Abstract
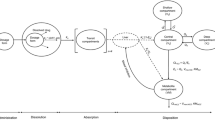
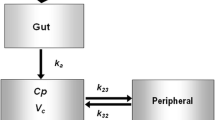
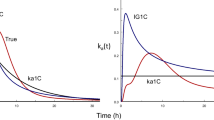
In this study, the population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis of rebamipide (Reba) in healthy male Korean subjects was analyzed using the nonlinear mixed effects modeling method. The possible effects of physiological covariates and the multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene 3435C>T polymorphism on PK parameters were also investigated. Data were collected from a bioequivalence study, in which 26 subjects who participated in the study were administered a single oral dose of 100 mg Reba; only data from the reference formulation were used. Reba showed a relatively large inter-individual variability (from 2.6- to 3.3-fold) in the PK parameters with double peaks or the concentration plateau after the peak concentration in its serum concentration–time profiles. The population PKs of Reba was best described by a one-compartment model with three fraction absorption processes followed a single Weibull-type function and two first-order kinetics, and lag times. The study suggests that the efflux transporter MDR1 3435C>T allele affects the substantial inter-individual variability in the absorption of Reba according to genetic polymorphism. A significant difference was found in the absorption rate ka 1 among the MDR1 3435C>T genotype groups (P < 0.05) (CT group, 79.8% increase; and TT group, 115% increase). The use of combined MDR1 3435C>T and body mass index as covariates for ka 1 exerted a more significant effect (P < 0.05). In addition, body surface area significantly affected the apparent total clearance (P < 0.05).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamasaki K, Ishiyama H, Imaizumi T, Kanbe T, Yabuuchi Y (1989) Effect of OPC-12759, a novel antiulcer agent, on chronic and acute experimental gastric ulcer, and gastric secretion in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol 49:441–448
Yamasaki K, Kanbe T, Chijiwa T, Ishiyama H, Morita S (1987) Gastric mucosal protection by OPC-12759, a novel antiulcer compound, in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 142:23–29
Arakawa T, Kobayashi K, Yoshikawa T, Tarnawski A (1998) Rebamipide: overview of its mechanisms of action and efficacy in mucosal protection and ulcer healing. Dig Dis Sci 43:5S–13S
Ishihara K, Komuro Y, Nishiyama N, Yamasaki K, Hotta K (1992) Effect of rebamipide on mucus secretion by endogenous prostaglandin-independent mechanism in rat gastric mucosa. Arzneimittelforschung 42:1462–1466
Aihara M, Imagawa K, Funakoshi Y, Ohmoto Y, Kikuchi M (1998) Effects of rebamipide on production of several cytokines by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Dig Dis Sci 43:160S–166S
Nagano C, Wakebe H, Azuma A, Imagawa K, Kikuchi M (1998) IFN-gamma-induced iNOS mRNA expression is inhibited by rebamipide in murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Dig Dis Sci 43:118S–124S
Kim JS, Kim JM, Jung HC, Song IS (2001) Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human neutrophils activated by Helicobacter pylori water-soluble proteins: possible involvement of NF-kappaB and MAP kinase signaling pathway. Dig Dis Sci 46:2277–2284
Naito Y, Kuroda M, Mizushima K, Takagi T, Handa O, Kokura S, Yoshida N, Ichikawa H, Yoshikawa T (2007) Transcriptome analysis for cytoprotective actions of rebamipide against indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. J Clin Biochem Nutr 41:202–210
Ogino K, Hobara T, Ishiyama H, Yamasaki K, Kobayashi H, Izumi Y, Oka S (1992) Antiulcer mechanism of action of rebamipide, a novel antiulcer compound, on diethyldithiocarbamate-induced antral gastric ulcers in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 212:9–13
Sakurai K, Sasabe H, Koga T, Konishi T (2004) Mechanism of hydroxyl radical scavenging by rebamipide: identification of mono-hydroxylated rebamipide as a major reaction product. Free Radic Res 38:487–494
Suzuki M, Miura S, Mori M, Kai A, Suzuki H, Fukumura D, Suematsu M, Tsuchiya M (1994) Rebamipide, a novel antiulcer agent, attenuates Helicobacter pylori induced gastric mucosal cell injury associated with neutrophil derived oxidants. Gut 35:1375–1378
Yoshida N, Yoshikawa T, Iinuma S, Arai M, Takenaka S, Sakamoto K, Miyajima T, Nakamura Y, Yagi N, Naito Y, Mukai F, Kondo M (1996) Rebamipide protects against activation of neutrophils by Helicobacter pylori. Dig Dis Sci 41:1139–1144
Yoshikawa T, Naito Y, Tanigawa T, Kondo M (1993) Free radical scavenging activity of the novel anti-ulcer agent rebamipide studied by electron spin resonance. Arzneimittelforschung 43:363–366
Shin BS, Kim CH, Jun YS, Yoon CH, Rho JI, Lee KC, Han HS, Yoo SD (2004) Oral absorption and pharmacokinetics of rebamipide and rebamipide lysinate in rats. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 30:869–876
