Abstract
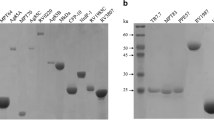
The antibody response to the 38kDa, 16kDa and Lipoarabinomannan (LAM) antigens ofMycobacterium tuberculosis was evaluated using three different ELISAs based on these antigens. The study group included tuberculosis patients (n=52), patients with HIV and TB co-infection (n=10), other chest symptomatics (n=5), HIV infected individuals (n=10), leprosy cases (n=7) and healthy controls (n=75). The results indicate that the 38kDa and LAM based ELISA for IgM/IgG has a low specificity (ranging from 69–85%) and sensitivity (ranging from 55–78%). When three ELISAs are carried out on a single patient the probability of detection of tuberculosis was significantly increased to 95.2% indicating that a single ELISA test is of low sensitivity and that a combination of ELISA’s may be needed to be of any value as a diagnostic test for tuberculosis. Additionally, a western blot assay of the serum antibody response to protein fraction ofM. tuberculosis was analysed in 15 tuberculosis patients and five healthy controls. A multiple antibody response to various M.tuberculosis proteins was observed which varied from patient to patient as compared to controls who showed a single 38–39 kDa protein band positivity. These finding suggest that a western blot assay which determines the antibody response to a set of antigenic components ofM. tuberculosis could be a better serological test for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in our population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Tuberculosis fact sheet. WHO Tuberculosis site (cited 2000 Sept 15); 1(3screens), Available from; URL;http:// www.who.int/gtb/ publications/factsheet/ index.htm.
Davies, P.D.O. (1997) Clinical tuberculosis. (Ed 1st). Chapman & Hall Medical Publishers.
Bhatia, A.S., Kumar, S. and Harinath, B.C. (2003) Immunodiagnosis of tuberculosis: An update. Indian. J. Clin. Biochem. 18(2), 1–5.
Banerjee, S., Gupta, S., Shende, N., Kumar, S. and Harinath, B.C. (2003) Serodiagnosis of tuberculosis using two ELISA systems. Indian. J. Clin. Biochem. 18(2), 48–53.
Kaur, J., Arora D.R., Sikka, R. and Gupta, K.B. (1999) Evaluation of ELISA test using antigen 60 in the serodiagnosis of TB. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 17(2), 72–73.
Chander, I., Subrahmanayam, S. and Gupta, R. (1960) Sensitivity of EIA in the diagnosis of tuberculosis using 38kDa antigen. J. Ind. Med. Assoc. 94, 376–378.
Mathai, E., Rajkumari, R., Kuruvilla, P.J., Kirubakaran, H., Brahmadathan, K.N., Inbamalar, & Abraham, O.C. (2002) Evaluation of serological tests for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 45(4), 439–441.
Papiha, S.S., Wentzel, J., Behjati, F. and Agarwal, S.S. (1985) HLA and circulating immunoglobulin levels in Indian patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Tubercle 66, 25–33.
Sada, E., Brennan, P.J., Herrera, T. & Torres, M. (1990) Evaluation of lipoarabinomannan for the serological diagnosis of tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 28(12), 2587–2590.
Wilkinson, R.J., Haslov, K., Rappuoli, R., Giovannoni, F., Narayanan, P.R., Desai, C.R., Vordermeier, H.M., Paulsen, J., Paslov, G., Ivanyi, J. & Singh, M. (1997) Evaluation of the Recombinant 38kDa antigen ofMycobacterium tuberculosis as a Potential Immunodiagnostic Reagent. J. Clin. Micro. 35(3), 553–557.
Zaher, F. & Marks, J. (1977) Methods and medium for the culture of tubercle bacilli. Tubercle. 58, 143–5.
Lodam, A.N., Reddy, M.V., Narang, P., Gupta, O.P., & Harinath, B.C. (1996) Fractionation, analysis and diagnostic utility ofMycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra excretory-secretory antigen in pulmonary tuberculosis. Indian. J. Biochem. Biophys. 33(1), 66–71.
Lowry, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., & Randall, R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., & Gordon, J. (1979) Electrophorectic transfer of protein from polyacrylamide gels to NCM sheets: Procedures and some applications. Proc Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 76, 4350.
World Health Organization. (1994) Operational characteristics of commercially available assays to detect antibodies to HIV-1 and or HIV-2 in human sera. Geneva: WHO. GPA/RID/CRD/94.4.
Cole, S.T., Eigilmeier, K., Parkhill, J., James, K.D. et al. (2001) Massive gene decay in the leprosy bacillus. Nature. 409, 1007–1011.
Van den Akker, T.W., Naafs, B., Kolk, A.H., De Glopper-van der Veer, E., Chin, R.A., Lien, A., & Van Joost, T. (1992) Similarity between mycobacterial and human epidermal antigens. Br. J. Dermatol; 127(4), 352–358.
Harboe, M. (1994) Overview of host-parasite relations. In: Robert C. Hasting, editor. Leprosy. (Ed 2nd) London: Churchill Livingstone. pp 87–111.
Rovatti, E., Corradi, M.P., Amicosante, M., Tartoni, P.L., Panini, W., Ancora, A., Cenci, A.M., Zucchi, L., Monno, L., Angarano, G., & Saltini, C. (1996) Evaluation of a western blot serum test for the diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Eur. Respir. J. 9(2), 288–92.
Franco, J., Camarena, J.J., Nogueira, J.M., Blanquer, R., Ruiz, M.J. & Marin, J. (2001) Serological response (Western blot) to fractions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis sonicate antigen in tuberculosis patients and contacts. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung. Dis. 5(10), 958–62.
Lu, X.D., Sun, H.P., & Zhang, Y.H. (1993) Application of western blotting technique in the serodiagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi; 16(6), 357–9, 375–6.
Stead, W.W., Sender, J.W., Reddick, W.T. & Lofgren, J.P. (1990) Racial differences in susceptibility to infection byMycobacterium tuberculosis. New Engl J. Med. 322, 422–427.
Smith, P.G. (1994) Clinical tuberculosis. In: Davies PDO, editor. Prevention: BCG vaccination. (Ed 1st). London: Chapman Hall; pp: 297–320.
Hoal-van Helden, E.G., Hon, D., Lewis, L.A., Beyers, N., & van Helden, P.D. (2001) Mycobacterial growth in human macrophages: variation according to donor, inoculum and bacterial strain. Cell. Biol. Int. 25(1), 71–81.
Fine, P.E.M., Floyd, S., Stanford, J.L., Nkhosa, P., Kasunga, A., Chaguluka, S., Warndorff, D.K., Jenkins, P.A., Yates, M., & Ponnighaus, J.M. (2001) Environmental mycobacteria in northern Malawi: implications for the epidemiology of tuberculosis and leprosy. Epidemiol. Infect. 126, 379–387.
UNAIDS/AIDS.AIDS epidemic update. UNAIDS, Geneva, December 2000.
www.naco.nic, www.unaids.com.
Walia, K. (2002) Current issues in HIV/TB co-infection. Ind. J. Tub. 49, 21–26.
Farajollahi, M.M. & Moghaddamnia, H. (2002) Development of a new capture ELISA assay of whole pathogen for diagnosis of tuberculosis in body fluids. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 6(10), 165.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raju, R., Suneetha, S., Sagili, K. et al. Diagnostic role of the antibody response to the 38kDa, 16kDa proteins and lipoarabinomannan of mycobacterium tuberculosis. Indian J Clin Biochem 20, 123–128 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893056
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02893056