Abstract
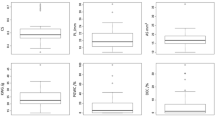
Improving eating quality and nutrition is one of the most important objectives in rice breeding program. Palatability factors and seed protein patterns of 69 Korean rice landraces were compared in this study. Of seven palatability factors, setback viscosity (SBV) had the largest variance, ranging from -144 to 45. Water content (WC) had the lowest variance, ranging from 11.0 to 13.0. In correlation analysis, eating quality was positively correlated with all palatability factors except gelatinization temperature (GT). In principal component analyses (PCA), the first PC with Eigen value of 5.06 explained 42.2% of the total variance. Cool paste viscosity (CPV) was the variable that had the largest positive loading. The second PC with Eigen value of 2.09 explained an additional 17.4% of the total variance. SBV was a variable that had the highest negative loading. Peak viscosity (PKV) had positive variance between PC1 and PC2. The 69 Korean rice landraces were clustered into four groups based on physicochemical properties and palatability factors, with groups I and II showing higher EQ than other groups. SDS-PAGE analyses revealed five seed storage patterns in the 69 Korean rice landraces. Among them, 84% (58 landraces) had pattern I. These results indicate that it is possible to develop high palatability cultivars using Korean rice landraces. In addition, screening of landraces based on variation in seed storage protein profile using SDS-PAGE could be highly effective for the identification of valuable rice genetic resources.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis. 1984. 14th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington VA
Bao JS, Corke H, Sun M. 2006 Microsatellites, single nucleotide polymorphisms and a sequence tagged site in relation to starch physicochemical properties in nonwaxy rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 113: 1185–1196
Bao JS, Xia YW. 1999. Genetic control of the paste viscosity characteristics in indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. and Appl. Genet. 98: 1120–1124
Batey IL, Curtin BM, Moore SA. 1997. Optimization of rapid-visco analyser test conditions for predicting Asian noodle quality. Cereal Chem. 74: 497–501
Bhat RS, Gowda MVC. 2004. Specialty native rice (Oryza sativa L.) germplasm of Uttara Kannada, India. Plant Genet. Resour. Newsl. 140: 42–47
Blakeney AB, Welsh LA, Bannon DR. 1991. Rice quality analysis using a computer controlled RVA. In: DJ Martin, WC Wrigley, eds, Cereals International. Melbourne: Royal Australian Chemical Institute. pp. 180–182
Chung J-W, Cho Y-H, Lee J-R, Lee S-Y, Ma K-H, Lee K-S, Baek H-J, Lee D-J, Kang H-K, Kim S-M, Park Y-J. 2009. Characters of RVA from grain mutants of a rice variety Shindongjin. J. Kor. Soc. Inter. Agri. 21: 261–267
Das GK, Oudhia P. 2000. Rice as a medicinal plant in Chhattisgarh, India. Plant Genet. Resour. Newsl. 122: 46
Ghafoor A, Ahmad Z, Qureshi AS, Bashir M. 2002. Genetic relationship in Vigna mungo L. Hepper and V. radiata L. R. Wilczek based on morphological traits and SDS-PAGE. Euphytica. 123: 367–378
Ghose RLM, Ghatge B, Subramanyan V. 1960. Breakfast Foods and Ready-to-Eat Dishes. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, India
Hameed A, Shah TM, Baber MA, Nayyer I, Haq MA, Ali H. 2009. Comparative seed storage protein profiling of Kabuli chickpea genotypes. Pak. J. Bot. 41: 703–710
Hammer O, Harper DAT, Ryan PD. 2001. PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Paleontol. Electron. 4: 1–9
Hoisington D, Khairallah M, Reeves T, Ribaut JM, Skovmand B, Taba S, Warburton M. 1999. Plant genetic resources: what can they contribute toward increased crop productivity? Proceed. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA, 96: 5937–5943
Hosoya LA, Sato YI, Fuller DQ. 2010. Editorial: the archaeobotany of early agriculture in Asia. Archaeolog. Anthropolog. Sci. 2: 57–59
Iqbal SH, Ghafoor A, Ayub N. 2005. Relationship between SDS-PAGE markers and Ascochyta blight in chickpea. Pak. J. Bot. 37: 87–96
Jin W, Li N, Hong D. 2006. Genetic diversity of seed storage proteins in different ecotype varieties of japonica rice and its application. Rice Sci. 13: 85–92
Juliano GB, Jefferson LMC, Altamir FG, Luciano RBA, Rubens ON. 2014. Agronomic potential of genebank landrace elite accessions for common bean. Sci. Agri. 71: 120–125
Laemmli UK. 1970. Cleavage of structural protein during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685
Lee WJ, Suh JK, Oh HK, Kim SS, Shelton D. 2001. Relationship of grain hardness to physiochemical and processing properties of sorghum. Food Sci. Biotech. 10: 423–428
Lestari P, Ham TH, Lee HH, Woo MO, Jiang WZ, Chu SH, Kwon SW, Ma KH, Lee JH, Cho YC, Koh HJ. 2009. PCR marker-based evaluation of the eating quality of japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Agri. Food Chem. 57: 2754–2762
Little RR, Hilder GB, Dawson EH. 1958. Differential effect of dilute alkali on 25 varieties of milled white rice. Cereal Chem. 35: 111–126
Matsue Y. 1993. The effects of environmental conditions on palatability and physicochemical properties of rice and the evaluation of good eating quality rice varieties. Special Bull. Fukuoka Agricultural Research Center. No. 6.
