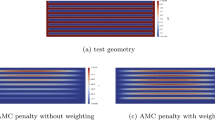
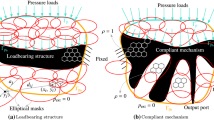
Abstract
This article describes a parametric shape optimization approach using vertical or horizontal structures with a fine parametrization of their center lines and profiles. In this context horizontal means a lateral connection from left to right and vertical means a bottom-up connection. These structures are projected to a pseudo density field associated with a fixed mesh using a differentiable mapping. This enables the use of existing topology optimization tools with respect to the solution of the state problem based on the pseudo density field. The approach belongs to a class of geometry projection onto a fictitious domain methods. It therefore shares the property that sensitivity analysis is reduced to extend the well known gradient calculation from topology optimization by chain using the sensitivity of the mapping from shape variables to pseudo density. The contribution lies in the combination with our specific shape parametrization and the associated regularization. Optimization problems can be formulated concurrently in terms of shape variables and pseudo density. We discuss regularization, periodicity constraints, symmetry formulations and overhang constraints in terms of shape variables. Volume and perimeter constraints are easily formulated in terms of the pseudo density. We see our approach as being particularly beneficial for certain problem classes where it may be difficult to restrict the design space, e.g. restricting isolated structures or holes or where a strict control of solid to void transition is necessary. Consequently, we show examples for phononic band gap maximization, boundary driven heat optimization and perimeter maximization for a flow problem. We also present a formulation of overhang constraints for additive manufacturing in terms of shape variables.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization.
Local mesh refinement, as in Maute and Ramm (1995), does not appear to be widely applied.
We note that the periodic design constraint is no replacement for periodic boundary conditions on the state problem.
See Gill et al. (2002).
Slope constraints, curvature constraints and possibly overhang constraints.
References
Allaire G, Jouve F, Michailidis G (2016) Thickness control in structural optimization via a level set method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53(6):1349–1382
Andreassen E, Clausen A, Schevenels M, Lazarov B, Sigmund O (2011) Efficient topology optimization in matlab using 88 lines of code. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(1):1–16
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1:193–202
Bilal OR, Hussein MI (2012) Topologically evolved phononic material: breaking the world record in band gap size. In: SPIE OPTO, International society for optics and photonics, pp 826,911–826,911
Braibant V, Fleury C (1984) Shape optimal design using b-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 44 (3):247–267
Bruggi M (2008) On an alternative approach to stress constraints relaxation in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 36(2):125–141
Bruns TE, Tortorelli DA (2001) Topology optimization of non-linear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(26-27):3443–3459
Christiansen AN, Bærentzen JA, Nobel-Jørgensen M, Aage N, Sigmund O (2015) Combined shape and topology optimization of 3d structures. Comput Graph 46:25–35
Dunning PD (2017) Design parameterization for topology optimization by intersection of an implicit function. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 317:993–1011
Gangl P, Langer U, Laurain A, Meftahi H, Sturm K (2015) Shape optimization of an electric motor subject to nonlinear magnetostatics. SIAM J Sci Comput 37(6):B1002–B1025
Gaynor AT, Guest JK (2016) Topology optimization considering overhang constraints: Eliminating sacrificial support material in additive manufacturing through design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 5(54):1157–1172
Gersborg AR, Andreasen CS (2011) An explicit parameterization for casting constraints in gradient driven topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44(6):875–881
Gill PE, Murray W, Saunders MA (2002) SNOPT: An SQP algorithm for large-scale constrained optimization. SIAM J Optim 12(4):979–1006
Guest JK (2009) Imposing maximum length scale in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37 (5):463–473
Guest J, Prévost J, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(2):238–254
Haftka RT, Grandhi RV (1986) Structural shape optimization: a survey. Comput Methods Appl. Mech Eng 57(1):91–106
Haslinger J, Mäkinen R (2003) Introduction to Shape Optimization: Theory, vol 7. Siam