Guo Y, Wang Y, Xu L (2015) Enhanced bioavailability of rebamipide nanocrystal tablets: formulation and in vitro/in vivo evaluation. Asian J Pharm Sci 10:223–229
Pradhan R, Tran TH, Choi JY, Choi IS, Choi HG, Yong CS, Kim JO (2015) Development of a rebamipide solid dispersion system with improved dissolution and oral bioavailability. Arch Pharm Res 38:522–533
Tung NT, Park CW, Oh TO, Kim JY, Ha JM, Rhee YS, Park ES (2011) Formulation of solid dispersion of rebamipide evaluated in a rat model for improved bioavailability and efficacy. J Pharm Pharmacol 63:1539–1547
Huang BB, Li GF, Luo JH, Duan L, Nobuaki K, Akira Y (2008) Permeabilities of rebamipide via rat intestinal membranes and its colon specific delivery using chitosan capsule as a carrier. World J Gastroenterol 14:4928–4937
Liu J, Shen-Tu J, Wu L, Dou J, Xu Q, Zhou H, Wu G, Hu X (2012) Development of a simple LC-MS/MS method for determination of rebamipide in human plasma and its application to a bioequivalence study. Pharmazie 67:906–911
Hasegawa S, Sekino HH, Matsuoka O, Saito K, Sekino HH, Morikawa A, Uchida K, Koike M, Azuma J (2003) Bioequivalence of rebamipide granules and tablets in healthy adult male volunteers. Clin Drug Investig 23:771–779
Cho HY, Yoon H, Park GK, Lee YB (2009) Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence of two formulations of rebamipide 100-mg tablets: a randomized, single-dose, two-period, two-sequence crossover study in healthy Korean male volunteers. Clin Ther 31:2712–2721
Gerloff T (2004) Impact of genetic polymorphisms in transmembrane carrier-systems on drug and xenobiotic distribution. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 369:69–77
Lown KS, Mayo RR, Leichtman AB, Hsiao HL, Turgeon DK, Schmiedlin-Ren P, Brown MB, Guo W, Rossi SJ, Benet LZ, Watkins PB (1997) Role of intestinal P-glycoprotein (mdr1) in interpatient variation in the oral bioavailability of cyclosporine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 62:248–260
Sparreboom A, van Asperen J, Mayer U, Schinkel AH, Smit JW, Meijer DK, Borst P, Nooijen WJ, Beijnen JH, van Tellingen O (1997) Limited oral bioavailability and active epithelial excretion of paclitaxel (Taxol) caused by P-glycoprotein in the intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2031–2035
Lin JH, Yamazaki M (2003) Role of P-glycoprotein in pharmacokinetics: clinical implications. Clin Pharmacokinet 42:59–98
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmoller J, Johne A, Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Roots I, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U (2000) Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3473–3478
Brinkmann U, Roots I, Eichelbaum M (2001) Pharmacogenetics of the human drug-transporter gene MDR1: impact of polymorphisms on pharmacotherapy. Drug Discov Today 6:835–839
Pauli-Magnus C, Kroetz DL (2004) Functional implications of genetic polymorphisms in the multidrug resistance gene MDR1 (ABCB1). Pharm Res 21:904–913
Drescher S, Schaeffeler E, Hitzl M, Hofmann U, Schwab M, Brinkmann U, Eichelbaum M, Fromm MF (2002) MDR1 gene polymorphisms and disposition of the P-glycoprotein substrate fexofenadine. Br J Clin Pharmacol 53:526–534
Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Johne A, Meisel C, Hoffmeyer S, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Roots I (2001) Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 69:169–174
Kim RB, Leake BF, Choo EF, Dresser GK, Kubba SV, Schwarz UI, Taylor A, Xie HG, McKinsey J, Zhou S, Lan LB, Schuetz JD, Schuetz EG, Wilkinson GR (2001) Identification of functionally variant MDR1 alleles among European Americans and African Americans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 70:189–199
Van Asperen J, Van Tellingen O, Beijnen JH (1998) The pharmacological role of P-glycoprotein in the intestinal epithelium. Pharmacol Res 37:429–435
Wu CY, Benet LZ (2005) Predicting drug disposition via application of BCS: transport/absorption/elimination interplay and development of a biopharmaceutics drug disposition classification system. Pharm Res 22:11–23
Akamatsu T, Nakamura N, Furuya N, Shimizu T, Gotou A, Kiyosawa K, Katsuyama T, Osumi T, Hirao Y, Miyamoto G (2002) Local gastric and serum concentrations of rebamipide following oral ingestion in healthy volunteers. Dig Dis Sci 47:1399–1404
Boeckmann AJ, Beal SL, Sheiner LB (1998) NONMEM User’s Guide, Part I. NONMEM Project Group, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Mandema JW, Verotta D, Sheiner LB (1992) Building population pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models. I. Models for covariate effects. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 20:511–528