Mo HD. 1993. Quality improvement of rice grain in China. Sci. Agri. Sinica 26: 8–14
Nisar M, Ghafoor A, Khan MR, Subhan M. 2009. Genetic Similarity of Pakistani pea (Pisum sativum L.) germplasm with world collection using cluster analysis and Jaccard’s similarity index. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 31: 138–144
Okadome H, Toyoshima H, Ohtsubo K. 1998. Evaluation of gelatinization properties of rice grains with a rapid visco analyser. In: L O’Brien, AB Blakney, AS Ross, CW Wrigley, eds, Rapid Food Analysis, 48th Annual RACI Cereal Chemistry Conference, Cairns. pp. 545–552
Sano Y, Katsumata M, Okuno K. 1986. Genetic studies of speciation in cultivated rice: 5. Inter- and intra-specific differentiation in the waxy gene expression of rice. Euphytica 35: 1–9
Sano Y, Makekawa M, Kikuchi H. 1985. Temperature effects on Wx protein level and amylose content in the endosperm of rice. Heredity 76: 221–222
Shastri R. 2004. ‘Bhattada Taligala Mayaloka’ World of native rice landraces. Vijaya Karnataka, 21 January 2004
Shen P, Qian CR, Jin ZX, Luo QX, Jin XY. 2006. Relationship between variation in activities of key enzymes related to starch synthesis during grain filling period and quality of eating and cooking in rice. Rice Sci. 13: 43–50
Sui JM, Li X, Yan S, Yan CJ, Zhang R, Tang SZ, Lu JF, Chen ZX, Gu MH. 2005. Studies on the rice RVA profile characteristics and its correlation with the quality. Sci. Agri. Sinica 38: 657–663
Sun M-M, Abodul SE, Lee H-J, Cho Y-C, Han L-Z, Koh HJ, Cho Y-G. 2011. Molecular aspect of glld eating quality formation in japonica rice. PLOS ONE 6: 1–12
Takeuchi Y, Nonoue Y, Ebitani T, Suzuki K, Aoki N, Sato H, Ideta O, Hirabayashi H, Hirayama M, Ohta H, Nemoto H, Kato H, Ando I, Ohtsubo K, Yano M, Imbe T. 2007. QTL detection for eating quality including glossiness, stickness, taste and hardness of cooked rice. Breed. Sci. 57: 231–242
Tian ZX, Qian Q, Liu QQ, Yan MX, Liu XF, Yan CJ, Liu GF, Gao ZY, Tang SZ, Zeng DL, Wang YH, Yu JM, Gu MH, Li JX. 2009. Allelic diversities in rice starch biosynthesis lead to a diverse array of rice eating and cooking qualities. Proceed. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 106: 21760–21765
Wu DX, Shu QY, Xia YW. 2001. Rapid identification of starch viscosity property of early indica rice varieties with different apparent amylose content by RVA profile. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 15: 57–59
Yamasaki M, Ideta O. 2013. Population structure in Japanese rice population. Breed. Sci. 63: 49–57
Yoon M-R, Lee S-C, Kang M-Y. 2012. The lipid composition of rice cultivars with different eating qualities. J. Kor. Soc. Appl. Biolog. Chem. 55: 291–295
Yu T-Q, Jiang W, Ham T-H, Chu S-H, Lestari P, Lee J-H, Kim M-K, Xu F-R, Han L, Dai L-Y, Koh H-J. 2008. Comparision of grain quality traits between japonica rice cultivars from Korean and Yunna Province of China. J. Crop Sci. Biotech 11: 135–140
Zhenshan W, Hong C, Ping Y, Xiangkun W, Lihuang Z. 1996. Polymorphism of Chinese common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon) and cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.) as deter mined by RAPDs. J. Genet. Breed. 50: 299–307
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K.J., Lee, GA., Lee, JR. et al. Comparison of eating quality and seed storage protein among Korean rice landraces. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 19, 241–247 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-016-0039-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-016-0039-y