Abstract
Key message
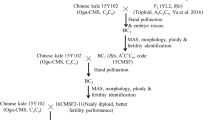
A novel allele-specific Rfo marker was developed and proved to be effective for MAS of Rfo gene in B. oleracea background and six Ogu-CMS fertility-restored interspecific hybrids were created for the first time.
Abstract
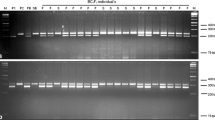
Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility (Ogu-CMS) has been extensively used for Brassica oleracea hybrid production. However, because of maternal inheritance, all the hybrids produced by CMS lines are male sterile and cannot be self-pollinated, which prohibits germplasm maintenance and innovation. This problem can be overcome by using the Ogu-CMS restorer line, but restorer material is absent in B. oleracea crops. Here, Rfo, a fertility-restored gene of Ogu-CMS, was transferred from rapeseed restorer lines into a Chinese kale Ogu-CMS line using interspecific hybridization combined with embryo rescue. Nine interspecific, triploid plant progenies were identified at morphological and ploidy level, with phenotypes intermediate between those of rapeseed and Chinese kale. Because the Rfo marker (Hu et al., Mol Breeding 22:663–674, 2008) cannot distinguish the Rfo and its homologies under a B. oleracea background, a novel allele-specific Rfo marker was developed based on the BLAST analysis of highly homologous Rfo sequences in B. oleracea. Screening using the novel Rfo marker found that six interspecific hybrids carrying Rfo were also fertile, although fertility varied during different flowering periods. Furthermore, BC1 offsprings with the Rfo gene were selected with the allele-specific Rfo marker and showed restored fertility. These results indicated that the novel allele-specific marker could be used for the MAS of Rfo gene in B. oleracea, and this study lays the foundation for the development of Ogu-CMS restorer material in cabbage and its related other subspecies.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayotte R, Harney PM, Machado VS (1987) The transfer of triazine resistance from Brassica napus L. to B. oleracea L. I. Production of F1 hybrids through embryo rescue. Euphytica 36(2):615–624
Bannerrot H, Boulidard L, Couderon Y, Temple J (1974) Transfer of cytoplasmic male sterility from Raphanus sativus to Brassica oleracea. In: Wills AB, North C (eds) Proc Eucarpia Meet Cruciferae. Scottish Hortic Res Inst, Invergavrie, pp 52–54
Bonhomme S, Budar F, Ferault M, Pelletier G (1991) A 2.5 kb NcoI fragment of Ogura radish mitochondrial DNA is correlated with cytoplasmic male-sterility in Brassica cybrids. Curr Genet 19:121–127
Bonhomme S, Budar F, Lancelin D, Small I, Defrance MC, Pelletier G (1992) Sequence and transcript analysis of the Nco2.5 Ogura-specific fragment correlated with cytoplasmic male sterility in Brassica cybrids. Mol Gen Genet 235:340–348
Bridgen MP (1994) A review of plant embryo culture. HortScience 29:1243–1246
Brown GG (1999) Unique aspects of cytoplasmic male sterility and fertility restoration in Brassica napus. J Hered 90:351–356
Brown GG, Formanova N, Jin H, Wargachuk R, Dendy C, Patil P et al (2003) The radish Rfo restorer gene of Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility encodes a protein with multiple pentatricopeptide repeats. Plant J 35:262–272
Budar F, Delourme R, Pelletier G (2004) Male sterility. In EC Pua, Douglas (eds) Biotechnology in agriculture and forestry 54. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 43–64
Chalhoub B, Denoeud F, Liu SY et al (2014) Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 345:950
Chen HG (2006) Studies on fertility and crossability of amphidiploids between Raphanus sativus and Brassica alboglabra. Dissertation, Wuhan; Huazhong Agricultural University
Chen WJ, Li M, Wang TH, Hui RK, Tu JX, Fu TD (2013) Development of New Restorer Materials with Ogu CMS in Brassica napus. Agri Sci Technol 14:18–25
Chiang MS, Chiang BY, Grant WF (1977) Transfer of resistance to race 2 of plasmodiophora Brassica from Brassica napus to cabbage (B. oleracea var. capitata). I. Interspecific hybridization between B. napus and B. oleracea var. capitata. Euphytica 26:319–336