Davies NM, Takemoto JK, Brocks DR, Yanez JA (2010) Multiple peaking phenomena in pharmacokinetic disposition. Clin Pharmacokinet 49:351–377
Zhou H (2003) Pharmacokinetic strategies in deciphering atypical drug absorption profiles. J Clin Pharmacol 43:211–227
Bressolle F, Gomeni R, Alric R, Royer-Morrot MJ, Necciari J (1994) A double Weibull input function describes the complex absorption of sustained-release oral sodium valproate. J Pharm Sci 83:1461–1464
Murata K, Noda K, Kohno K, Samejima M (1987) Pharmacokinetic analysis of concentration data of drugs with irregular absorption profiles using multi-fraction absorption models. J Pharm Sci 76:109–113
Strandgården K, Höglund P, Grönquist L, Svensson L, Gunnarsson PO (2000) Absorption and disposition including enterohepatic circulation of (14C) roquinimex after oral administration to healthy volunteers. Biopharm Drug Dispos 21:53–67
Gibaldi M (1967) Pharmacokinetics of absorption and elimination of doxycycline in man. Chemotherapy 12:265–271
Clements JA, Heading RC, Nimmo WS, Prescott LF (1978) Kinetics of acetaminophen absorption and gastric emptying in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther 24:420–431
Plusquellec Y, Houin G (1994) Pharmacokinetic compartmental model with n sites of absorption along the gastrointestinal tract. Arzneimittelforschung 44:679–682
Williams MF, Dukes GE, Heizer W, Han YH, Hermann DJ, Lampkin T, Hak LJ (1992) Influence of gastrointestinal site of drug delivery on the absorption characteristics of ranitidine. Pharm Res 9:1190–1194
Siegmund W, Ludwig K, Engel G, Zschiesche M, Franke G, Hoffmann A, Terhaag B, Weitschies W (2003) Variability of intestinal expression of P-glycoprotein in healthy volunteers as described by absorption of talinolol from four bioequivalent tablets. J Pharm Sci 92:604–610. doi:10.1002/jps.10327
Jin SJ, Bae KS, Cho SH, Jung JA, Kim U, Choe S, Ghim JL, Noh YH, Park HJ, Kim HS, Lim HS (2014) Population pharmacokinetic analysis of simvastatin and its active metabolite with the characterization of atypical complex absorption kinetics. Pharm Res 31:1801–1812
Henn RM, Isenberg JI, Maxwell V, Sturdevant RAL (1975) Inhibition of gastric acid secretion by cimetidine in patients with duodenal ulcer. N Engl J Med 293:371–375
Yoo HD, Kim MS, Cho HY, Lee YB (2011) Population pharmacokinetic analysis of glimepiride with CYP2C9 genetic polymorphism in healthy Korean subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67:889–898
Rietbrock S, Merz PG, Fuhr U, Harder S, Marschner JP, Loew D, Biehl J (1995) Absorption behavior of sulpiride described using Weibull functions. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 33:299–303
Lin JH, Lu AY (1997) Role of pharmacokinetics and metabolism in drug discovery and development. Pharmacol Rev 49:403–449
Kerb R, Aynacioglu AS, Brockmöller J, Schlagenhaufer R, Bauer S, Szekeres T, Hamwi A, Fritzer-Szekeres M, Baumgartner C, Öngen HZ, Güzelbey P, Roots I, Brinkmann U (2001) The predictive value of MDR1, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 polymorphisms for phenytoin plasma levels. Pharmacogenomics J 1:204–210
Fellay J, Marzolini C, Meaden ER, Back DJ, Buclin T, Chave J-P, Decosterd LA, Furrer H, Opravil M, Pantaleo G, Retelska D, Ruiz L, Schinkel AH, Vernazza P, Eap CB, Telenti A (2002) Response to antiretroviral treatment in HIV-1-infected individuals with allelic variants of the multidrug resistance transporter 1: a pharmacogenetics study. Lancet 359:30–36
Daly AK (2010) Pharmacogenetics and human genetic polymorphisms. Biochem J 429:435–449
Roden DM, George AL Jr (2002) The genetic basis of variability in drug responses. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:37–44
Verstuyft C, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Kerb R, Brinkmann U, Jaillon P, Funck-Brentano C, Becquemont L (2003) Digoxin pharmacokinetics and MDR1 genetic polymorphisms. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 58:809–812
Fromm MF (2002) The influence of MDR1 polymorphisms on P-glycoprotein expression and function in humans. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54:1295–1310
Cho HY, Yoo HD, Lee YB (2010) Influence of ABCB1 genetic polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of levosulpiride in healthy subjects. Neuroscience 169:378–387
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education (2014R1A1A2056937).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ngo, L., Yoo, HD., Tran, P. et al. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of rebamipide in healthy Korean subjects with the characterization of atypical complex absorption kinetics. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 44, 291–303 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-017-9519-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10928-017-9519-z