Abstract
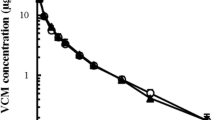
Because of the relatively poor intestinal absorption of ampicillin sodium, efforts have been made to enhance ampicillin absorption by co-administration of absorption promoters. In the present study the enhancing effect of sodium decanoate on rate and extent of rectal ampicillin absorption in rats has been evaluated after rate-controlled and site-controlled delivery of aqueous solutions. Rectal absorption without enhancer was extremely low (8±7%), and the addition of 0.032M sodium decanoate gave comparable values. However, administration in 0.16M decanoate considerably increased ampicillin bioavailability, to 79±30%, whereas the absorption rate was not significantly affected.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reese RE, Betts RF. Antibiotic use. In: Reese RE, Douglas RG, eds. A practical approach to infectious diseases. 2nd ed. Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 1986:559–679.
Sjövall J, Alvan G, Westerlund D. Oral cyclacillin interacts with the absorption of oral ampicillin, amoxycillin, and bacampicillin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1985;29:495–502.
Yamashita S, Yamazaki Y, Mizuno M, et al. Further investigations on the transport mechanism of cephalexin and ampicillin across rat jejunum. J Pharmacobiodyn 1984:7:227–33.
Iseki K, Iemura A, Sato H, Sunada K, Miyazaki K, Arita T. Intestinal absorption of several β-lactam antibiotics, v. Effect of amino β-lactam analogues and dipeptides on the absorption of amino β-lactam antibiotics. J Pharmacobiodyn 1984;7:768–75.
Murakami T, Sasaki Y, Yamajo R, Yata N. Effect of bile salts on the rectal absorption of sodium ampicillin in rats. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1984;32:1948–55.
Nishihata T, Kawabe S, Miyake M, Kim S, Kamada A. Effect of sodium ion on the adjuvant action of sodium salicylate in enhancing rectal ampicillin absorption in rats. Int J Pharm 1984;22:147–57.
Yaginuma H, Isoda Y, Wada Y, et al. Rectal delivery of antiinflammatory drugs. m. Effect of basic amino acid salts of diclofenac on the rectal absorption of ampicillin sodium. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1982;30:1073–6.
Yata N, Wu WM, Yamajo R, Murakami T, Higashi Y, Higuchi T. Enhanced rectal absorption of sodium ampicillin byN-acyl derivatives of collagen peptide in rabbits and rats. J Pharm Sci 1985;74:1058–61.
Murakami T, Tamauchi H, Yamazaki M, Kubo K, Kamada A, Yata N. Biopharmaceutical study on the oral and rectal administrations of enamine prodrugs of amino acid-like β-lactam antibiotics in rabbits. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1981;29:1986–97.
Murakami T, Yata N, Tamauchi H, Nakai J, Yamazaki M, Kamada A. Studies on absorption promoters for rectal delivery preparations. I. Promoting efficacy of enamine derivatives of amino acids for the rectal absorption of β-lactam antibiotics in rabbits. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1981;29:1998–2004.
Murakami T, Yata N, Tamauchi H, Kamada A. Studies of absorption promoters for rectal delivery preparations. II. A possible mechanism of promoting efficacy of enamine derivatives in rectal absorption. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1982;30:659–65.
Yata N, Higashi Y, Murakami T, et al. A possible mechanism of absorption promoters. J Pharmacobiodyn 1983;6(suppl):78.
Yaginuma Y, Nakata T, Toya H, Murakami T, Yamazaki M, Kamada A. Rectal delivery of antiinflammatory drugs. I. The influence of antiinflammatory drugs on rectal absorption of β-lactam antibiotics. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1981;29:2974–82.
Yata N, Sugihara N, Yamajo R, et al. Enhanced rectal absorption of β-lactam antibiotics in rat by monodesmosides isolated from pericarps ofSapindus mukurossi (Enmei-hi). J Pharmacobiodyn 1985;8:1041–7.
Nishimura K-I, Nozaki Y, Yoshimi A, et al. Studies on the promoting effects of carboxylic acid derivatives on the rectal absorption of β-lactam antibiotics in rats. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1985;33:282–91.
Van Hoogdalem EJ, Hardens MA, De Boer AG, Breimer DD. Rectal absorption enhancement of cefoxitin sodium and ampicillin sodium by medium chain fatty acids in rats [Abstract]. Pharm Weekbl [Sci] 1987;10:304.
Van Hoogdalem EJ, Van Kan HJM, De Boer AG, Breimer DD. Rate-controlled absorption enhancement of rectally administered cefoxitin in rats by salicylate. J Contr Rel (in press).
Van Hoogdalem EJ, Stijnen AM, De Boer AG, Breimer DD. Rate-controlled absorption enhancement of rectally administered cefazolin in rats by a glyceride mixture (MGK®). J Pharm Pharmacol (in press).
Rumble RH, Roberts MS. Determination of benzylpenicillin in plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr 1985;342:436–41.
Chiou WL. Critical evaluation of the potential error in pharmacokinetic studies of using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level-time curve. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1978;6:539–46.
Gibaldi M, Perrier D. Pharmacokinetics. 2nd ed. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc., 1982:409–17.
Muranushi N, Takagi N, Muranishi S, Sezaki H. Effect of fatty acids and monoglycerides on permeability of lipid bilayer. Chem Phys Lipids 1981;28:269–79.
Perlman B, Goldstein DB. Membrane-disordering potency and anticonvulsant action of valproic acid and other short-chain fatty acids. Mol Pharmacol 1984;26:83–9.
Kajii H, Horie T, Hayashi M, Awazu S. Effects of sodium salicylate and caprylate as adjuvants of drug absorption on isolated rat small intestinal epithelial cells. Int J Pharm 1986;33:253–5.
Hunt JN. Does calcium mediate slowing of gastric emptying by fat in humans? Am J Physiol 1983;244:G89–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Hoogdalem, E.J., De Boer, A.G. & Breimer, D.D. Rectal absorption enhancement of rate-controlled delivered ampicillin sodium by sodium decanoate in conscious rats. Pharmaceutisch Weekblad Scientific Edition 10, 76–79 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01962682
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01962682