Delourme R, Eber F, Renard M (1991) Radish cytoplasmic male sterility in rapeseed: breeding restorer lines with a good female fertility. Proc 8th Int Rapeseed Congr. University Extension Press, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, pp 1506–1510
Delourme R, Eber F, Renard M (1995) Breeding double low restorer lines in radish cytoplasmic male sterility of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). In: Proc 9th Int Rapeseed Congr, vol 1. Cambridge, UK, pp 6–8
Delourme R, Foisset N, Horvais R, Barret P, Champagne G, Cheung WY, Landry BS, Renard M (1998) Characterisation of the radish introgression carrying the Rfo restorer gene for the Ogu-INRA cytoplasmic male sterility in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 97:129–134
Delourme R, Horvais R, Valle´e P, Renard M (1999) Double low restored F1 hybrids can be produced with the Ogu-INRA CMS in rapeseed. In: Proc 10th Int Rapeseed Congr. Canberra, pp 26–29
Desloire S, Gherbi H, Laloui W, Marhadour S, Clouet V, Catolico L et al (2003) Identification of the fertility restoration locus, Rfo, in radish, as a member of the pentatricopeptide-repeat protein family. EMBO Rep 4:588–594
Dolezel J, Greilhuber J, Suda J (2007) Estimation of nuclear DNA content in plants using flow cytometry. Nat Protoc 2:2233–2244
Eenink AH (1974a) Matromorphy in Brassica oleracea L. I. Terminology, parthenogenesis in Cruciferae and the formation and usability of matromorphic plants. Euphytica 23:429–433
Eenink AH (1974b) Matromorphy in Brassica oleracea L. II. Differences in parthenogenetic ability and parthenogenesis inducing ability. Euphytica 23:435–445
Fang ZY, Sun PT, Liu YM (1983) A Preliminary study on distant hybridization between Raphanus sativus L. and Brassica oleracea L. Acta Horticulturae Sinica 3:008
Fang ZY, Sun PT, Liu YM, Yang LM, Wang XW, Hou AF, Bian CS (1997) A male sterile line with dominant gene (MS) in cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata) and its utilization for hybrid seed production. Euphytica 97:265–268
Fang ZY, Sun PT, Liu YM et al (2001) Investigation of different types of male sterility and application of dominant male sterility in cabbage. China Veg 1:6–10
Feng W, Chen YH (1981) Artificial amphidiploids in an interspecific cross (Brassica oleracea L. × B. pekinensis Rupr.). Acta Horticulturae Sinica 8:37–40
Feng J, Primomo V, Li Z, Zhang Y, Jan CC, Tulsieram L, Xu SS (2009) Physical localization and genetic mapping of the fertility restoration gene Rfo in canola (Brassica napus L.). Genome 52:401–407
Fu TD, Yang XN, Yang GS (1989) Development and research of Polima cytoplasmic Male Sterility in Brassica napus. J Huazhong Agri Univ 8:201–207
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Expt Cell Res 50:151–158
Gu AX, Shen SX, Chen XP, Zhang CH, Li XF (2006) Allotriploid hybrids obtained from interspecific hybridization between Chinese cabbage and cabbage and the preliminary research on reproductive characters. Acta Horticulturae Sinica 33:73–77
Han FQ, Yang C, Fang Z et al (2015) Inheritance and InDel markers closely linked to petal color gene (cpc-1) in Brassica oleracea. Mol Breeding 35:160
Heyn FW (1976) Transfer of restorer genes from Raphanus to cytoplasmic male sterile Brassica napus. Cruciferae Newsl 1:15–16
Honma S, Summers WL (1976) Interspecific hybridization between Brassica napus L. (Napobrassica group) and B. oleracea L. (Botrytis group). J Am Soc Hortic Sci 101:299–302
Hu X, Sullivan-Gilbert M, Kubik T, Danielson J, Hnatiuk N, Marchione W, Greene T, Thompson S (2008) Mapping of the Ogura fertility restorer gene Rfo and development of Rfo allele-specific markers in canola (Brassica napus L.). Mol Breeding 22:663–674
Inomata N (1979) Production of interspeciWc hybrids in Brassica campestris × B. oleracea by culture in vitro of excised ovaries II. Development of excised ovaries on various culture media. Jpn J Breed 29:115–120
Jing B, Heng S, Tong D, Wan Z, Fu T et al (2012) A male sterility-associated cytotoxic protein ORF288 in Brassica juncea causes aborted pollen development. J Exp Bot 63:1285–1295
Kaul MLH (1988) Male Sterility in Higher Plants. Springer, Berlin
Li DR (1980) Preliminary report on breeding of three-line system in Brassica napus. Shanxi J Agri Sci 1:26–29
Li S, Yang D, Zhu Y (2007) Characterization and use of male sterility in hybrid rice breeding. J Integr Plant Biol 49:791–804
