) has been thoroughly checked by Prof. Peter Zipper (University of Graz, Austria) and Prof. Helmut Durchschlag (University of Regensburg, Germany), whose comments and suggestions have been most valuable for the present work. Supported by grant CTQ2006-06831 (including FEDER funds) from Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (MICINN), which also provided a predoctoral grant to D.A. and a postdoctoral fellowship to A.O. Our group is recipient of grant from the program Grupos de Excelencia de la Region de Murcia, 04531/GERM/06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
AUC&HYDRO 2008—Contributions from 17th International Symposium on Analytical Ultracentrifugation and Hydrodynamics, Newcastle, UK, 11–12 September 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García de la Torre, J., Amorós, D. & Ortega, A. Intrinsic viscosity of bead models for macromolecules and nanoparticles. Eur Biophys J 39, 381–388 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0405-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-009-0405-5