Abstract
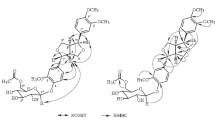
Besides solasonine, three new glycosides, namely, 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→3)-solasodine, 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranosyl solasodine, and 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-galactopyranosyl solasodine, were isolated fromSolanum unguiculatum (A.) Rich. Their structures were determined on the basis of chemical and spectral methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubaie AS, Abd El-Fatah RI. Taxonomic studies on the genusSolanum L. in Yemen (YAR). Egypt J Appl Sci 1980;5(7):277–87.
Tackholm V. Student's flora of Egypt. 2nd ed. Cairo: Cairo University, 1974: 473–4.
Bhatnager JK, Puri RK.Solanum platanifolium, a new source of solasodine. Lloydia 1974;37:318–9.
Chandel RS, Rastogi RP. Triterpenoid saponins and sapogenins. Phytochemistry 1980;19:1889–908.
Vogel AI. Textbook of practical organic chemistry. 3rd ed. London: Longmanns, Green & Co., 1966.
Kalsuya F, Isao K. Isolation of steroidal glycoalkaloids fromSolanum incanum by two countercurrent chromatographic methods. Phytochemistry 1991;30(2):685–7.
Mahato SB, Sahu NP, Ganguly AN, Kasal R, Tanoky O. Steroidal alkaloids fromSolanum khasianum. Application of13C NMR spectroscopy to their structural elucidation. Phytochemistry 1980;19:2017–20.
Eddy CR, Wall ME, Klumpp-Scott M. Catalog of infrared absorption spectra of steroidal sapogenin acetates. Anal Chem 1953;25:266–71.
Wall ME, Eddy CR, Macclennen ML, Klumpp-Scott M. Detection and estimation of steroidal sapogenins in plant tissues. Anal Chem 1952;24:1337–41.
Budzikiewicz H, Djerassi C, William DH. Structural elucidation of natural products by mass spectrometry. Vol. II. San Francisco: Holden-Day, 1964.
Raman P, Tuck CW. Solasodine and diosgenin:1H and13C assignments by two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Chem 1993;31:278–82.
Andres N, Daisy M, Marruan SM.13CNMR spectroscopy of solasodine glycosides fromSolanum laciniatum. Phytochemistry 1988;27(2):603–5.
Eggert H, Van Antwerp CL, Bahacca NS, Djerassi C. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of hydroxysteroids. J Org Chem 1976;41:71–84.
Stothers JB. Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy. New York: Academic Press, 1972.
Soe S, Tomita Y, Tori K, Yoshimura Y. Determination of the absolute configuration of secondary hydroxy group in a chiral secondary alcohol using glycosidation shifts in carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 1978;100(11):3331–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarg, T.M., Glombitza, K.W., Hafez, S.S. et al. Solasodine glycosides of Solanum unguiculatum (A.) Rich. Pharm World Sci 17, 191–194 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870610
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870610