Li Q, Zhou Q, Mei J, Zhang Y, Qian W et al (2014) Improvement of Brassica napus via interspecific hybridization between B. napus and B. oleracea. Mol Breeding 34:1955–1963
Liu XP, Liu ZW, Tu JX, Chen BY, Fu TD (2003) Improvement of microspores culture techniques in Brassica napus L. Hereditas (Beijing) 25:433–436 (in Chinese with English summary)
Liu Z, Liu P, Long FR, Hong DF, He QB, Yang GS (2012) Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of the nuclear restorer gene Rfp for pol CMS in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 125:773–779
Lv HH, Yang LM, Kang JG et al (2013) Development of InDel markers linked to Fusarium wilt resistance in cabbage. Mol Breeding 32(4):961–967
Mayr E (1986) Joseph Gottlieb Kolreuter’s contributions to biology. Osiris 2:135–176
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiol 15:473–497
Nishi S, Kawata J, Toda M (1959) In the breeding of interspecific hybrids between two genomes “c” and “a” of Brassica through the application of embryo culture techniques. Jpn J Breed 5:215–222
Ogura H (1968) Studies on the new male sterility in Japanese radish, with special reference to the utilization of this sterility towards practical raising of hybrid seed. Mem Fac Agric Kagoshima Univ 6:39–78
Pelletier G, Primard C, Vedel F, Chetrit P, Remy R, Rousselle P, Renard M (1983) Intergeneric cytoplasmic hybridization in Cruciferae by protoplast fusion. Mol Gen Genet 191:244–250
Pelletier G, Primard C, Ferault M, Vedel F, Chetrit P, Renard M, Delourme R (1988) Uses of protoplasts in plant breeding: cytoplasmic aspects. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 12:173–180
Primard-Brisset C, Poupard JP, Horvais R, Eber F, Pelletier G, Remard M, Delourme R (2005) A new recombined double low restorer line for the Ogu-INRA cms in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 111:736–746
Pu Z, Shimizu M, Zhang Y, Tomohiko N, Takeshi H, Hidetaka M, Ryo F, Keiichi O (2012) Genetic mapping of a fusarium wilt resistance gene in Brassica oleracea. Mol Breeding 30(2):809–818
Qiao HY (2012) Study on the interspecific Hybrids between Brassica rapa and Brassica oleracea. Dissertation, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing
Qin X, Warguchuk R, Arnal N, Gaborieau L, Mireau H, Brown G (2014) In vivo functional analysis of a nuclear restorer PPR protein. BMC Plant Biol 14:313
Quazi MH (1988) Interspecific hybrids between Brassica napus L. and B. oleracea L. developed by embryo culture. Theor Appl Genet 75:309–318
Rahman MH, Bennett RA, Yang RC et al (2011) Exploitation of the late flowering species Brassica oleracea L. for the improvement of earliness in B. napus L.: an untraditional approach. Euphytica 177(3):365–374
Ripley VL, Beversdorf WD (2003) Development of self-incompatible Brassica napus (I) introgression of S-alleles from Brassica oleracea through interspecific hybridization. Plant Breeding 122:1–5
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:8014–8018
Schmitz-Linneweber C, Small I (2008) Pentatricopeptide repeat proteins: a socket set for organelle gene expression. Trends Plant Sci 13:663–670
Tanaka Y, Tsuda M, Yasumoto K, Yamagishi H, Terachi T (2012) A complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Ogura-type male-sterile cytoplasm and its comparative analysis with that of normal cytoplasm in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). BMC Genom 13:352
Thompson KF (1972) Cytoplasmic male sterility in oilseed rape. Heredity 29:253–257
Uyttewaal M, Arnal N, Quadrado M, Martin-Canadell A, Vrielynck N, Hiard S, Gherbi H, Bendahmane A, Budar F, Mireau H (2008) Characterization of Raphanus sativus pentatricopeptide repeat proteins encoded by the fertility restorer locus for Ogura cytoplasmic male sterility. Plant Cell 20:3331–3345
Vedel F, Pla M, Vitart V, Gutierres S, Chetrit P, De Paepe R (1994) Molecular basis of nuclear and cytoplasmic male sterility in higher plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 32:601–608
Virmani SS, Ilyas-Ahmed M (2001) Environment-sensitive genic male sterility (EGMS) in crops. Adv Agron 72:139–195
Walters WT, Mutschler AM, Earle DE (1992) Protoplast fusion-derived Ogura male-sterile cauliflower with cold tolerance. Plant Cell Rep 10:624–628