Hoang VN, Jang GW (2016) Topology optimization using moving morphable bars for versatile thickness control. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering
Imam MH (1982) Three-dimensional shape optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 18(5):661–673
Langelaar M (2017) An additive manufacturing filter for topology optimization of print-ready designs. Struct Multidisc Optim 55(3): 871–883
Lazarov B, Wang F, Sigmund O (2016) Length scale and manufacturability in density-based topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 86(1-2):189–218
Le C, Bruns T, Tortorelli D (2011) A gradient-based, parameter-free approach to shape optimization. Comput Meth Appl Mech Eng 200(9):985–996
Maute K, Ramm E (1995) Adaptive topology optimization. Struct Optim 10(2):100–112
Norato J, Haber R, Tortorelli D, Bendsøe MP (2004) A geometry projection method for shape optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 60(14):2289–2312
Norato J, Bell B, Tortorelli D (2015) A geometry projection method for continuum-based topology optimization with discrete elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 293:306–327
Novotny AA, Sokołowski J (2012) Topological derivatives in shape optimization. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Petersson J, Sigmund O (1998) Slope constrained topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 41:1417–1434
Petersson J, Beckers M, Duysinx P (1999) Almost isotropic perimeters in topology optimization: Theoretical and numerical aspects. In: Third world congress of structural and multidisciplinary optimization
Pingen G, Evgrafov A, Maute K (2007) Topology optimization of flow domains using the lattice Boltzmann method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 34(6):507–524
Saxena A (2008) A material-mask overlay strategy for continuum topology optimization of compliant mechanisms using honeycomb discretization. J Mech Des 130(8):082,304
Saxena A (2011) Topology design with negative masks using gradient search. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44 (5):629–649
Semmler J, Pflug L, Stingl M, Leugering G (2015) Shape optimization in electromagnetic applications. In: New trends in shape optimization. Springer, pp 251–269
Sigmund O (2001) A 99 Line topology optimization code written in MATLAB. Struct Multidiscip Optim 21:120–127
Sigmund O (2007) Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(4):401–424
Sigmund O, Jensen JS (2003) Systematic design of phononic band-gap materials and structures by topology optimization. Philos Trans R Soc Math Phys Eng Sci 361(1806):1001–1019
Sigmund O, Maute K (2013) Topology optimization approaches. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(6):1031–1055
Sigmund O, Petersson J (1998) Numerical instabilities in topology optimization: A survey on procedures dealing with checkerboards, mesh-dependencies and local minima. Struct Multidiscip Optim 16:68–75
Sokolowski J, Zolesio JP (1992) Introduction to shape optimization. In: Introduction to shape optimization. Springer, pp 5–12
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes-a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
van Dijk NP, Maute K, Langelaar M, Van Keulen F (2013) Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: a review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(3):437–472
Wang F, Lazarov B, Sigmund O (2011) On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(6):767–784
Warmuth F, Körner C (2015) Phononic band gaps in 2d quadratic and 3d cubic cellular structures. Materials 8(12):8327–8337
Yurkin MA, Hoekstra AG (2007) The discrete dipole approximation: an overview and recent developments. J Quant Spectrosc Radiat Transfer 106(1):558–589
Zhang W, Zhang J, Guo X (2016) Lagrangian description based topology optimization: A revival of shape optimization. J Appl Mech 83(4):041,010
Zhou M, Lazarov B, Wang F, Sigmund O (2015) Minimum length scale in topology optimization by geometric constraints. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 293:266–282
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the Cluster of Excellence ‘Engineering of Advanced Materials’ at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, which is funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the framework of its ‘Excellence Initiative’. The implementation of the heat and flow problems was done by Bich Ngoc Vu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wein, F., Stingl, M. A combined parametric shape optimization and ersatz material approach. Struct Multidisc Optim 57, 1297–1315 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1812-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-017-1812-3