Wang QB, Zhang YY, Fang ZY, Liu YM, Yang LM, Zhuang M (2012) Chloroplast and mitochondrial SSR help to distinguish allo-cytoplasmic male sterile types in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Mol Breeding 30:709–716
Wen J, Tu JX, Li ZY, Fu TD, Ma CZ, Shen JX (2008) Improving ovary and embryo culture techniques for efficient resynthesis of Brassica napus from reciprocal crosses between yellow-seeded diploids B. rapa and B. oleracea. Euphytica 162:81–89
Yang LM, Liu YM, Wang XW, Sun PT, Zhuang M, Fang ZY (1997) Preliminary observation on main botanical characteristics of cytoplasmic male sterile cabbage. China Veg 6:24–25
Yang J, Liu X, Yang X, Zhang M (2010) Mitochondrially-targeted expression of a cytoplasmic male sterility-associated orf220 gene causes male sterility in Brassica juncea. BMC Plant Biol 10:231
Yin J, Chen S, Tang Z, Chen L, Li J (2004) Resynthesis of Brassica napus through interspecific hybridization between yellow-seeded B. oleracea var. acephala and B. campestris. South West China J Agri Sci 2:149
Zhang GQ, Tang GX, Song WJ, Zhou WJ (2004) Resynthesizing Brassica napus from interspecific hybridization between Brassica rapa and B. oleracea through ovary culture. Euphytica 140:181–187
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Prof. Jianjun Lei, Prof. Yunchang Li, Prof. Hanzhong Wang, and Prof. Wei Qian for providing materials. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31272180), the Major State Basic Research Development Program (973 Program, 2012CB113906), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2012AA100102), the Key Projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan Period (2012BAD02B01), and the earmarked fund for the Modern Agro-Industry Technology Research System, China (nycytx-35-gw01). This work was performed in the Key Laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Horticultural Crops (North China), Ministry of Agriculture, Beijing 100097, People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Richard G.F. Visser.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

122_2016_2728_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S1 Multiple sequence alignment of Rfo sequences with Rfo-homologous sequences in B.oleracea, B.napus, B.rapa (JPEG 2678 kb)

122_2016_2728_MOESM2_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S2 Sequence alignment of Rfo fragment with Rfo-like fragment amplified by primers Con-F/Con-R. The red arrows represent the location of the primers BnRFO-AS2F/BnRFO-NEW-R (JPEG 4826 kb)

122_2016_2728_MOESM3_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S3 Embryo development during the embryo rescue process. (a) Freshly removed pods. (b) Excised embryos. (c) Collapsed embryos. (d) Development of pods during the embryo rescue process. (e) Development of embryos in the early period (< 15 days after pollination). (f) Development of embryos in the late period (> 25 days after pollination) (JPEG 631 kb)

122_2016_2728_MOESM4_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S4 Fertility performance of (a) YL2, and (b) YL5 at different days after flowering (DAF). The red arrows represent the variation of pollen at different DAFs. Left panels: pollen performance; Right panels: pollen viability (JPEG 290 kb)

122_2016_2728_MOESM5_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S5 (a) PCR amplification in partial BC1 progenies using the novel allele-specific Rfo marker. Lanes 1-8: non-restored BC1 progenies, lanes 9-16: restored- fertility BC1 progenies. Pollen performance in non-restored BC1 progenies (b) and restored- fertility BC1 progenies (c,d) (JPEG 146 kb)

122_2016_2728_MOESM6_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Fig. S6 Protein sequence alignment of Rfo with Rfo homologous sequences in B.oleracea, B.napus, B.rapa (JPEG 2342 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Hl., Fang, Zy., Liu, Ym. et al. Development of a novel allele-specific Rfo marker and creation of Ogura CMS fertility-restored interspecific hybrids in Brassica oleracea . Theor Appl Genet 129, 1625–1637 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2728-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-016-2728-9